
ZELAPAR- selegiline hydrochloride tablet, orally disintegrating
Bausch Health US, LLC
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ZELAPAR safely and
effectively. See full prescribing information for ZELAPAR.
ZELAPAR (selegiline hydrochloride) orally disintegrating tablets
Initial U.S. Approval: 2006
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Contraindications (4) 6/2021
Warnings and Precautions,
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ZELAPAR, a monoamine oxidase type B (MAO-B) inhibitor, is indicated as an adjunct in the management
of patients with Parkinson’s disease being treated with levodopa/carbidopa who exhibit deterioration in the
quality of their response to this therapy (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
•
•
•
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Orally Disintegrating Tablets: 1.25 mg (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
ZELAPAR is contraindicated in patients using the following drugs: opioid drugs (e.g., meperidine, tramadol,
methadone), MAO inhibitors including selective MAO-B inhibitors, dextromethorphan, St. John’s wort, and
cyclobenzaprine (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (incidence at least 3% greater than on placebo) are constipation,
skin disorders, vomiting, dizziness, dyskinesia, insomnia, dyspnea, myalgia, and rash (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Bausch Health US, LLC at 1-800-321-
4576 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
•
•
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
®
Melanoma-removal (5.9) 6/2021
Risk for Patients with Phenylketonuria (5.10) 6/2021
Initiate treatment with 1.25 mg given once a day for at least 6 weeks; after 6 weeks, the dose may be
escalated to 2.5 mg once a day (2.1)
Place tablet on top of the tongue where the tablet will disintegrate in seconds; avoid food and liquid
intake 5 minutes before and after each dose (2.1)
In patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment, the dose should be reduced to 1.25 mg;
ZELAPAR is not recommended in patients with severe (Child-Pugh score >9) hepatic impairment (2.2)
May cause hypertension above 2.5 mg/day (5.1)
May cause serotonin syndrome when used with antidepressants (5.2)
May cause falling asleep during activities of daily living (5.3)
May cause hypotension/orthostatic hypotension (5.4)
May cause or exacerbate dyskinesia (5.5)
May cause hallucinations and psychotic-like behavior (5.6)
May cause problems with impulse control and compulsive behaviors (5.7)
Abrupt discontinuation may cause hyperpyrexia and confusion (5.8)
May cause irritation of the buccal mucosa (5.9)
Increased risk for patients with phenylketonuria (5.10)
Pregnancy: Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm (8.1)
Renal Impairment: ZELAPAR is not recommended in patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr <30
mL/min) (2.3, 8.7)

See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 6/2021
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosage Recommendations
2.2 Patients with Hepatic Impairment
2.3 Patients with Renal Impairment
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypertension
5.2 Serotonin Syndrome
5.3 Falling Asleep During Activities of Daily Living and Somnolence
5.4 Hypotension/Orthostatic Hypotension
5.5 Dyskinesia
5.6 Hallucinations/Psychotic-Like Behavior
5.7 Impulse Control/Compulsive Behaviors
5.8 Withdrawal Emergent Hyperpyrexia and Confusion
5.9 Irritation of the Buccal Mucosa
5.10 Risk for Patients with Phenylketonuria
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Opioid Drugs
7.2 Dextromethorphan
7.3 MAO Inhibitors
7.4 Sympathomimetic Medications
7.5 Tyramine/Selegiline Interaction
7.6 Tricyclic Antidepressants and Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors
7.7 Drugs that Induce CYP450
7.8 Dopaminergic Antagonists
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
8.7 Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
10.1 Selegiline
10.2 Overdose with Non-selective MAO Inhibitors
10.3 Treatment or Management of Overdose
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action

12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
*
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ZELAPAR is indicated as an adjunct in the management of patients with Parkinson’s
disease being treated with levodopa/carbidopa who exhibit deterioration in the quality of
their response to this therapy. There is no evidence from controlled studies that
ZELAPAR has any beneficial effect in the absence of concurrent levodopa therapy [see
Clinical Studies (14)].
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosage Recommendations
Initiate treatment with 1.25 mg given once a day for at least 6 weeks. After 6 weeks, the
dose may be increased to 2.5 mg given once a day if a desired benefit has not been
achieved and the patient is tolerating ZELAPAR. There is no evidence that doses greater
than 2.5 mg a day provide additional benefit, and they should ordinarily be avoided
because of the potential increased risk of adverse events.
Take ZELAPAR in the morning before breakfast and without liquid. Patients should avoid
ingesting food or liquids for 5 minutes before and after taking ZELAPAR.
Patients should not attempt to push ZELAPAR through the foil backing. Patients should
PEEL BACK the backing of one or two blisters (as prescribed) with dry hands, and
GENTLY remove the tablet(s). Patients should IMMEDIATELY place the ZELAPAR tablet(s)
on top of the tongue where it will disintegrate in seconds.
2.2 Patients with Hepatic Impairment
In patients with mild to moderate hepatic disease (Child-Pugh score 5 to 9), the daily
dose of ZELAPAR should be reduced (from 2.5 to 1.25 mg daily), depending on the
clinical response. ZELAPAR is not recommended in patients with severe hepatic
impairment (Child-Pugh score greater than 9) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and
Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.3 Patients with Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment of ZELAPAR is required in patients with mild to moderate renal
Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.

impairment (creatinine clearance [CLcr] 30 to 89 mL/min). The maintenance dose of
ZELAPAR (1.25 mg or 2.5 mg) is determined by the individual clinical response.
ZELAPAR is not recommended in patients with severe renal impairment and patients
with end-stage renal disease [ESRD] (creatinine clearance [CLcr] <30 mL/min) [see Use
in Specific Populations (8.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
ZELAPAR Orally Disintegrating Tablets are pale yellow, imprinted with a stylized “V”, and
contain 1.25 mg selegiline hydrochloride.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
ZELAPAR is contraindicated in patients with:
•
•
•
•
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypertension
ZELAPAR should not be used at daily doses exceeding those recommended
(2.5 mg/day) because of the risks associated with non-selective inhibition of MAO [see
Drug Interactions (7.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
The selectivity of ZELAPAR for MAO-B may not be absolute even at the recommended
daily dose of 2.5 mg daily. The selectivity of MAO-B inhibitors typically decreases, and it
is ultimately lost as the dose is increased beyond recommended doses. Hypertensive
reactions associated with ingestion of tyramine-containing foods have been reported
even in patients taking the recommended daily dose of swallowed selegiline, a dose
which is generally believed to be selective for MAO-B. Selectivity for MAO-B inhibition is
gradually lost with increasing daily doses. An increase in tyramine sensitivity for blood
pressure responses appears to begin at a dose of 5 mg ZELAPAR daily [see Drug
Interactions (7.5)]. However, the precise dose at which ZELAPAR becomes a non-
selective inhibitor of all MAO enzymes in individual patients is unknown.
Reports of hypertensive reactions have occurred in patients who ingested tyramine-
containing consumables (i.e., food or drink) while receiving swallowed selegiline at the
Concomitant use of opioid drugs (e.g., meperidine, tramadol, or methadone).
Serotonin syndrome, a potentially serious condition, which can result in death, has
been reported with concomitant use of meperidine (e.g., Demerol and other trade
names). At least 14 days should elapse between discontinuation of ZELAPAR and
initiation of treatment with these medications [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Concomitant use of other drugs in the monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) class or
other drugs that are potent inhibitors of monoamine oxidase, including linezolid),
because of an increased risk for hypertensive crisis [see Warnings and Precautions
(5.1)]. At least 14 days should elapse between discontinuation of ZELAPAR and
initiation of treatment with any MAO inhibitor.
Concomitant use of St. John’s wort or cyclobenzaprine (a tricyclic muscle relaxant).
Concomitant use of dextromethorphan, because of reported episodes of psychosis
or bizarre behavior.

recommended dose (a dose believed to be relatively selective for MAO-B).
The safe use of ZELAPAR at doses above 2.5 mg daily without dietary tyramine
restrictions has not been established.
A pharmacodynamic study showed increased tyramine sensitivity for increasing blood
pressure and decreased selectivity for MAO-B with dosing above the recommended level
(2.5 mg daily) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
Uncontrolled hypertension has been reported when taking the recommended dose of
swallowed selegiline and a sympathomimetic medication (ephedrine).
After starting ZELAPAR, monitor patients for new onset hypertension or exacerbation of
hypertension that is not adequately controlled.
5.2 Serotonin Syndrome
Serotonin syndrome and hyperpyrexia have been reported with the combined treatment
of an antidepressant (e.g., selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors-SSRIs, serotonin-
norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors-SNRIs, tricyclic antidepressants, tetracyclic
antidepressants, triazolopyridine antidepressants) and a non-selective MAOI (e.g.,
phenelzine, tranylcypromine) or selective MAO-B inhibitors, such as selegiline
(ELDEPRYL), rasagiline (AZILECT), and Zydis selegiline (ZELAPAR).
Serotonin syndrome is a potentially serious condition, which can result in death. Typical
clinical signs and symptoms include behavioral and cognitive/mental status changes
(e.g., confusion, hypomania, hallucinations, agitation, delirium, headache, and coma),
autonomic effects (e.g., syncope, shivering, sweating, high fever/hyperthermia,
hypertension, hypotension, tachycardia, nausea, diarrhea), and somatic effects (e.g.,
muscular rigidity, myoclonus, muscle twitching, hyperreflexia manifested by clonus, and
tremor).
In the post-marketing period, fatal and non-fatal cases of serotonin syndrome have
been reported in patients treated with antidepressants concomitantly with ZELAPAR
[see Contraindications (4) and Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.2, 7.3)].
Clinical studies of ZELAPAR did not allow concomitant use of any selective serotonin re-
uptake inhibitor (e.g., fluoxetine-Prozac, fluvoxamine-Luvox, paroxetine-Paxil, sertraline,
venlafaxine-Effexor, or nefazodone-Serzone) or any non-selective serotonin reuptake
inhibiting antidepressant drug (except when taken at a low dose and only at night for the
purpose of effective sleep) with ZELAPAR.
Because the mechanisms responsible for these reactions are not fully understood, avoid
the combination of ZELAPAR with any antidepressant. At least 14 days should elapse
between discontinuation of ZELAPAR and initiation of treatment with a SSRI, SNRI,
tricyclic, tetracyclic, or triazolopyridine antidepressant. In patients taking
antidepressants with a long half-life (e.g., fluoxetine and its active metabolite), allow at
least five weeks (perhaps longer, especially if fluoxetine has been prescribed chronically
and/or at higher doses) to elapse between discontinuation of fluoxetine and initiation of
ZELAPAR [see Drug Interactions (7.6)].
5.3 Falling Asleep During Activities of Daily Living and Somnolence
Patients with Parkinson’s disease treated with ZELAPAR or other drugs increasing
dopaminergic tone have reported falling asleep while engaged in activities of daily living,

including the operation of motor vehicles, which sometimes resulted in accidents.
Although many of these patients reported somnolence, some did not perceive warning
signs, such as excessive drowsiness, and believed that they were alert immediately prior
to the event. Some of these events have been reported as late as one year after
initiation of treatment.
It has been reported that falling asleep while engaged in activities of daily living always
occurs in a setting of pre-existing somnolence, although patients may not give such a
history. For this reason, prescribers should reassess patients for drowsiness or
sleepiness especially since some of the events occur well after the start of treatment.
Somnolence may occur in patients receiving ZELAPAR. There was an increased risk for
somnolence in geriatric patients (≥65 years) vs. non-geriatric patients treated with
ZELAPAR. Prescribers should also be aware that patients may not acknowledge
drowsiness or sleepiness until directly questioned about drowsiness or sleepiness during
specific activities. Patients should be advised to exercise caution while driving, operating
machines, or working at heights during treatment with ZELAPAR. Patients who have
already experienced somnolence and/or an episode of sudden sleep onset should not
participate in these activities during treatment with ZELAPAR.
Before initiating treatment with ZELAPAR, advise patients about the potential to develop
drowsiness and specifically ask about factors that may increase this risk, such as
concomitant sedating medications and the presence of sleep disorders. If a patient
develops daytime sleepiness or episodes of falling asleep during activities that require
active participation (e.g., conversations, eating, etc.), ZELAPAR should ordinarily be
discontinued. If a decision is made to continue ZELAPAR, patients should be advised not
to drive and to avoid other potentially dangerous activities. There is insufficient
information to establish whether dose reduction will eliminate episodes of falling asleep
while engaged in activities of daily living.
5.4 Hypotension/Orthostatic Hypotension
Assessments of orthostatic (supine and standing) blood pressures at different times
throughout the 12 week study period in two controlled trials showed that the frequency
of orthostatic hypotension (>20 mm Hg decrease in systolic blood pressure and/or >10
mm Hg decrease in diastolic blood pressure) was greater with ZELAPAR treatment than
with placebo treatment. Patients taking ZELAPAR were most likely to experience a
decline in systolic and diastolic blood pressure at 8 weeks (2 weeks after initiating 2.5
mg ZELAPAR). At that time, the incidence of systolic orthostatic hypotension was about
21% in ZELAPAR-treated patients and 9% in placebo-treated patients. The incidence of
diastolic orthostatic hypotension was about 12% in ZELAPAR-treated patients and about
4% in placebo-treated patients. Thus, it appears that there may be an increased risk for
orthostatic hypotension in the period after increasing the daily dose of ZELAPAR from
1.25 to 2.5 mg.
The incidence of orthostatic hypotension was higher in geriatric patients (≥65 years)
than in non-geriatric patients. In the geriatric patients, orthostatic hypotension occurred
in about 3% of ZELAPAR-treated patients compared to 0% of placebo-treated patients.
5.5 Dyskinesia
ZELAPAR may potentiate dopaminergic side effects of levodopa and may cause
dyskinesia or exacerbate preexisting dyskinesia. In controlled trials, the incidence of

dyskinesia was 6% in ZELAPAR-treated patients and 3% in placebo-treated patients.
Decreasing the dose of levodopa may lessen dyskinesia. The incidence of dyskinesia
causing study discontinuation was greater on ZELAPAR than on placebo.
5.6 Hallucinations/Psychotic-Like Behavior
In controlled trials, hallucination was reported by 4% of ZELAPAR-treated patients and
2% in placebo-treated patients. Hallucinations led to drug discontinuation and premature
withdrawal from clinical trials in about 1% of ZELAPAR-treated patients, compared to no
patient on placebo.
Postmarketing reports indicate that patients may experience new or worsening mental
status and behavioral changes, which may be severe, including psychotic-like behavior
during ZELAPAR treatment or after starting or increasing the dose of ZELAPAR. Other
drugs prescribed to improve the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease can have similar
effects on thinking and behavior. This abnormal thinking and behavior can consist of one
or more of a variety of manifestations including paranoid ideation, delusions,
hallucinations, confusion, psychotic-like behavior, disorientation, aggressive behavior,
agitation, and delirium.
Patients with a major psychotic disorder should ordinarily not be treated with ZELAPAR
because of the risk of exacerbating psychosis. In addition, certain medications used to
treat psychosis may exacerbate the symptoms of Parkinson's disease and may
decrease the effectiveness of ZELAPAR [see Drug Interactions (7.8)].
5.7 Impulse Control/Compulsive Behaviors
Case reports suggest that patients can experience intense urges to gamble, increased
sexual urges, intense urges to spend money, binge eating, and/or other intense urges,
and the inability to control these urges while taking one or more of the medications,
including ZELAPAR, that increase central dopaminergic tone and that are generally used
for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. In some cases, although not all, these urges
were reported to have stopped when the dose was reduced or the medication was
discontinued. Because patients may not recognize these behaviors as abnormal, it is
important for prescribers to specifically ask patients or their caregivers about the
development of new or increased gambling urges, sexual urges, uncontrolled spending,
binge eating, or other urges while being treated with ZELAPAR. Physicians should
consider dose reduction or stopping the medication if a patient develops such urges
while taking ZELAPAR.
5.8 Withdrawal Emergent Hyperpyrexia and Confusion
Although not reported with ZELAPAR in the clinical development program, a symptom
complex resembling the neuroleptic malignant syndrome (characterized by elevated
temperature, muscular rigidity, altered consciousness, and autonomic instability), with
no other obvious etiology, has been reported in association with rapid dose reduction,
withdrawal of, or changes in antiparkinsonian therapy.
5.9 Irritation of the Buccal Mucosa
In the controlled clinical trials, periodic examinations of the tongue and oral mucosa were
performed. At the end of the study, the frequency of mild oropharyngeal abnormality
(e.g., swallowing pain, mouth pain, discrete areas of focal reddening, multiple foci of

reddening, edema, and/or ulceration) in patients without similar abnormality at baseline
was 10% in ZELAPAR-treated patients compared to 3% in placebo-treated patients.
5.10 Risk for Patients with Phenylketonuria
Phenylalanine can be harmful to patients with phenylketonuria (PKU). ZELAPAR contains
phenylalanine, a component of aspartame. Each ZELAPAR 1.25 mg tablet contains 1.25
mg phenylalanine. Patients taking the 2.5 mg dose of ZELAPAR will receive 2.5 mg
phenylalanine. Before prescribing ZELAPAR to a patient with PKU, consider the
combined daily amount of phenylalanine from all sources, including ZELAPAR.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in more detail in the Warnings and
Precautions section of labeling:
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, the incidence of
adverse reactions (number of unique patients experiencing an adverse reaction per total
number of patients treated) observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly
compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the incidence
of adverse reactions observed in clinical practice.
Because the controlled trials performed during premarketing development both used a
titration design (1.25 mg per day for 6 weeks, followed by 2.5 mg per day for 6 weeks),
with a resultant confounding of time and dose, it was impossible to adequately evaluate
the effects of dose on the incidence of adverse reactions.
The most common adverse reactions (treatment difference incidence at least 3%
greater than placebo incidence) reported in the double-blind, placebo-controlled trials
during ZELAPAR treatment were constipation, skin disorders, vomiting, dizziness,
dyskinesia, insomnia, dyspnea, myalgia, and rash (see Table 1).
Of the 194 patients treated with ZELAPAR in the double-blind, placebo-controlled trials,
5% discontinued due to adverse reactions compared to 1% of the 98 patients who
received placebo. Most common adverse reactions causing discontinuation of treatment
included dizziness, chest pain, accidental injury, and myasthenia.
Incidence in Controlled Clinical Trials
Risk for Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Risk of Serotonin Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
Falling Asleep During Activities of Daily Living and Somnolence [see Warnings and
Precautions (5.3)]
Hypotension/Orthostatic Hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
Dyskinesia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
Hallucinations/Psychotic-Like Behavior [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
Impulse Control/Compulsive Behaviors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
Withdrawal Emergent Hyperpyrexia and Confusion [see Warnings and Precautions
(5.8)]
Irritation of the Buccal Mucosa [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
Risk for Patients with Phenylketonuria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]

Table 1 lists the adverse reactions reported in the placebo-controlled trials after at least
one dose of ZELAPAR (incidence 2% or greater).
Table 1: Adverse Reactions in Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trials
with an Incidence ≥2% of Patients Treated with ZELAPAR and More
Frequent than the Placebo Group
Body System/
Adverse Event
ZELAPAR
1.25/2.5 mg
N=194
%
Placebo
N=98
%
Body as a Whole
Pain 8 7
Back Pain 5 3
Chest Pain 2 0
Cardiovascular System
Hypertension 3 2
Digestive System
Nausea 11 9
Stomatitis 5 4
Dyspepsia 5 3
Constipation 4 0
Vomiting 3 0
Diarrhea 2 1
Dysphagia 2 1
Flatulence 2 1
Tooth Disorder 2 1
Hemic and Lymphatic
System
Ecchymosis 2 0
Metabolic and Nutritional
Disorders
Hypokalemia 2 0
Musculoskeletal System
Leg Cramps 3 1
Myalgia 3 0
Nervous System
Dizziness 11 8
Headache 7 6
Insomnia 7 4
Dyskinesia 6 3
Dry Mouth 4 2
Hallucinations 4 2
Somnolence 3 2
Tremor 3 1
Ataxia 3 1
*

*
†
Depression 2 1
Respiratory System
Pharyngitis 4 2
Rhinitis 7 6
Dyspnea 3 0
Skin and Appendages
Rash 4 1
Skin Disorders 6 2
Certain adverse reactions were reported at a higher frequency by patients ≥65 years of
age compared to patients <65 years [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
No consistent differences in the incidences of adverse reactions were observed between
male and female patients.
There were insufficient data to assess the impact of race on the incidence of adverse
reactions.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Opioid Drugs
Because serious, sometimes fatal reactions have been precipitated with concomitant use
of opioid drugs (e.g., meperidine and its derivatives, methadone, or tramadol) and
MAOIs, including selective MAO-B inhibitors, concomitant use of these drugs with
ZELAPAR is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions
(5.2)]. At least 14 days should elapse between discontinuation of ZELAPAR and initiation
of treatment with these drugs.
7.2 Dextromethorphan
The combination of MAO inhibitors and dextromethorphan has been reported to cause
brief episodes of psychosis or bizarre behavior. Therefore, in view of ZELAPAR’s MAO
inhibitory activity, dextromethorphan should not be used concomitantly with ZELAPAR
[see Contraindications (4)].
7.3 MAO Inhibitors
ZELAPAR is contraindicated for concomitant use with other drugs in the MAOI class or
other drugs that are potent inhibitors of monoamine oxidase (including linezolid, an
oxazolidinone antibacterial, which also has reversible nonselective MAO inhibition activity)
because of the increased risk for hypertensive crisis [see Contraindications (4) and
Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. At least 14 days should elapse between discontinuation
of ZELAPAR and initiation of treatment with other MAOIs.
Patients may have reported multiple adverse experiences during the study or at
discontinuation; thus patients may be included in more than one category.
Skin disorders represent any new skin abnormality that would not be characterized as
rash or neoplastic lesion. These include events such as skin ulcer, fungal dermatitis,
skin hypertrophy, contact dermatitis, herpes simplex, dry skin, sweating, urticaria, and
pruritus.
†

7.4 Sympathomimetic Medications
Uncontrolled hypertension, including hypertensive crisis, has been reported when taking
the recommended dose of swallowed selegiline and a sympathomimetic medication
(ephedrine).
7.5 Tyramine/Selegiline Interaction
The enzyme, monoamine oxidase (MAO) (primarily type A), in the gastrointestinal tract
and liver provides protection from ingested amines (e.g., tyramine) that, if absorbed,
have the capacity to cause uncontrolled hypertension (tyramine reaction). If MAO is
inhibited in the gastrointestinal tract and liver, ingestion of exogenous amines contained
in some foods such as fermented cheese, herring, or over-the-counter cough/cold
medicines may be absorbed systemically causing release of norepinephrine and a rise in
systemic blood pressure with the potential for uncontrolled hypertension. Selective
MAO-B inhibitors lose their selectivity for MAO-B when taken in doses higher than
recommended. Non-selective MAO-A inhibitors or MAO-B inhibitors in higher than
recommended doses may result in MAO-A inhibition in the gastrointestinal tract and liver.
Results of a tyramine challenge study indicate that ZELAPAR is relatively selective for
MAO-B at the recommended dose. In most cases, there is no need for dietary tyramine
restriction in patients prescribed ZELAPAR [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)] at the
recommended dose. Because the selectivity for inhibiting MAO-B diminishes as the dose
of ZELAPAR is increased above the recommended daily dose, patients should not take
more than 2.5 mg of ZELAPAR daily.
Reports of hypertensive reactions have occurred in patients who ingested tyramine-
containing consumables (i.e., food or drink) while receiving swallowed selegiline at the
recommended dose (a dose believed to be relatively selective for MAO-B). Hypertensive
crisis has also been reported with ZELAPAR use that was not above the recommended
dosing.
Uncontrolled hypertension has been reported when taking the recommended dose of
swallowed selegiline and a sympathomimetic medication (ephedrine).
7.6 Tricyclic Antidepressants and Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors
Severe toxicity has also been reported in patients receiving the combination of tricyclic
antidepressants and swallowed selegiline, or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and
swallowed selegiline [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
7.7 Drugs that Induce CYP450
Adequate studies have not been done investigating the effect of CYP3A4 inducers on
selegiline. Drugs that induce CYP3A4 (e.g., phenytoin, carbamazepine, nafcillin,
phenobarbital, and rifampin) should be used with caution.
7.8 Dopaminergic Antagonists
It is possible that dopamine antagonists, such as antipsychotics or metoclopramide,
could diminish the effectiveness of ZELAPAR.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS

8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate data on the developmental risk associated with the use of
ZELAPAR in pregnant women. In animal studies, administration of selegiline during
pregnancy was associated with developmental toxicity (decreased embryofetal and
postnatal offspring growth and survival) at doses greater than those used clinically.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and
of miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%,
respectively. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in the indicated
population is unknown.
Data
Animal Data
In rats administered selegiline orally (5, 10, and 40 mg/kg/day) throughout the period of
organogenesis, a decrease in fetal body weight was observed at the mid and high
doses. The no-effect dose for embryofetal developmental toxicity in rats (5 mg/kg/day)
is approximately 20 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 2.5
mg/day on a mg/m basis.
In rabbits administered selegiline orally (5, 30, and 60 mg/kg/day) throughout the period
of organogenesis, embryolethality was observed at the highest dose tested and reduced
fetal body weight was observed at the mid and high doses. The no-effect dose for
embryofetal developmental toxicity in rabbits (5 mg/kg/day) is approximately 40 times
the MRHD on a mg/m basis.
In rats administered selegiline orally (0.3, 1, and 10 mg/kg/day) during gestation and
lactation, decreases in offspring survival and body weights were observed at the highest
dose tested. The no-effect dose for pre- and postnatal developmental toxicity (1
mg/kg/day) is approximately 4 times the MRHD on a mg/m basis.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of selegiline or its metabolites in human milk, the
effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Selegiline and
metabolites were detected in rat milk at levels higher than those in maternal plasma.
Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants from
ZELAPAR, including the potential for hypertensive reactions, advise a woman that
breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with ZELAPAR and for 7 days after
the final dose.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
The overall incidence of adverse reactions was increased in geriatric patients (≥65
years) compared to non-geriatric patients (<65 years). Clinical studies did not include a
2
2
2

years) compared to non-geriatric patients (<65 years). Clinical studies did not include a
sufficient number of geriatric subjects older than 75 years to determine whether they
respond differently to ZELAPAR.
Analysis of adverse reaction incidence in each group was conducted to calculate and
compare relative risk (ZELAPAR % / Placebo %) for each treatment. The relative risk was
≥2 fold higher for ZELAPAR treatment in the geriatric patients compared to the non-
geriatric patients for hypertension, orthostatic/postural hypotension [see Warnings and
Precautions (5.4)]. The incidence of orthostatic hypotension by measurement of blood
pressure was also higher in geriatric patients than in non-geriatric patients. In the
geriatric patients, the treatment difference for incidence of orthostatic hypotension
determined by supine and standing blood measurements was 3%.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score 5 to 9) may require
a dose reduction of ZELAPAR (from 2.5 to 1.25 mg daily) depending on the clinical
response. ZELAPAR is not recommended in patients with severe hepatic impairment
(Child-Pugh score >9)[see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Pharmacology
(12.3)].
8.7 Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment of ZELAPAR is required in patients with mild to moderate renal
impairment (creatinine clearance [CLcr] 30 to 89 mL/min). ZELAPAR is not
recommended in patients with severe renal impairment and patients with end-stage renal
disease [ESRD] (CLcr <30 mL/min) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Clinical
Pharmacology (12.3)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
10.1 Selegiline
Experience gained during development of the 5 mg swallowed dosage form reveals that
some individuals exposed to doses of 600 mg of d,l-selegiline suffered severe
hypotension and psychomotor agitation. Small increments in serum BUN and creatinine
have been observed in patients who received ZELAPAR 10 mg daily (4 times the
recommended dose).
Since the selective inhibition of MAO-B by ZELAPAR is achieved only at doses in the
range recommended for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease (e.g., 2.5 mg/day),
overdoses are likely to cause significant inhibition of both MAO-A and MAO-B.
Consequently, the signs and symptoms of overdose may resemble those observed with
marketed non-selective MAO inhibitors [e.g., tranylcypromine (PARNATE ),
isocarboxazid (MARPLAN ), and phenelzine (NARDIL )]. For this reason, in cases of
overdose with selegiline, dietary tyramine restriction should be observed for several
weeks to avoid the risk of a hypertensive reaction.
10.2 Overdose with Non-selective MAO Inhibitors
NOTE: The following description of presenting symptoms and clinical course is based
upon overdose descriptions of non-selective MAO inhibitors and does not include
information from patients who have overdosed on oral selegiline or ZELAPAR.
®
® ®

Characteristically, signs and symptoms of non-selective MAO inhibitor overdose may not
appear immediately. Delays of up to 12 hours between ingestion of drug and the
appearance of signs may occur. Importantly, the peak intensity of the syndrome may
not be reached for upwards of a day following the overdose. Death has been reported
following overdosage. Therefore, immediate hospitalization, with continuous patient
observation and monitoring for a period of at least two days following the ingestion of
such drugs in overdose, is strongly recommended.
The clinical picture of MAO inhibitor overdose varies considerably; its severity may be a
function of the amount of drug consumed. The central nervous and cardiovascular
systems are prominently involved.
Signs and symptoms of overdosage may include, alone or in combination, any of the
following: drowsiness, dizziness, faintness, irritability, hyperactivity, agitation, severe
headache, hallucinations, trismus, opisthotonos, convulsions, and coma; rapid and
irregular pulse, hypertension, hypotension and vascular collapse; precordial pain,
respiratory depression and failure, hyperpyrexia, diaphoresis, and cool, clammy skin.
10.3 Treatment or Management of Overdose
Treatment of overdose with non-selective MAO inhibitors is symptomatic and supportive.
Induction of emesis or gastric lavage with instillation of charcoal slurry may be helpful in
early poisoning, provided the airway has been protected against aspiration. Signs and
symptoms of central nervous system stimulation, including convulsions, should be
treated with diazepam, given slowly intravenously. Phenothiazine derivatives and central
nervous system stimulants should be avoided. Hypotension and vascular collapse
should be treated with intravenous fluids and, if necessary, blood pressure titration with
an intravenous infusion of a dilute pressor agent. It should be noted that adrenergic
agents may produce a markedly increased pressor response.
Support respiration, including management of the airway, use of supplemental oxygen,
and mechanical ventilatory assistance, as required.
Body temperature should be monitored closely. Intensive management of hyperpyrexia
may be required. Maintenance of fluid and electrolyte balance is essential.
11 DESCRIPTION
ZELAPAR Orally Disintegrating Tablets contain selegiline hydrochloride, a levorotatory
acetylenic derivative of phenethylamine. Selegiline hydrochloride is described chemically
as: (-)-(R)-N, α-dimethyl-N-2-propynylphenethylamine hydrochloride and its structural
formula is:

Its empirical formula is C H N∙HCl, representing a molecular weight of 223.74.
Selegiline hydrochloride is a white to almost white crystalline powder that is freely soluble
in water and in methanol, slightly soluble in acetone.
ZELAPAR Orally Disintegrating Tablets are available for oral administration (not to be
swallowed) in a strength of 1.25 mg. Each lyophilized orally disintegrating tablet contains
the following inactive ingredients: aspartame, citric acid, gelatin, glycine, mannitol, opatint
yellow, and grapefruit flavor.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Selegiline is an irreversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase (MAO), which regulates the
metabolic degradation of catecholamines and serotonin in the central nervous system
and peripheral tissues. At recommended doses, selegiline is selective for MAO type B
(MAO-B), the major form in the brain. Inhibition of MAO-B activity, by blocking the
catabolism of dopamine, may result in increased dopamine levels; however, there is
evidence that selegiline may act through other mechanisms to increase dopaminergic
activity.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
A pharmacodynamic study investigating daily ZELAPAR doses of 2.5 mg, 5 mg, and 10
mg for tyramine sensitivity showed that increased tyramine sensitivity resulting in
increased blood pressure (because of MAO-A inhibition and decreased selectivity for
MAO-B) occurred with dosing above the recommended level (2.5 mg daily). An increase
in tyramine sensitivity for blood pressure responses appears to begin at a dose of 5 mg
ZELAPAR daily [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
ZELAPAR disintegrates within seconds after placement on the tongue and is rapidly
13 17

absorbed. Detectable levels of selegiline from ZELAPAR have been measured at
5 minutes after administration, the earliest time point examined.
Selegiline is more rapidly absorbed from the 1.25 or 2.5 mg dose of ZELAPAR (T
range: 10-15 minutes) than from the swallowed 5 mg selegiline tablet (T range: 40-90
minutes). Mean (SD) maximum plasma concentrations of 3.34 (1.68) and 4.47 (2.56)
ng/mL are reached after single dose of 1.25 and 2.5 mg ZELAPAR compared to 1.12
ng/mL (1.48) for the swallowed 5 mg selegiline tablets (given as 5 mg bid). On a dose-
normalized basis, the relative bioavailability of selegiline from ZELAPAR is greater than
from the swallowed formulation.
The pre-gastric absorption from ZELAPAR and the avoidance of first-pass metabolism
results in higher concentrations of selegiline and lower concentrations of the metabolites
compared to the 5 mg swallowed selegiline tablet.
Plasma C and AUC of ZELAPAR were dose proportional at doses between 2.5 and
10 mg daily.
Food Effects
When ZELAPAR is taken with food, the C and AUC of selegiline are about 60% of
those seen when ZELAPAR is taken in the fasted state. Since ZELAPAR is placed on the
tongue and absorbed through the oral mucosa, the intake of food and liquid should be
avoided 5 minutes before and after ZELAPAR administration [see Dosage and
Administration (2.1)].
Distribution
Up to 85% of plasma selegiline is reversibly bound to proteins.
Metabolism
Following a single dose, the median elimination half-life of selegiline was 1.3 hours at the
1.25 mg dose. Under steady-state conditions, the median elimination half-life increases
to 10 hours. Upon repeat dosing, accumulation in the plasma concentration of selegiline
is observed both with ZELAPAR and the swallowed 5 mg tablet. Steady state is achieved
after 8 days.
Selegiline is metabolized in vivo to l-methamphetamine and N-desmethylselegiline and
subsequently to l-amphetamine; which in turn are further metabolized to their
hydroxymetabolites.
ZELAPAR also produces a smaller fraction of the administered dose recoverable as the
metabolites than the conventional, swallowed formulation of selegiline.
In vitro metabolism studies indicate that CYP2B6 and CYP3A4 are involved in the
metabolism of selegiline. CYP2A6 may play a minor role in the metabolism.
Elimination
Following metabolism in the liver, selegiline is excreted primarily in the urine as
metabolites (mainly as l-methamphetamine) and as a small amount in the feces.
Specific Populations
Age: The effect of age on the pharmacokinetics of selegiline following ZELAPAR
administration has not been adequately characterized.
Gender: There are no differences between male and female subjects in overall (AUC ),
max
max
max
max
∞

time to maximum exposure (T ), and elimination half-life (t ) after administration of
ZELAPAR. Female subjects have an approximate 25% decrease in C compared to
male subjects. However, since the overall exposure (AUC ) is not different between the
genders, this pharmacokinetic difference is not likely to be clinically relevant.
Race: No studies have been conducted to evaluate the effects of race on the
pharmacokinetics of ZELAPAR.
Renal Impairment: Following once-daily dosing of ZELAPAR 2.5 mg to selegiline steady-
state (10 days) in 6 subjects with mild renal impairment (CLcr >50 to 89 mL/min) and in
6 subjects with moderate renal impairment (CLcr >30 to 50 mL/min), AUC and C of
selegiline and desmethylselegiline were not substantially different from healthy subjects;
however, methamphetamine and amphetamine exposures were increased by 34-67% in
subjects with moderate renal impairment. Following once-daily dosing of ZELAPAR 1.25
mg to steady-state (10 days) in 6 end-stage renal disease patients, off dialysis, selegiline
exposure was not substantially different from that in healthy subjects, however
methamphetamine and amphetamine exposures were increased approximately 4-fold
compared to healthy subjects [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Use in Specific
Populations (8.7)].
Hepatic Impairment: Subjects with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score 5 to 6),
received once-daily dosing of ZELAPAR 2.5 mg to selegiline until they attained steady-
state (10 days). The AUC and C of selegiline were 1.5-fold higher and the AUC and
C of the metabolite desmethylselegiline were 1.4-fold and 1.2-fold higher. In subjects
with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score 7 to 9), the AUC of selegiline and
desmethylselegiline increased 1.5-fold and 1.8-fold, respectively, whereas the C of
selegiline and desmethylselegiline were comparable to healthy subjects. Patients with
severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score >9) had a 4-fold increased AUC of
selegiline, 3-fold increased C of selegiline, a 1.25-fold increased AUC of
desmethylselegiline and 50% reduced C of desmethylselegiline. Methamphetamine
and amphetamine metabolite AUC values were not affected by liver dysfunction [see
Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Drug Interactions
No studies have been conducted to evaluate drug interactions on the pharmacokinetics
of ZELAPAR.
Effect of CYP3A inhibitor itraconazole: Itraconazole (200 mg once daily) did not affect
the pharmacokinetics of selegiline (single 10 mg oral, swallowed dose).
Although adequate studies to investigate the effect of CYP3A4-inducers on selegiline
have not been performed, drugs that induce CYP3A4 (e.g., phenytoin, carbamazepine,
nafcillin, phenobarbital, and rifampin) should be used with caution.
Drug Interaction Studies
No drug interaction studies have been conducted to evaluate the effects of other drugs
on the pharmacokinetics of ZELAPAR or the effect of selegiline on other drugs. In vitro
studies have demonstrated that selegiline is not an inhibitor of CYP450 enzymes.
Selegiline and two of its metabolites, methamphetamine and desmethylselegiline, have
little or no potential to induce CYP1A2 and CYP3A4/5 under clinical conditions.
∞
max ½
max
∞
max
max
max
max
max
max

13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenicity studies of orally administered selegiline are not available for ZELAPAR.
Carcinogenicity studies of selegiline have not been conducted using the buccal route.
Mutagenesis
Selegiline was negative in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay in and the
in vivo micronucleus assay. In the in vitro chromosomal aberration assay in mammalian
cells, selegiline was negative in the absence of metabolic activation but was clastogenic in
the presence of metabolic activation.
Impairment of Fertility
When selegiline was administered orally to male (5, 10, and 40 mg/kg/day) and female
(1, 5, and 25 mg/kg/day) rats prior to and during mating and continuing in females to
gestation day 7, a decreased number of implantations was observed at the highest
doses tested. In males, a reduction in sperm count and density was observed at the
highest dose tested. The no-effect doses for reproductive impairment in rats (10
mg/kg/day in males and 5 mg/kg/day in females) are approximately 40 (males) and 20
(females) times the maximum recommended human dose of 2.5 mg/day on a mg/m
basis.
No fertility studies have been conducted with selegiline using the buccal route.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The effectiveness of ZELAPAR as an adjunct to levodopa/carbidopa in the treatment of
Parkinson’s disease was established in a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled
trial (n=140; 94 received ZELAPAR, 46 received placebo) of three months’ duration.
Patients randomized to ZELAPAR received a daily dose of 1.25 mg for the first 6 weeks,
and a daily dose of 2.5 mg for the last 6 weeks. All patients were treated with
concomitant levodopa products and could additionally have been on concomitant
dopamine agonists, anticholinergics, amantadine, or any combination of these during the
trial. COMT (catechol-O-methyl-transferase) inhibitors were not allowed.
Patients with idiopathic Parkinson’s disease receiving levodopa were enrolled if they
demonstrated an average of at least 3 hours of “OFF” time per day on weekly diaries
collected during a 2-week screening period. The patients enrolled had a mean duration of
Parkinson’s disease of 7 years, with a range from 0.3 years to 22 years.
At selected times during the 12-week study, patients were asked to record the amount
of “OFF,” “ON,” “ON with dyskinesia,” or “sleep” time per day for two separate days
during the week prior to each scheduled visit. The primary efficacy outcome was the
reduction in average percentage daily “OFF” time during waking hours from baseline to
the end of the trial (averaging results at Weeks 10 and 12). Both treatment groups had
an average of 7 hours per day of “OFF” time at baseline. Table 2 shows the primary
efficacy results. Patients treated with ZELAPAR had a 13% reduction from baseline in
daily “OFF” time, compared with a 5% reduction for patients treated with placebo.
2
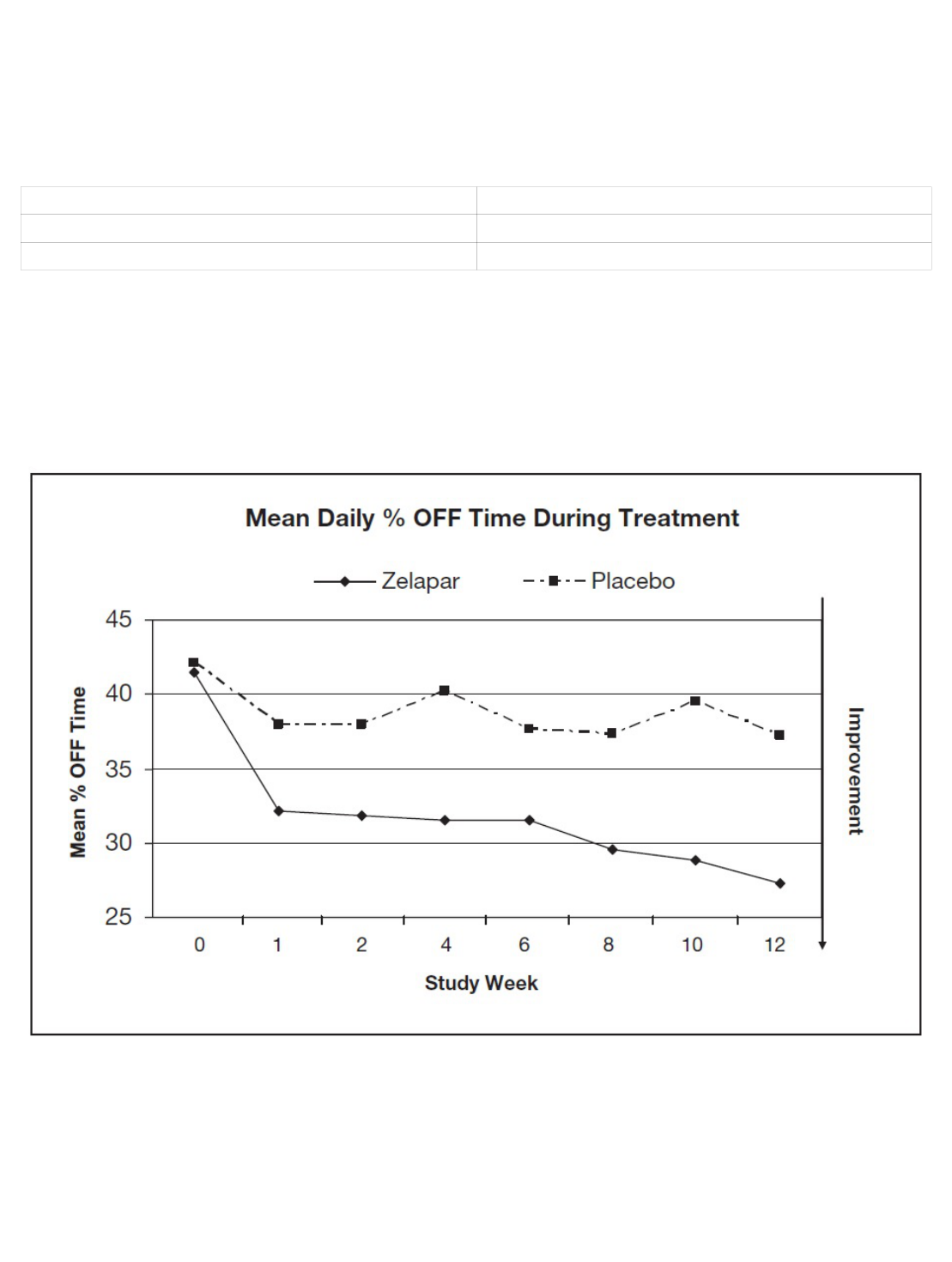
ZELAPAR-treated patients had an average reduction from baseline of “OFF” time of 2.2
hours per day, compared with a reduction of 0.6 hours in placebo-treated patients.
Table 2: Mean Percentage Change from Baseline in Daily "Off" Hours at End
of Treatment
(Average of Weeks 10 and 12) for Intent-to-Treat Population
Treatment Change from Baseline
Placebo - 5%
ZELAPAR - 13%
Figure 1 shows the mean daily percent “OFF” time during treatment over the whole
study period for patients treated with ZELAPAR vs. patients treated with placebo.
Figure 1: Mean Daily Percent "OFF" Time During Treatment Over the Whole Study Period
for Patients Treated with ZELAPAR vs. Patients Treated with Placebo
Dosage reduction of levodopa was allowed during this study if dopaminergic side
effects, including dyskinesia and hallucinations, emerged. In those patients who had
levodopa dosage reduced, the dose was reduced on average by 24% in ZELAPAR-
treated patients and by 21% in placebo-treated patients.
No difference in effectiveness based on age (patients >66 years old vs. <66 years) was
detected. The treatment effect size in males was twice that in females, but, given the

size of this single trial, this finding is of doubtful significance.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
ZELAPAR Orally Disintegrating Tablets are available containing 1.25 mg selegiline
hydrochloride in a Zydis formulation. Each pale yellow tablet is imprinted with a stylized
“V”. Ten tablets in a blister card are provided in a sachet pouch. The sachet pouch is
stored inside a clear child-resistant outer pouch and is packaged in a carton. The blister
card and sachet pouch are not child-resistant. The clear outer pouch is child-resistant.
ZELAPAR (selegiline hydrochloride) is available as:
Store at controlled room temperature, 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to
30°C (59°F to 86°F). Use within 3 months of opening pouch and immediately upon
opening individual blister. Store blister tablets in sachet pouch at all times. Keep sachet
pouch sealed or closed inside clear child-resistant pouch provided. Potency
cannot be guaranteed after 3 months of opening the sachet pouch.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Hypertension and Non-selective Inhibition of MAO Above the Recommended
Dose
Advise patients (or their caregivers) not to exceed the daily recommended dose of 2.5
mg. Explain the risk of using higher daily doses of ZELAPAR and provide a brief
description of the hypertensive tyramine reaction provided. Rare hypertensive reactions
with oral selegiline at recommended doses associated with dietary influences have been
reported.
Inform patients (or their caregivers) about the potential for MAOI-induced hypertensive
reactions and describe their signs and symptoms. Instruct patients to report,
immediately, severe headache or other atypical or unusual symptoms not previously
experienced or very high blood pressure.
The possibility exists that very tyramine-rich foods (e.g., aged cheese such as Stilton)
could possibly cause an increase in blood pressure. Patients should be advised to avoid
certain foods (e.g., aged cheese) containing a very large amount of tyramine while
taking recommended doses of ZELAPAR because of the potential for large increases in
blood pressure. If patients eat foods very rich in tyramine and do not feel well soon after
eating, they should contact their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions
(5.1)].
Serotonin Syndrome
Inform patients if they are taking, or planning to take, any prescription or over-the-
counter drugs, especially antidepressants and over-the-counter cold medications,
because there is a potential for interaction with ZELAPAR. Because patients should not
use meperidine or certain other analgesics with ZELAPAR, they should contact their
healthcare provider before taking analgesics [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Falling Asleep During Activities of Daily Living and Somnolence
®
NDC 0187-0453-02 1.25 mg per tablet carton of 6 sachet pouches (60 tablets)

Advise patients about the potential for sedating effects associated with ZELAPAR,
including somnolence and particularly to the possibility of falling asleep while engaged in
activities of daily living. Because somnolence can be a frequent adverse reaction with
potentially serious consequences, patients should neither drive a car nor engage in
other potentially dangerous activities until they have gained sufficient experience with
ZELAPAR to gauge whether or not it affects their mental and/or motor performance
adversely. Advise patients that if they experience increased somnolence or new
episodes of falling asleep during activities of daily living (e.g., watching television,
passenger in a car, etc.) at any time during treatment, they should not drive or
participate in potentially dangerous activities until they have contacted their physician.
Advise patients not to drive, operate machinery, or work at heights during treatment if
they have previously experienced somnolence and/or have fallen asleep without warning
prior to use of ZELAPAR [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Hypotension/Orthostatic Hypotension
Advise patients that they may develop symptomatic (or asymptomatic) hypotension
while taking ZELAPAR, especially if they are elderly. Hypotension may occur more
frequently during initial therapy. Accordingly, caution patients against rising rapidly after
sitting or lying down, especially if they have been doing so for prolonged periods and
especially at the initiation of treatment with ZELAPAR [see Warnings and Precautions
(5.4)].
Dyskinesia
Inform patients that ZELAPAR may cause and/or exacerbate pre-existing dyskinesias
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Hallucinations/Psychotic-Like Behavior
Inform patients that hallucinations and other psychotic-like behavior can occur while
taking ZELAPAR and that the elderly are at a higher risk than younger patients with
Parkinson's disease. Tell patients to report hallucinations or psychotic-like behavior to
their healthcare provider promptly should they develop [see Warnings and Precautions
(5.6)].
Impulse Control/Compulsive Behaviors
Advise patients that they may experience impulse control and/or compulsive behaviors
while taking one or more of the medications generally used for the treatment of
Parkinson’s disease, including ZELAPAR. Although it is not proven that the medications
caused these events, these urges were reported to have stopped in some cases when
the dose was reduced or the medication was stopped. Prescribers should ask patients
about the development of new or increased gambling urges, sexual urges or other
urges while being treated with ZELAPAR. Patients should inform their physician if they
experience new or increased gambling urges, increased sexual urges or other intense
urges while taking ZELAPAR. Physicians should consider dose reduction or stopping the
medication if a patient develops such urges while taking ZELAPAR [see Warnings and
Precautions (5.7)].
Withdrawal Emergent Hyperpyrexia and Confusion
Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if they wish to discontinue ZELAPAR
or decrease the dose of ZELAPAR [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].

Irritation of the Buccal Mucosa
Inform patients that ZELAPAR may cause irritation of the buccal mucosa including
swallowing pain, mouth pain, discrete areas of focal reddening, edema, and/or ulceration
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Risk for Phenylketonuric Patients
Advise patients that ZELAPAR contains aspartame which could cause problems in
patients with phenylketonuria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
Instructions for Use
Instruct patients not to remove the blister from the sachet pouch until just prior to
dosing. The blister pack should then be peeled open with dry hands and the orally
disintegrating tablet placed on the tongue, where the tablet will disintegrate. Patients
should also avoid drinking liquids or eating food 5 minutes before and after taking
ZELAPAR. Use ZELAPAR within 3 months of opening sachet pouch and immediately
upon opening individual blister. Store blister tablets in sachet pouch at all times. Keep
sachet pouch inside clear child-resistant pouch provided. Potency cannot be
guaranteed after 3 months of opening the pouch.
How should I store ZELAPAR?
•
•
•
•
•
BLISTER PACKS AND SACHET POUCHES ARE NOT CHILD-RESISTANT. THE
CLEAR OUTER POUCH IS CHILD-RESISTANT.
Distributed by:
Bausch Health US, LLC
Bridgewater, NJ 08807 USA
Manufactured by:
Catalent Pharma Solutions Limited
Swindon, Wiltshire, SN5 8RU, UK
ZELAPAR is a trademark of Bausch Health Companies Inc. or its affiliates.
Zydis® is a registered trademark of Catalent Pharma Solutions or one of its subsidiaries,
used under license.
All other product/brand names are trademarks of their respective owners.
© 2021 Bausch Health Companies Inc. or its affiliates
9603102
Store ZELAPAR at controlled room temperature 25°C (77°F).
Store blister tablets in sachet pouch at all times.
Keep sachet pouch sealed or closed inside of clear child-resistant pouch
provided.
Potency cannot be guaranteed after 3 months of opening the sachet
pouch.
Keep ZELAPAR and all medicines out of the reach of children.
