
Countdown Chapter 2
Livestock

Lift-Off 2–77
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Countdown Chapter 2
Livestock
Contents
Sheep Feet and Leg Structure .............................37
Swine Feet and Leg Structure .............................39
Quality Assurance
Beef Quality Assurance.......................................41
Dairy Cattle Quality Assurance.............................43
Goat Quality Assurance ......................................45
Sheep Quality Assurance ....................................47
Swine Quality Assurance ....................................49
Poultry Quality Assurance ...................................51
How to Read a Feed Tag
Beef................................................................53
Dairy...............................................................55
Goat................................................................57
Lamb ..............................................................59
Pig..................................................................61
Broiler .............................................................63
Turkey .............................................................65
Rabbit .............................................................67
Word Searches
Beef................................................................69
Goat................................................................71
Sheep .............................................................73
Swine .............................................................75
Breeds
Beef Breeds .......................................................1
Dairy Cattle Breeds..............................................3
Goat Breeds .......................................................5
Sheep Breeds .....................................................7
Swine Breeds .....................................................9
Parts
Beef Parts (Beginner) ........................................11
Beef Parts (Intermediate and
Advanced)...................................................13
Dairy Cow Parts (Beginner) ................................15
Dairy Cow Parts (Intermediate and
Advanced)...................................................17
Goat Parts (Beginner)........................................19
Goat Parts (Intermediate and
Advanced)...................................................21
Sheep Parts (Beginner)......................................23
Sheep Parts (Intermediate and
Advanced)...................................................25
Pig Parts (Beginner) ..........................................27
Pig Parts (Intermediate and
Advanced)...................................................29
Structure
Beef Feet and Leg Structure................................31
Dairy Cattle Feet and Leg Structure ......................33
Goat Mammary Structure ...................................35

Lift-Off 2–1
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Fill in the Blanks
• learn the breeds of beef, where the breeds
originated from, and what they look like.
Beef Breeds
Read the descriptions and fill in the blanks with the breed names.
1. __ __ __ __ __
8. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
9. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
10. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
11. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
12. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
2. __ __ __ __ __ __ __
3. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
4. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
5. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
6. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
7. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
Clues
1. This breed originated in Scotland, is polled with a black
smooth coat, and is known for carcass quality, milking,
mothering, and reproductive abilities.
2. This breed was developed in the southwestern United
States by crossing Angus with Brahman cattle from India.
It is black and known for the ability to withstand heat and
insects.
3. This breed was developed in France and imported into the
United States from Mexico in 1936. It is large, white, and
is noted for fast growth and lean carcasses.
4. Developed in Italy, this breed is white with black
pigmentation. It is the largest breed and is noted for
growth and beef producing abilities.
5. Originating in Germany, this breed is a solid cream to a
reddish-yellow in color. It is a general purpose breed with
good mothering abilities.
6. This breed was developed in England and brought to the
United States in 1817. It is red with a white face, and is
known for its vigor, hardiness, foraging ability, and quiet
disposition.
7. This is a breed that originated in west-central France. It is
light to golden red in color with lighter circles around the
eyes and muzzle. When this breed is slaughtered at an
early age, it yields a high percentage of lean meat with a
minimum amount of fat.
8. Developed in the United States from the Hereford breed,
this breed displays the same characteristics as Herefords
except for the polled trait.
9. This breed was developed on the King Ranch in Texas, is
five-eighths Shorthorn and three-eighths Brahman, and is
known for its hardiness, growth rate, long life, heat
tolerance, and insect resistance.
10. This breed was brought to the United States from England
in 1783. Animals can be red, white, or roan in color, and
are also noted for their good disposition, mothering, and
milking ability.
11. Imported into the United States from Switzerland, France,
and Germany, this breed is red to dark red, spotted with a
white face, and is noted for its fast growth and milking
ability.
12. This breed originated from Spanish Antilysin cattle and has
long horns and several different color patterns. It is known
for longevity, hardiness, strong survival instincts, and
resistant to disease and parasites.
References: Beef Learning Laboratory Kit; 4-H Beef Resource Handbook

2–2 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
8. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
9. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
10. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
11. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
12. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
2. __ __ __ __ __ __ __
3. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
4. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
5. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
6. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
7. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
Beef Breeds
Read the descriptions and fill in the blanks with the breed names.
1. __ __ __ __ __
A n g u s
T e x a s L o n g h o r n
S i m m e n t a l
S h o r t h o r n
S a n t a G e r t r u d i s
P o l l e d H e r e f o r d
L i m o u s i n
H e r e f o r d
G e l b v i e h
C h i a n i n a
C h a r o l a i s
B r a n g u s
In this activity you will:
Fill in the Blanks—Key
• learn the breeds of beef, where the breeds
originated from, and what they look like.
Clues
1. This breed originated in Scotland, is polled with a black
smooth coat, and is known for carcass quality, milking,
mothering, and reproductive abilities.
2. This breed was developed in the southwestern United
States by crossing Angus with Brahman cattle from India.
It is black and known for the ability to withstand heat and
insects.
3. This breed was developed in France and imported into the
United States from Mexico in 1936. It is large, white, and
is noted for fast growth and lean carcasses.
4. Developed in Italy, this breed is white with black
pigmentation. It is the largest breed and is noted for
growth and beef producing abilities.
5. Originating in Germany, this breed is a solid cream to a
reddish-yellow in color. It is a general purpose breed with
good mothering abilities.
6. This breed was developed in England and brought to the
United States in 1817. It is red with a white face, and is
known for its vigor, hardiness, foraging ability, and quiet
disposition.
7. This is a breed that originated in west-central France. It is
light to golden red in color with lighter circles around the
eyes and muzzle. When this breed is slaughtered at an
early age, it yields a high percentage of lean meat with a
minimum amount of fat.
8. Developed in the United States from the Hereford breed,
this breed displays the same characteristics as Herefords
except for the polled trait.
9. This breed was developed on the King Ranch in Texas, is
five-eighths Shorthorn and three-eighths Brahman, and is
known for its hardiness, growth rate, long life, heat
tolerance, and insect resistance.
10. This breed was brought to the United States from England
in 1783. Animals can be red, white, or roan in color, and
are also noted for their good disposition, mothering, and
milking ability.
11. Imported into the United States from Switzerland, France,
and Germany, this breed is red to dark red, spotted with a
white face, and is noted for its fast growth and milking
ability.
12. This breed originated from Spanish Antilysin cattle and has
long horns and several different color patterns. It is known
for longevity, hardiness, strong survival instincts, and
resistant to disease and parasites.
References: Beef Learning Laboratory Kit; 4-H Beef Resource Handbook

Lift-Off 2–3
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Fill in the Blanks
• learn the breeds of dairy cattle, where
the breeds originated from, and what
they look like.
Dairy Cattle Breeds
Read the descriptions and fill in the blanks with the breed names.
1. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
2. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
3. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
4. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
5. __ __ __ __ __ __
6. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
Clues
1. This breed was developed in 1750 in the county of Ayr,
Scotland, is medium in size with average milk production,
and has strongly-attached, well-shaped udders. Cows are
known for their extreme hardiness and good foraging
ability. They are red or mahogany, and white in color.
2. Originated in Switzerland, this breed is large with high
milk production and was developed to graze the
mountains and produce high protein milk for cheese. Cows
are known for their strength, ruggedness, and good feet
and leg structure. Animals are solid brown with a black
nose, switch, and hooves.
3. This breed was developed on an island in the English
Channel to produce high fat milk for making butter. Cows
are known for their gentle nature and their yellow-tinted
milk, and they can be characterized by their fawn and
white markings.
4. This breed originated in the Netherlands. It is largest and
most numerous breed. Cows are known for producing the
highest volume of milk of all breeds. They are black and
white, or red and white in color.
5. This breed was developed on an island in the English
Channel. They are the smallest cows and produce milk that
is the highest in fat and protein. They are characterized by
a shade of fawn with or without white markings.
6. Developed from an English breed of cattle, this breed
association was formed in 1972, from cattle who are
intermediate in size and milk production, are efficient in
converting feed into meat or milk, and have a high heat
tolerance. They can be red, white, or roan in color.
Reference: Dairy Learning Laboratory Kit

2–4 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Ayr sh i r e
Brown
Swi s
s
Gue r n se y
H
o
l
stein
Jersey
Mi l k i ng
Shor t hor n
In this activity you will:
Fill in the Blanks—Key
• learn the breeds of dairy cattle, where the
breeds originated from, and what they
look like.
1. This breed was developed in 1750 in the county of Ayr,
Scotland, is medium in size with average milk production,
and has strongly-attached, well-shaped udders. Cows are
known for their extreme hardiness and good foraging
ability. They are red or mahogany, and white in color.
2. Originated in Switzerland, this breed is large with high
milk production and was developed to graze the
mountains and produce high protein milk for cheese. Cows
are known for their strength, ruggedness, and good feet
and leg structure. Animals are solid brown with a black
nose, switch, and hooves.
3. This breed was developed on an island in the English
Channel to produce high fat milk for making butter. Cows
are known for their gentle nature and their yellow-tinted
milk, and they can be characterized by their fawn and
white markings.
4. This breed originated in the Netherlands. It is largest and
most numerous breed. Cows are known for producing the
highest volume of milk of all breeds. They are black and
white, or red and white in color.
5. This breed was developed on an island in the English
Channel. They are the smallest cows and produce milk that
is the highest in fat and protein. They are characterized by
a shade of fawn with or without white markings.
6. Developed from an English breed of cattle, this breed
association was formed in 1972, from cattle who are
intermediate in size and milk production, are efficient in
converting feed into meat or milk, and have a high heat
tolerance. They can be red, white, or roan in color.
Dairy Cattle Breeds
Read the descriptions and fill in the blanks with the breed names.
1. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
2. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
3. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
4. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
5. __ __ __ __ __ __
6. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
Clues
Reference: Dairy Learning Laboratory Kit

Lift-Off 2–5
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Goat Breeds
Read the descriptions and fill in the blanks with the breed names.
1. __ __ __ __ __ __
2. __ __ __ __ __ __
3. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
4. __ __ __ __ __ __
5. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
6. __ __ __ __ __
7. __ __ __ __ __ __
8. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
Clues
1. This breed originated in France, has upright ears, and can
be any color or combination of colors. It has a straight
face, medium to short hair, and is medium to large in size.
2. This is the only breed developed in the United States. It
has either “gopher” or “elf ears.” Any color or
combination of colors is acceptable, and it has short, fine,
glossy hair.
3. A Swiss breed of rugged bone, it is medium to large in
size, and either white or cream in color. It has short and
fine hair, is erect-eared, and has either a straight or dished
face.
4. A Swiss breed known for upright ears, straight faces, and
chamiosee color, it has a black belly and a light gray to
black udder. One of the smaller Swiss breeds, it is a
minimum of 28 inches in height and is the newest
recognized breed by the A.D.G.A.
5. This breed was originated in the Himalaya Mountains of
Asia, has a straight or concave nose, pendulous ears, and
twisted horns. It is usually a small, white, breed, with a
long, fine, and lustrous mohair fiber coat. The fine
underwool is a valuable product called cashmere. This
breed is known primarily as a browsing animal.
6. This breed came from West and Central Africa and the
Caribbean. Dwarf, short legged, hardy and alert, its profile
should have a dished appearance with a broad, strong, and
well-muscled jaw. It has a small compact body and its
main colors are white caramel, caramel, gray agouti, black
agouti, and charcoal.
7. This breed originated in India and Egypt, is known for its
high quality, high butterfat, and milk production. It has a
strong convex facial profile between the ears and the
muzzle and long, bell shaped, wide ears. It can have any
color pattern and have short, glossy, fine hair.
8. Of Swiss origin, this breed is medium in size, has upright
ears and a dished or straight face, is solid colored varying
from light fawn to dark chocolate. It has white ears with
dark spots in the middle, two white stripes down the face
from each eye to the muzzle, white hind legs, and a white
triangle on either side of the tail. It is known for its high
milk productivity.
In this activity you will:
Fill in the Blanks
• learn the breeds of goats, where the
breeds originated from, and what
they look like.
References: Goat Learning Laboratory Kit; 4-H Goat Resource Handbook

2–6 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Goat Breeds
Read the descriptions and fill in the blanks with the breed names.
1. __ __ __ __ __ __
2. __ __ __ __ __ __
3. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
4. __ __ __ __ __ __
5. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
6. __ __ __ __ __
7. __ __ __ __ __ __
8. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
Clues
underwool is a valuable product called cashmere. This
breed is known primarily as a browsing animal.
6. This breed came from West and Central Africa and the
Caribbean. Dwarf, short legged, hardy and alert, its profile
should have a dished appearance with a broad, strong, and
well-muscled jaw. It has a small compact body and its
main colors are white caramel, caramel, gray agouti, black
agouti, and charcoal.
7. This breed originated in India and Egypt, is known for its
high quality, high butterfat, and milk production. It has a
strong convex facial profile between the ears and the
muzzle and long, bell shaped, wide ears. It can have any
color pattern and have short, glossy, fine hair.
8. Of Swiss origin, this breed is medium in size, has upright
ears and a dished or straight face, is solid colored varying
from light fawn to dark chocolate. It has white ears with
dark spots in the middle, two white stripes down the face
from each eye to the muzzle, white hind legs, and a white
triangle on either side of the tail. It is known for its high
milk productivity.
1. This breed originated in France, has upright ears, and can
be any color or combination of colors. It has a straight
face, medium to short hair, and is medium to large in size.
2. This is the only breed developed in the United States. It
has either “gopher” or “elf ears.” Any color or
combination of colors is acceptable, and it has short, fine,
glossy hair.
3. A Swiss breed of rugged bone, it is medium to large in
size, and either white or cream in color. It has short and
fine hair, is erect-eared, and has either a straight or dished
face.
4. A Swiss breed known for upright ears, straight faces, and
chamiosee color, it has a black belly and a light gray to
black udder. One of the smaller Swiss breeds, it is a
minimum of 28 inches in height and is the newest
recognized breed by the A.D.G.A.
5. This breed was originated in the Himalaya Mountains of
Asia, has a straight or concave nose, pendulous ears, and
twisted horns. It is usually a small, white, breed, with a
long, fine, and lustrous mohair fiber coat. The fine
A l p i n e
T o g g e n b u r g
S a a n e n
P y g m y
O b e r h a s l i
N u b i a n
L a m a n c h a
A n g o r a
In this activity you will:
Fill in the Blanks—Key
• learn the breeds of goats, where the breeds
originated from, and what they look like.
References: Goat Learning Laboratory Kit; 4-H Goat Resource Handbook

Lift-Off 2–7
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Sheep Breeds
Read the descriptions and fill in the blanks with the breed names. The circled
letters will then spell out one remaining breed.
1. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
2. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
3. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
4. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
5. __ __ __ __ __ __ __
6. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
7. __ __ __ __ __ __ __
8. __ __ __ __ __ __
9. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
Clues
In this activity you will:
Fill in the Blanks
• learn the breeds of sheep, where the
breeds originated from, and what
they look like.
The last breed name is
_____________________________________
1. This breed is fine-boned, produces medium grade wool,
reaches sexual maturity early, and is very prolific,
producing two to four lambs each lambing.
2. This breed is white faced and was developed in New
Zealand from a Lincoln and Leicester X Merino crosses. It is
medium in size and yields heavy, medium wool fleeces.
3. This breed was developed in the United States from a
Lincoln ram and Rambouillet ewe cross. It is known for
size, wool producing ability, and productivity under range
conditions. It is a white faced, polled breed and has wool
on the legs.
4. This breed was developed in England, is dark faced, polled,
has wool on the head and face, and is heavy muscled and
milks well.
5. This breed is polled with a black head and legs and has the
greatest number of purebred registrations in the United
States. It is a sire breed known for its meatiness and
carcass quality.
6. This is the oldest breed from England and is known for
producing a meaty carcass. It is polled with a gray to a
mouse-brown colored face, has wool on the legs, and
produces a medium wool.
7. This breed was developed in Scotland and is adaptable to
a variety of climates. It is small in size, white faced, bare
legged and headed, and is a good milker possessing
excellent lamb vigor.
8. This breed, developed in Southern England, is polled,
scurred, or horned. A ewe breed, it is known for breeding
out of season, heavy milking ability, and producing more
than one lamb crop per year. This breed also yields heavily
muscled carcasses.
9. This breed was developed in France. It is long lived,
rugged, and will breed out of season. It has fine wool, is
large and white faced, and has wool on the head and legs.
The circled answer is a breed that was developed in Southern
England. It is large framed, wool capped, black faced, and
medium wooled. It has good milking ability and high carcass
cutability.
References: Sheep Learning Laboratory Kit; 4-H Sheep Resource Handbook

2–8 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Sheep Breeds
Read the descriptions and fill in the blanks with the breed names. The circled
letters will then spell out one remaining breed.
1. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
2. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
3. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
4. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
5. __ __ __ __ __ __ __
6. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
7. __ __ __ __ __ __ __
8. __ __ __ __ __ __
9. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
Clues
In this activity you will:
Fill in the Blanks—Key
• learn the breeds of sheep, where the
breeds originated from, and what
they look like.
The last breed name is
_____________________________________
1. This breed is fine-boned, produces medium grade wool,
reaches sexual maturity early, and is very prolific,
producing two to four lambs each lambing.
2. This breed is white faced and was developed in New
Zealand from a Lincoln and Leicester X Merino crosses. It is
medium in size and yields heavy, medium wool fleeces.
3. This breed was developed in the United States from a
Lincoln ram and Rambouillet ewe cross. It is known for
size, wool producing ability, and productivity under range
conditions. It is a white faced, polled breed and has wool
on the legs.
4. This breed was developed in England, is dark faced, polled,
has wool on the head and face, and is heavy muscled and
milks well.
5. This breed is polled with a black head and legs and has the
greatest number of purebred registrations in the United
States. It is a sire breed known for its meatiness and
carcass quality.
6. This is the oldest breed from England and is known for
producing a meaty carcass. It is polled with a gray to a
mouse-brown colored face, has wool on the legs, and
produces a medium wool.
7. This breed was developed in Scotland and is adaptable to
a variety of climates. It is small in size, white faced, bare
legged and headed, and is a good milker possessing
excellent lamb vigor.
8. This breed, developed in Southern England, is polled,
scurred, or horned. A ewe breed, it is known for breeding
out of season, heavy milking ability, and producing more
than one lamb crop per year. This breed also yields heavily
muscled carcasses.
9. This breed was developed in France. It is long lived,
rugged, and will breed out of season. It has fine wool, is
large and white faced, and has wool on the head and legs.
The circled answer is a breed that was developed in Southern
England. It is large framed, wool capped, black faced, and
medium wooled. It has good milking ability and high carcass
cutability.
F
innsheep
Corr i eda l e
C
ol
u
mb i a
Shr opsh i re
Suf fo lk
S
ou t hdown
C
heviot
Dor set
R
ambou i l le t
Hampshire.
References: Sheep Learning Laboratory Kit; 4-H Sheep Resource Handbook

Lift-Off 2–9
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Swine Breeds
Read the descriptions and fill in the blanks with the breed names.
1. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
2. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
3. __ __ __ __ __
4. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
5. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
6. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
7. __ __ __ __ __ __ __
8. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
In this activity you will:
Fill in the Blanks
• learn the breeds of swine, where the
breeds originated from, and what
they look like.
Clues
1. This breed originated in England. It is black with white
feet, tail, and face. It is known for having sound skeletons,
dish-faced snouts, and short erect ears.
2. This breed was developed in Pennsylvania, is white, has
medium sized droopy ears, and is a maternal breed.
3. Developed in America from a cross between red hogs from
New York and red hogs from New Jersey, these hogs are
light red to dark red and droopy eared. They are quick,
efficient growers and are good mothers.
4. This breed, developed in England, is black with a white
belt around the shoulders and both front legs. They are
erect-eared and heavily muscled.
5. Originally from Denmark, this is a long bodied breed with
large floppy ears and strong maternal traits.
6. This breed, developed in Ohio, is black with six white
points (four white legs, tail, and nose). It is lean, droopy
eared, and heavily muscled.
7. This breed was developed in Indiana. It is medium in size
with black and white spots, and droopy eared. It is a fast
gainer and an aggressive breeder.
8. This breed came from England. It is white colored, erect
eared, and has a long, large frame. It is known as the
mother breed because they produce large litters and are
heavy milkers.
References: Swine Learning Laboratory Kit; 4-H Swine Resource Handbook

2–10 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Swine Breeds
Read the descriptions and fill in the blanks with the breed names.
1. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
2. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
3. __ __ __ __ __
4. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
5. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
6. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
7. __ __ __ __ __ __ __
8. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
B
erkshire
Chester
Wh i t e
Duroc
Hampshi re
Landrace
P
oland
Ch i na
Spot ted
Yo r ks h i r e
In this activity you will:
Fill in the Blanks—Key
• learn the breeds of swine, where the
breeds originated from, and what
they look like.
Clues
1. This breed originated in England. It is black with white
feet, tail, and face. It is known for having sound skeletons,
dish-faced snouts, and short erect ears.
2. This breed was developed in Pennsylvania, is white, has
medium sized droopy ears, and is a maternal breed.
3. Developed in America from a cross between red hogs from
New York and red hogs from New Jersey, these hogs are
light red to dark red and droopy eared. They are quick,
efficient growers and are good mothers.
4. This breed, developed in England, is black with a white
belt around the shoulders and both front legs. They are
erect-eared and heavily muscled.
5. Originally from Denmark, this is a long bodied breed with
large floppy ears and strong maternal traits.
6. This breed, developed in Ohio, is black with six white
points (four white legs, tail, and nose). It is lean, droopy
eared, and heavily muscled.
7. This breed was developed in Indiana. It is medium in size
with black and white spots, and droopy eared. It is a fast
gainer and an aggressive breeder.
8. This breed came from England. It is white colored, erect
eared, and has a long, large frame. It is known as the
mother breed because they produce large litters and are
heavy milkers.
References: Swine Learning Laboratory Kit; 4-H Swine Resource Handbook

Lift-Off 2–11
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Beef Parts
Activity level: Beginners or members ages 9 to 11
Write in the number that corresponds to the correct part of the animal.
In this activity you will:
Identification
• learn the parts of a steer.
_____ throat
_____ neck
_____ point of shoulder
_____ loin
_____ hoof
_____ heart girth
_____ pastern
_____ poll
_____ crest
_____ face
_____ pin
_____ muzzle
_____ dewlap
_____ rump
_____ brisket
_____ back
_____ knee
_____ rib
_____ sheath/navel
_____ rear flank
_____ ear
_____ hook
_____ dewclaw
_____ hock
_____ cannon
_____ stifle joint
_____ forearm
_____ switch
_____ tail head
_____ hindquarter
_____ belly
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
References: Ohio 4-H Beef, Sheep, and Swine Selection and Evaluation Book #103R; Beef Learning Laboratory Kit

2–12 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Beef Parts
Activity level: Beginners or members ages 9 to 11
Write in the number that corresponds to the correct part of the animal.
In this activity you will:
Identification—Key
• learn the parts of a steer.
_____ throat
_____ neck
_____ point of shoulder
_____ loin
_____ hoof
_____ heart girth
_____ pastern
_____ poll
_____ crest
_____ face
_____ pin
_____ muzzle
_____ dewlap
_____ rump
_____ brisket
_____ back
_____ knee
_____ rib
_____ sheath/navel
_____ rear flank
_____ ear
_____ hook
_____ dewclaw
_____ hock
_____ cannon
_____ stifle joint
_____ forearm
_____ switch
_____ tail head
_____ hindquarter
_____ belly
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
7
10
1
11
13
3
15
5
17
30
19
20
9
28
22
24
23
26
16
25
2
27
29
12
31
14
4
18
6
21
8
References: Ohio 4-H Beef, Sheep, and Swine Selection and Evaluation Book #103R; Beef Learning Laboratory Kit
18

Lift-Off 2–13
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Identification
• learn the parts of a steer.
Beef Parts
Activity level: Intermediate and advanced members ages 12 to 18
Write in the name that corresponds to the correct part of the animal.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
1. ____________________
2. ____________________
3. ____________________
4. ____________________
5. ____________________
6. ____________________
7. ____________________
8. ____________________
9. ____________________
10. ____________________
11. ____________________
12. ____________________
13. ____________________
14. ____________________
15. ____________________
16. ____________________
17. ____________________
18. ____________________
19. ____________________
20. ____________________
21. ____________________
22. ____________________
23. ____________________
24. ____________________
25. ____________________
26. ____________________
27. ____________________
28. ____________________
29. ____________________
30. ____________________
31. ____________________
18
References: Ohio 4-H Beef, Sheep, and Swine Selection and Evaluation Book #103R; Beef Learning Laboratory Kit

2–14 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
pin
tail head
rump
loin
back
heart girth
crest
poll
ear
face
In this activity you will:
Identification—Key
• learn the parts of a steer.
Beef Parts
Activity level: Intermediate and advanced members ages 12 to 18
Write in the name that corresponds to the correct part of the animal.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
1. ____________________
2. ____________________
3. ____________________
4. ____________________
5. ____________________
6. ____________________
7. ____________________
8. ____________________
9. ____________________
10. ____________________
11. ____________________
12. ____________________
13. ____________________
14. ____________________
15. ____________________
16. ____________________
17. ____________________
18. ____________________
19. ____________________
20. ____________________
21. ____________________
22. ____________________
23. ____________________
24. ____________________
25. ____________________
26. ____________________
27. ____________________
28. ____________________
29. ____________________
30. ____________________
31. ____________________
18
References: Ohio 4-H Beef, Sheep, and Swine Selection and Evaluation Book #103R; Beef Learning Laboratory Kit
muzzle
throat
dewlap
point of shoulder
brisket
forearm
knee
hoof
sheath/navel
rear flank
pastern
dewclaw
cannon
hock
switch
stifle joint
hindquarter
hook
belly
rib
neck

Lift-Off 2–15
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Dairy Cow Parts
Activity level: Beginners or members ages 9 to 11
Write in the number that corresponds to the correct part of the animal.
In this activity you will:
Identification
• learn the parts of a dairy cow.
Reference: The Dairy Livestock Learning Laboratory Kit
_____ pin bone
_____ pastern
_____ back
_____ loin
_____ chine
_____ thurl
_____ teat
_____ withers
_____ hock
_____ rear udder
_____ heart girth
_____ shoulder blade
_____ point of shoulder
_____ hoof
_____ rump
_____ fore udder
_____ crops
_____ chest floor
_____ neck
_____ muzzle
_____ thigh
_____ tail
_____ hip
_____ stifle
_____ throat
_____ ribs
_____ barrel
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
Prepared By: Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student

2–16 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
1
18
5
4
6
23
17
Dairy Cow Parts
Activity level: Beginners or members ages 9 to 11
Write in the number that corresponds to the correct part of the animal.
In this activity you will:
Identification—Key
• learn the parts of a dairy cow.
Reference: The Dairy Livestock Learning Laboratory Kit
_____ pin bone
_____ pastern
_____ back
_____ loin
_____ chine
_____ thurl
_____ teat
_____ withers
_____ hock
_____ rear udder
_____ heart girth
_____ shoulder blade
_____ point of shoulder
_____ hoof
_____ rump
_____ fore udder
_____ crops
_____ chest floor
_____ neck
_____ muzzle
_____ thigh
_____ tail
_____ hip
_____ stifle
_____ throat
_____ ribs
_____ barrel
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
8
19
20
27
12
13
14
2
16
7
15
9
10
21
22
3
24
11
26
25
Prepared By: Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student

Lift-Off 2–17
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Dairy Cow Parts
Activity level: Intermediate and advanced members ages 12 to 18
Write in the name that corresponds to the correct part of the animal.
In this activity you will:
Identification
• learn the parts of a dairy cow.
1. ____________________
2. ____________________
3. ____________________
4. ____________________
5. ____________________
6. ____________________
7. ____________________
8. ____________________
9. ____________________
10. ____________________
11. ____________________
12. ____________________
13. ____________________
14. ____________________
15. ____________________
16. ____________________
17. ____________________
18. ____________________
19. ____________________
20. ____________________
21. ____________________
22. ____________________
23. ____________________
24. ____________________
25. ____________________
26. ____________________
27. ____________________
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
Reference: The Dairy Livestock Learning Laboratory Kit
Prepared By: Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student

2–18 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
pin bone
rump
hip (hooks)
loin
back
chine
crops
withers
neck
Dairy Cow Parts
Activity level: Intermediate and advanced members ages 12 to 18
Write in the name that corresponds to the correct part of the animal.
In this activity you will:
Identification—Key
• learn the parts of a dairy cow.
1. ____________________
2. ____________________
3. ____________________
4. ____________________
5. ____________________
6. ____________________
7. ____________________
8. ____________________
9. ____________________
10. ____________________
11. ____________________
12. ____________________
13. ____________________
14. ____________________
15. ____________________
16. ____________________
17. ____________________
18. ____________________
19. ____________________
20. ____________________
21. ____________________
22. ____________________
23. ____________________
24. ____________________
25. ____________________
26. ____________________
27. ____________________
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
Reference: The Dairy Livestock Learning Laboratory Kit
muzzle
throat
shoulder blade
point of shoulder
hoof
chest floor
fore udder
teat
pastern
hock
rear udder
thigh
tail
thurl
stifle
barrel
ribs
heart girth
Prepared By: Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
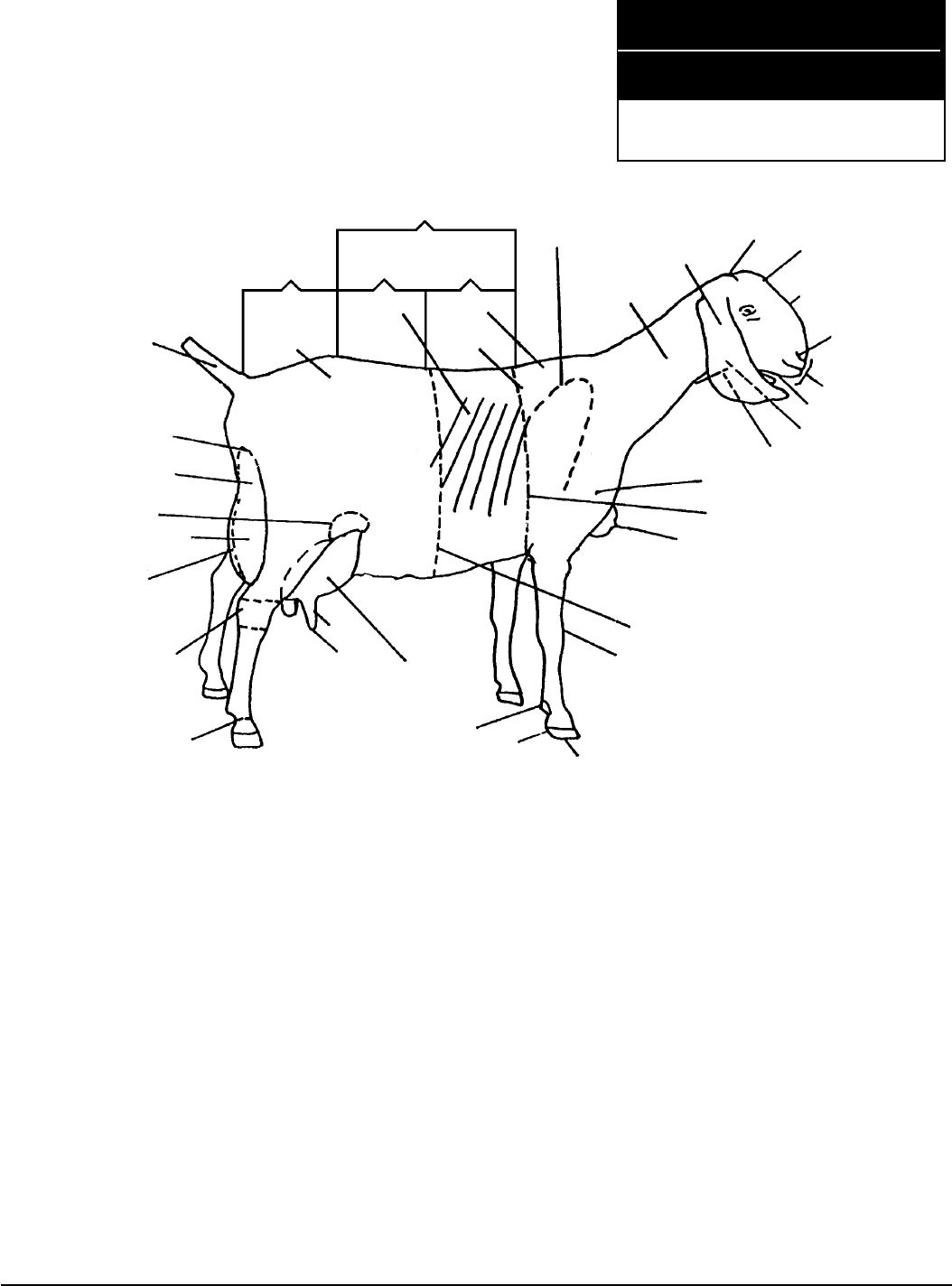
Lift-Off 2–19
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Goat Parts
Activity level: Beginners or members ages 9 to 11
Write in the number that corresponds to the correct part of the animal.
In this activity you will:
Identification
• learn the parts of a goat.
References: Goat Resource 4-H Handbook; Goat Livestock Learning Laboratory Kit
_____ rib
_____ ear
_____ point of shoulder
_____ throat
_____ withers
_____ heel
_____ jaw
_____ brisket
_____ hip
_____ orifice
_____ heart girth
_____ pastern
_____ forehead
_____ crop
_____ sole
_____ rump
_____ hock
_____ stifle joint
_____ loin
_____ dewclaw
_____ muzzle
_____ escutcheon
_____ fore udder
_____ neck
_____ bridge of nose
_____ chine
_____ barrel
_____ poll
_____ back
_____ rear udder
_____ nostril
_____ tail
_____ teat
_____ rear udder attachment
_____ knee
_____ dewlap
_____ shoulder blade
_____ medial suspensory ligament
1
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31

2–20 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Goat Parts
Activity level: Beginners or members ages 9 to 11
Write in the number that corresponds to the correct part of the animal.
In this activity you will:
Identification—Key
• learn the parts of a goat.
References: Goat Resource 4-H Handbook; Goat Livestock Learning Laboratory Kit
_____ rib
_____ ear
_____ point of shoulder
_____ throat
_____ withers
_____ heel
_____ jaw
_____ brisket
_____ hip
_____ orifice
_____ heart girth
_____ pastern
_____ forehead
_____ crop
_____ sole
_____ rump
_____ hock
_____ stifle joint
_____ loin
_____ dewclaw
_____ muzzle
_____ escutcheon
_____ fore udder
_____ neck
_____ bridge of nose
_____ chine
_____ barrel
_____ poll
_____ back
_____ rear udder
_____ nostril
_____ tail
_____ teat
_____ rear udder attachment
_____ knee
_____ dewlap
_____ shoulder blade
_____ medial suspensory ligament
5
12
21
19
8
27
18
23
2
31
22
32
14
9
26
3
33
36
4
28
17
38
29
11
15
7
24
13
6
35
16
1
30
37
35
20
10
34
1
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31

Lift-Off 2–21
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Identification
• learn the parts of a goat.
Goat Parts
Activity level: Intermediate and advanced members ages 12 to 18
Write in the name that corresponds to the correct part of the animal.
1. ____________________
2. ____________________
3. ____________________
4. ____________________
5. ____________________
6. ____________________
7. ____________________
8. ____________________
9. ____________________
10. ____________________
11. ____________________
12. ____________________
13. ____________________
14. ____________________
15. ____________________
16. ____________________
17. ____________________
18. ____________________
19. ____________________
20. ____________________
21. ____________________
22. ____________________
23. ____________________
24. ____________________
25. ____________________
26. ____________________
27. ____________________
28. ____________________
29. ____________________
30. ____________________
31. ____________________
32. ____________________
33. ____________________
34. ____________________
35. ____________________
36. ____________________
37. ____________________
38. ____________________
References: Goat Resource 4-H Handbook; Goat Livestock Learning Laboratory Kit
1
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31

2–22 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
tail
hip
rump
loin
rib
back
chine
withers
crop
shoulder blade
neck
In this activity you will:
Identification—Key
• learn the parts of a goat.
Goat Parts
Activity level: Intermediate and advanced members ages 12 to 18
Write in the name that corresponds to the correct part of the animal.
1. ____________________
2. ____________________
3. ____________________
4. ____________________
5. ____________________
6. ____________________
7. ____________________
8. ____________________
9. ____________________
10. ____________________
11. ____________________
12. ____________________
13. ____________________
14. ____________________
15. ____________________
16. ____________________
17. ____________________
18. ____________________
19. ____________________
20. ____________________
21. ____________________
22. ____________________
23. ____________________
24. ____________________
25. ____________________
26. ____________________
27. ____________________
28. ____________________
29. ____________________
30. ____________________
31. ____________________
32. ____________________
33. ____________________
34. ____________________
35. ____________________
36. ____________________
37. ____________________
38. ____________________
References: Goat Resource 4-H Handbook; Goat Livestock Learning Laboratory Kit
ear
poll
forehead
bridge of nose
nostril
muzzle
jaw
throat
dewlap
point of shoulder
heart girth
brisket
barrel
knee
sole
heel
dewclaw
fore udder
teat
orifice
pastern
hock
medial suspensory ligament
rear udder
stifle joint
rear udder attachment
escutcheon
1
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31

Lift-Off 2–23
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Sheep Parts
Activity level: Beginners or members ages 9 to 11
Write in the number that corresponds to the correct part of the animal.
In this activity you will:
Identification
• learn the parts of a sheep.
References: Sheep Breeding and Market Lamb 4-H Resource Handbook; Sheep Livestock Learning Laboratory Kit
1
2
3
4
5
6
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
_____ muzzle
_____ forearm
_____ twist
_____ belly
_____ neck
_____ top of shoulder
_____ face
_____ loin
_____ knee
_____ rump
_____ poll
_____ middle
_____ back/rack
_____ hip
_____ hock
_____ pastern
_____ rear flank
_____ hoof
_____ dock
_____ cannon
_____ forehead
_____ fore flank
_____ breast/brisket
_____ shoulder
_____ leg
7

2–24 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Sheep Parts
Activity level: Beginners or members ages 9 to 11
Write in the number that corresponds to the correct part of the animal.
In this activity you will:
Identification—Key
• learn the parts of a sheep.
1
2
3
4
5
6
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
_____ muzzle
_____ forearm
_____ twist
_____ belly
_____ neck
_____ top of shoulder
_____ face
_____ loin
_____ knee
_____ rump
_____ poll
_____ middle
_____ back/rack
_____ hip
_____ hock
_____ pastern
_____ rear flank
_____ hoof
_____ dock
_____ cannon
_____ forehead
_____ fore flank
_____ breast/brisket
_____ shoulder
_____ leg
7
1
23
13
19
5
6
2
8
22
10
4
12
7
9
15
16
18
17
11
21
3
20
24
25
14
References: Sheep Breeding and Market Lamb 4-H Resource Handbook; Sheep Livestock Learning Laboratory Kit

Lift-Off 2–25
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Identification
• learn the parts of a sheep.
Sheep Parts
Activity level: Intermediate and advanced members ages 12 to 18
Write in the name that corresponds to the correct part of the animal below.
1. ____________________
2. ____________________
3. ____________________
4. ____________________
5. ____________________
6. ____________________
7. ____________________
8. ____________________
9. ____________________
10. ____________________
11. ____________________
12. ____________________
13. ____________________
14. ____________________
15. ____________________
16. ____________________
17. ____________________
18. ____________________
19. ____________________
20. ____________________
21. ____________________
22. ____________________
23. ____________________
24. ____________________
25. ____________________
1
2
3
4
5
6
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
7
References: Sheep Breeding and Market Lamb 4-H Resource Handbook; Sheep Livestock Learning Laboratory Kit

2–26 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Identification—Key
• learn the parts of a sheep.
Sheep Parts
Activity level: Intermediate and advanced members ages 12 to 18
Write in the name that corresponds to the correct part of the animal below.
1. ____________________
2. ____________________
3. ____________________
4. ____________________
5. ____________________
6. ____________________
7. ____________________
8. ____________________
9. ____________________
10. ____________________
11. ____________________
12. ____________________
13. ____________________
14. ____________________
15. ____________________
16. ____________________
17. ____________________
18. ____________________
19. ____________________
20. ____________________
21. ____________________
22. ____________________
23. ____________________
24. ____________________
25. ____________________
1
2
3
4
5
6
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
7
middle
twist
leg
hock
pastern
hoof
rear flank
belly
fore flank
cannon
knee
forearm
breast or brisket
shoulder
muzzle
face
forehead
poll
neck
top of shoulder
back or rack
loin
hip
rump
dock
References: Sheep Breeding and Market Lamb 4-H Resource Handbook; Sheep Livestock Learning Laboratory Kit

Lift-Off 2–27
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Pig Parts
Activity level: Beginners or members ages 9 to 11
Write in the number that corresponds to the correct part of the animal.
In this activity you will:
Identification
• learn the parts of a pig.
_____ vulva
_____ rear flank
_____ stifle joint
_____ neck
_____ dewclaw
_____ forerib
_____ belly
_____ head
_____ foot
_____ tail
_____ snout
_____ ham
_____ ear
_____ hock
_____ shoulder
_____ side
_____ back
_____ teats
_____ rump
_____ pastern
_____ cannon
_____ knee
_____ jowl
_____ fore flank
_____ loin
_____ sheath
_____ elbow
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
References: Market Hog 4-H Handbook #135R; Beef, Sheep, and Swine Selection and Evaluation 4-H Book #103R; Swine Livestock Learning Laboratory Kit

2–28 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Pig Parts
Activity level: Beginners or members ages 9 to 11
Write in the number that corresponds to the correct part of the animal.
In this activity you will:
Identification—Key
• learn the parts of a pig.
_____ vulva
_____ rear flank
_____ stifle joint
_____ neck
_____ dewclaw
_____ forerib
_____ belly
_____ head
_____ foot
_____ tail
_____ snout
_____ ham
_____ ear
_____ hock
_____ shoulder
_____ side
_____ back
_____ teats
_____ rump
_____ pastern
_____ cannon
_____ knee
_____ jowl
_____ fore flank
_____ loin
_____ sheath
_____ elbow
11
27
13
4
15
6
17
2
19
10
1
12
3
14
5
26
7
18
9
20
21
22
23
25
8
16
24
References: Market Hog 4-H Handbook #135R; Beef, Sheep, and Swine Selection and Evaluation 4-H Book #103R; Swine Livestock Learning Laboratory Kit
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27

Lift-Off 2–29
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Identification
• learn the parts of a pig.
Pig Parts
Activity level: Intermediate and advanced members ages 12 to 18
Write in the name that corresponds to the correct part of the animal.
1. ____________________
2. ____________________
3. ____________________
4. ____________________
5. ____________________
6. ____________________
7. ____________________
8. ____________________
9. ____________________
10. ____________________
11. ____________________
12. ____________________
13. ____________________
14. ____________________
15. ____________________
16. ____________________
17. ____________________
18. ____________________
19. ____________________
20. ____________________
21. ____________________
22. ____________________
23. ____________________
24. ____________________
25. ____________________
26. ____________________
27. ____________________
References: Market Hog 4-H Handbook #135R; Beef, Sheep, and Swine Selection and Evaluation 4-H Book #103R; Swine Livestock Learning Laboratory Kit
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27

2–30 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
snout
head
ear
neck
shoulder
forerib area
back
loin
rump
In this activity you will:
Identification—Key
• learn the parts of a pig.
Pig Parts
Activity level: Intermediate and advanced members ages 12 to 18
Write in the name that corresponds to the correct part of the animal.
1. ____________________
2. ____________________
3. ____________________
4. ____________________
5. ____________________
6. ____________________
7. ____________________
8. ____________________
9. ____________________
10. ____________________
11. ____________________
12. ____________________
13. ____________________
14. ____________________
15. ____________________
16. ____________________
17. ____________________
18. ____________________
19. ____________________
20. ____________________
21. ____________________
22. ____________________
23. ____________________
24. ____________________
25. ____________________
26. ____________________
27. ____________________
tail
vuvla (Guilt)
ham
stifle joint
hock
dewclaw
sheath (Barrow)
belly
teats
foot (toes)
pastern
cannon
knee
jowl
elbow
fore flank
side
rear flank
References: Market Hog 4-H Handbook #135R; Beef, Sheep, and Swine Selection and Evaluation 4-H Book #103R; Swine Livestock Learning Laboratory Kit
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27

Lift-Off 2–31
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Identification
• identify the various feet and leg
structure diagrams.
References: Beef Resource 4-H Handbook; Beef Livestock Learning Laboratory Kit; Beef, Sheep and Swine Selection and Evaluation 4-H #103R
Beef Feet and Leg Structure
On the blanks, write the letter of the term that corresponds to the diagram below.
A. Knock kneed or splayfooted
B. Bowlegged or pigeon toed
C. Correct
D. Cow hocked or splayfooted
E. Bowlegged or pigeon toed
F. C orr ec t
G. Buck kneed
H. Calf kneed
I. Sickle hocked
J. Postlegged

2–32 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Identification—Key
• identify the various feet and leg
structure diagrams.
References: Beef Resource 4-H Handbook; Beef Livestock Learning Laboratory Kit; Beef, Sheep and Swine Selection and Evaluation 4-H #103R
D
Beef Feet and Leg Structure
On the blanks, write the letter of the term that corresponds to the diagram below.
A. Knock kneed or splayfooted
B. Bowlegged or pigeon toed
C. Correct
D. Cow hocked or splayfooted
E. Bowlegged or pigeon toed
F. Correct
G. Buck kneed
H. Calf kneed
I. Sickle hocked
J. Postlegged
A
G
B or E
B or E
C or F
C or F
H
I
J

Lift-Off 2–33
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Dairy Cattle Feet and Leg
Structure
On the blanks, write the letter of the term that corresponds to the diagram below.
A. Weak Pastern, Shallow Heel
B. Thurls Too Far Back
C. Sickle-Hocked
D. Cow-Hocked
E. Correct, Ideal Pastern
In this activity you will:
Identification
• identify the various feet and leg
structure diagrams.
Reference: Dairy Livestock Learning Laboratory Kit
F. Correct Set
G. Correct, Ideal Rear Legs
H. Post Legged
I. Correct, Thurl Placement
Prepared By: Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student

2–34 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Dairy Cattle Feet and Leg
Structure
On the blanks, write the letter of the term that corresponds to the diagram below.
A. Weak Pastern, Shallow Heel
B. Thurls Too Far Back
C. Sickle-Hocked
D. Cow-Hocked
E. Correct, Ideal Pastern
In this activity you will:
Identification—Key
• identify the various feet and leg
structure diagrams.
Reference: Dairy Livestock Learning Laboratory Kit
F. Correct Set
G. Correct, Ideal Rear Legs
H. Post Legged
I. Correct, Thurl Placement
A
B
C
D
E
F
GH
I
Prepared By: Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student

Lift-Off 2–35
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Goat Mammary Structure
On the blanks, write the letter of the term that corresponds to the diagram below.
A. Fore Udder Attachments, Broken
B. Rear Udder Attachments, Ideal
C. Medial Suspensory Ligaments, Broken
D. Medial Suspensory Ligaments, Ideal
E. Medial Suspensory Ligaments, Weakened
In this activity you will:
Identification
• identify the various udder structure
diagrams.
F. Bottle-shaped teats
G. Spur teat
H. Teats that point sideways
I. Pencil-shaped teats
J. Uneven teats
K. Extremely small teats
L. Ideal teats
Prepared By: Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
References: 4-H Goat Handbook; Goat Learning Laboratory Kit

2–36 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Goat Mammary Structure
On the blanks, write the letter of the term that corresponds to the diagram below.
A. Fore Udder Attachments, Broken
B. Rear Udder Attachments, Ideal
C. Medial Suspensory Ligaments, Broken
D. Medial Suspensory Ligaments, Ideal
E. Medial Suspensory Ligaments, Weakened
In this activity you will:
Identification—Key
• identify the various udder structure
diagrams.
References: 4-H Goat Handbook; Goat Learning Laboratory Kit
F. Bottle-shaped teats
G. Spur teat
H. Teats that point sideways
I. Pencil-shaped teats
J. Uneven teats
K. Extremely small teats
L. Ideal teats
A
BC
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
Prepared By: Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student

Lift-Off 2–37
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Sheep Feet and Leg Structure
On the blanks, write the letter of the term that corresponds to the diagram below.
In this activity you will:
Identification
• identify the various feet and leg
structure diagrams.
References: Sheep Resource 4-H Handbook; Sheep Livestock Learning Laboratory Kit; Beef, Sheep and Swine Selection and Evaluation 4-H #103R
A. Side View Rear Legs, Sickle-Hocked
B. Side View Front Legs, Correct
C. Side View Front Legs, Calf-Kneed
D. Front View, Pigeon-Toed
E. Side View Front Legs, Weak Pasterns
F. Rear View, Correct
G. Side View Front Legs, Buck-Kneed
H. Front View, Knock-Kneed
I. Front View, Splay-footed
J. Rear View, Cow-Hocked
K. Side View Rear Legs, Post-Legged
L. Front View, Bowlegged

2–38 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
A
B
D
E
FG
H
I
J
K
L
In this activity you will:
Identification—Key
• identify the various feet and leg
structure diagrams.
References: Sheep Resource 4-H Handbook; Sheep Livestock Learning Laboratory Kit; Beef, Sheep and Swine Selection and Evaluation 4-H #103R
Sheep Feet and Leg Structure
On the blanks, write the letter of the term that corresponds to the diagram below.
A. Side View Rear Legs, Sickle-Hocked
B. Side View Front Legs, Correct
C. Side View Front Legs, Calf-Kneed
D. Front View, Pigeon-Toed
E. Side View Front Legs, Weak Pasterns
F. Rear View, Correct
G. Side View Front Legs, Buck-Kneed
H. Front View, Knock-Kneed
I. Front View, Splay-footed
J. Rear View, Cow-Hocked
K. Side View Rear Legs, Post-Legged
L. Front View, Bowlegged
C

Lift-Off 2–39
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Identification
• identify the various feet and leg
structure diagrams.
Swine Feet and Leg Structure
On the blanks, write the letter of the term that corresponds to the diagram below.
A. Normal
B. Sickle-hocked
C. Post-legged
D. Weak pastern
E. Normal
F. Buck-kneed
G. Splayfooted
H. Pigeon-toed
Reference: National Pork Producers Council, “Producers to Evaluate Market Hogs”

2–40 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Identification—Key
• identify the various feet and leg
structure diagrams.
Swine Feet and Leg Structure
On the blanks, write the letter of the term that corresponds to the diagram below.
A. Normal
B. Sickle-hocked
C. Post-legged
D. Weak pastern
E. Normal
F. Buck-kneed
G. Splayfooted
H. Pigeon-toed
Reference: National Pork Producers Council, “Producers to Evaluate Market Hogs”
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H

Lift-Off 2–41
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making
• learn about Quality Assurance by
practicing how to record animal
medication information on the
treatment record.
Beef Quality Assurance
Read the situation statement and label of the medication and complete the
treatment record.
Situation Statement
“Curly,” the hereford steer (#351) you are planning to take to the fair next
month, is lame in the left front leg. Today your veterinarian has diagnosed the
steer’s problem as foot rot and has given it an initial treatment at the time of the examination. The veterinarian has left additional
prescribed medication with you to continue the treatment. The directions on the medication tell you to give the steer 1 cc per 50
pounds body weight once daily for 4 days, beginning tomorrow, and to give it by intramuscular injection. Your steer weighs 1,000
pounds. Remember, your veterinarian treated the steer today, April 3, around 4:00 p.m. and you will treat it 4 more days as
directed. The hold time on this product is 14 days.
Lesson plan by: Dr. Bill Shulaw, OSU Extension Veterinarian
Emily Edwards, DVM
100 Quality Avenue
Hometown, OH 43200
614-555-5050
Owner: Jennifer Wilson Date: April 3
Animal ID: Hereford #351 Indications: Foot rot
Directions: 1 cc per 50 pounds body weight IM once
daily for four days.
Precaution: Avoid injection into muscle of high carcass
value.
Warning: Use of this drug must be discontinued for 14 days
before slaughter or market for food.
Product/Active Ingredient(s): Hydrocillin
Expiration Date: September 30
Bottle Label
April
123
45678910
11 12 13 14 15 16 17
18 19 20 21 22 23 24
25 26 27 28 29 30
Treatment Record
Treatment Animal ID Condition Estimated Treatment Given Instructed Results Date If this is an extra label or Rx drug,
Date • Name Being Weight (Medication dispensed, Meat/Milk/Egg Withdrawal list the name, address, and phone
• Species Treated amount, and route) Withdrawal Complete number of the licensed
• ID Number veterinarian who prescribed or
• Description directed the treatment.
Teaching References: Caring for Animals Discussion Guide and video, and the 4-H Beef Resource Handbook. The Beef Learning Laboratory Kit contains a medicine
bottle, syringe, and skeletal poster which are helpful but not necessary for this exercise.

2–42 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making—Key
• learn about Quality Assurance by
practicing how to record animal
medication information on the
treatment record.
Lesson plan by: Dr. Bill Shulaw, OSU Extension Veterinarian
Teaching References: Caring for Animals Discussion Guide and video, and the 4-H Beef Resource Handbook. The Beef Learning Laboratory Kit contains a medicine
bottle, syringe, and skeletal poster which are helpful but not necessary for this exercise.
Emily Edwards, DVM
100 Quality Avenue
Hometown, OH 43200
614-555-5050
Owner: Jennifer Wilson Date: April 3
Animal ID: Hereford #351 Indications: Foot rot
Directions: 1 cc per 50 pounds body weight IM once
daily for four days.
Precaution: Avoid injection into muscle of high carcass
value.
Warning: Use of this drug must be discontinued for 14 days
before slaughter or market for food.
Product/Active Ingredient(s): Hydrocillin
Expiration Date: September 30
Bottle Label
Treatment Record
Treatment Animal ID Condition Estimated Treatment Given Instructed Results Date If this is an extra label or Rx drug,
Date • Name Being Weight (Medication dispensed, Meat/Milk/Egg Withdrawal list the name, address, and phone
• Species Treated amount, and route) Withdrawal Complete number of the licensed
• ID Number veterinarian who prescribed or
• Description directed the treatment.
April
123
45678910
11 12 13 14 15 16 17
18 19 20 21 22 23 24
25 26 27 28 29 30
Beef Quality Assurance
Read the situation statement and label of the medication and complete the
treatment record.
Situation Statement
“Curly,” the hereford steer (#351) you are planning to take to the fair next
month, is lame in the left front leg. Today your veterinarian has diagnosed the
steer’s problem as foot rot and has given it an initial treatment at the time of the examination. The veterinarian has left additional
prescribed medication with you to continue the treatment. The directions on the medication tell you to give the steer 1 cc per 50
pounds body weight once daily for 4 days, beginning tomorrow, and to give it by intramuscular injection. Your steer weighs 1,000
pounds. Remember, your veterinarian treated the steer today, April 3, around 4:00 p.m. and you will treat it 4 more days as
directed. The hold time on this product is 14 days.
4-3
4-4
4-5
4-6
4-7
Steer #351
Steer #351
Steer #351
Steer #351
Steer #351
Foot rot
Foot rot
Foot rot
Foot rot
Foot rot
Hydrocillin 20 cc IM
1,000 lb
1,000 lb
1,000 lb
1,000 lb
1,000 lb
14 days Meat
14 days Meat
14 days Meat
14 days Meat
14 days Meat
X
X
X
X
X
X = This information was not supplied in the situation,
therefore you do not need to complete this box.
4-17
4-18
4-19
4-20
4-21
Emily Edwards, DVM
100 Quality Avenue
Hometown, OH 43200
614-555-5050
Hydrocillin 20 cc IM
Hydrocillin 20 cc IM
Hydrocillin 20 cc IM
Hydrocillin 20 cc IM

Lift-Off 2–43
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Teaching References: Dairy Learning Laboratory Kit, Curriculum Guide and video. The dairy kit contains a medicine bottle, syringe, and skeletal poster which are
helpful but not necessary for this exercise.
Lesson plan by: Dr. Bill Shulaw, OSU Extension Veterinarian
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making
• learn about Quality Assurance by
practicing how to record animal
medication information on the
treatment record.
Dairy Cattle Quality Assurance
Read the situation statement and label of the medication and complete the
treatment record.
Situation Statement
Today is February 5. At the afternoon milking today, you notice the right front
quarter on cow #28, a 1,200 pound Holstein, has abnormal milk. You saw
several flakes and thick milk on the strip plate while preparing the cow for milking. You decide she has mastitis. The udder feels
normal as is the cow’s temperature and appetite. At the end of the milking, you medicate the right front quarter using an over-the-
counter (OTC) intramammary infusion product called SUPER-MAST™. The time of the treatment is 6:00 p.m. The label of the
product is seen below. You mark the cow as treated by attaching a red leg band to the rear leg. Fill out the treatment record for
today’s treatment.
Lesson plan by: Dr. Bill Shulaw, OSU Extension Veterinarian
Treatment Record
Treatment Animal ID Condition Estimated Treatment Given Instructed Results Date If this is an extra label or Rx drug,
Date • Name Being Weight (Medication dispensed, Meat/Milk/Egg Withdrawal list the name, address, and phone
• Species Treated amount, and route) Withdrawal Complete number of the licensed
• ID Number veterinarian who prescribed or
• Description directed the treatment.
SUPER-MAST™
Hydrocillin
Lactating Cow Intramammary Infusion
Each 10 ml single dose disposable syringe contains 50 mg hydrocillin in a base suitable for
the treatment of bovine mastitis during the lactating period.
Indications: For the intramammary treatment of bovine mastitis caused by susceptible
bacteria.
Administration: After milking, clean and disinfect the teat end with an alcohol swab.
Remove the protective covering from the tip and insert the tip into the teat orifice. Express
the contents of the tube into the quarter with gentle pressure. Withdraw the syringe and
massage the medication up into the affected quarter. Milk out the quarter at the next
routine milking.
Storage: Store between 45 and 75 degrees F.
WARNING: Milk that has been taken from animal during treatment and for 72 hours (3
days) after the last treatment must be discarded. Treated animal should not be slaughtered
for food purposes for 10 days following the last treatment.
Net contents: 10 ml
SKILLATHON ANIMAL HEALTH COMPANY
Veterinary use only—not for human use
Bottle Label
February
123456
7891011 12 13
14 15 16 17 18 19 20
21 22 23 24 25 26 27
28

2–44 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Teaching References: Dairy Learning Laboratory Kit, Curriculum Guide and video. The dairy kit contains a medicine bottle, syringe, and skeletal poster which are
helpful but not necessary for this exercise.
Lesson plan by: Dr. Bill Shulaw, OSU Extension Veterinarian
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making—Key
• learn about Quality Assurance by
practicing how to record animal
medication information on the
treatment record.
Dairy Cattle Quality Assurance
Read the situation statement and label of the medication and complete the
treatment record.
Situation Statement
Today is February 5. At the afternoon milking today, you notice the right front
quarter on cow #28, a 1,200 pound Holstein, has abnormal milk. You saw
several flakes and thick milk on the strip plate while preparing the cow for milking. You decide she has mastitis. The udder feels
normal as is the cow’s temperature and appetite. At the end of the milking, you medicate the right front quarter using an over-the-
counter (OTC) intramammary infusion product called SUPER-MAST™. The time of the treatment is 6:00 p.m. The label of the
product is seen below. You mark the cow as treated by attaching a red leg band to the rear leg. Fill out the treatment record for
today’s treatment.
Lesson plan by: Dr. Bill Shulaw, OSU Extension Veterinarian
Treatment Record
Treatment Animal ID Condition Estimated Treatment Given Instructed Results Date If this is an extra label or Rx drug,
Date • Name Being Weight (Medication dispensed, Meat/Milk/Egg Withdrawal list the name, address, and phone
• Species Treated amount, and route) Withdrawal Complete number of the licensed
• ID Number veterinarian who prescribed or
• Description directed the treatment.
SUPER-MAST™
Hydrocillin
Lactating Cow Intramammary Infusion
Each 10 ml single dose disposable syringe contains 50 mg hydrocillin in a base suitable for
the treatment of bovine mastitis during the lactating period.
Indications: For the intramammary treatment of bovine mastitis caused by susceptible
bacteria.
Administration: After milking, clean and disinfect the teat end with an alcohol swab.
Remove the protective covering from the tip and insert the tip into the teat orifice. Express
the contents of the tube into the quarter with gentle pressure. Withdraw the syringe and
massage the medication up into the affected quarter. Milk out the quarter at the next
routine milking.
Storage: Store between 45 and 75 degrees F.
WARNING: Milk that has been taken from animal during treatment and for 72 hours (3
days) after the last treatment must be discarded. Treated animal should not be slaughtered
for food purposes for 10 days following the last treatment.
Net contents: 10 ml
SKILLATHON ANIMAL HEALTH COMPANY
Veterinary use only—not for human use
Bottle Label
February
123456
7891011 12 13
14 15 16 17 18 19 20
21 22 23 24 25 26 27
28
2/5
6 p.m.
#28 Holstein
cow
mastitis
1,200 lb
Super-Mast 10 ml
intramammary in right
front quarter
Milk—3 days
Meat—10 days
X
Milk—2/8
6 p.m.
Meat—2/15
6 p.m.
X
X = This information was not supplied in the situation,
therefore you do not need to complete this box.
Lift-Off 2–45
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making
• learn about Quality Assurance by
practicing how to record animal
medication information on the
treatment record.
Goat Quality Assurance
Read the situation statement and label of the medication and complete the
treatment record.
Teaching References: Caring for Animals Discussion Guide and video; the 4-H Goat Handbook; and the Goat Learning Laboratory Kit, which contains a medicine bottle,
syringe, and skeletal poster which are helpful but not necessary for this exercise.
Lesson plan by: Dr. Gary Bowman, OSU Extension Veterinarian
Treatment Record
Treatment Animal ID Condition Estimated Treatment Given Instructed Results Date If this is an extra label or Rx drug,
Date • Name Being Weight (Medication dispensed, Meat/Milk/Egg Withdrawal list the name, address, and phone
• Species Treated amount, and route) Withdrawal Complete number of the licensed
• ID Number veterinarian who prescribed or
• Description directed the treatment.
Situation Statement
The market goat you have been planning to take to the fair is lame. Today
your veterinarian diagnosed the goat’s problem as foot rot and gave it an
initial treatment at the time of the examination. The veterinarian left addi-
tional medication with you to continue the treatment. The directions on the
medication tell you to give the goat 2 cc’s per 100 pounds body weight once
daily for 3 days, beginning tomorrow, and to give it by intramuscular injection.
Your goat weighs 50 pounds. Remember, your veterinarian treated the goat
today, June 8, and you will treat the goat 3 more days as directed.
Susan Q. Veterinarian, DVM
100 Quality Drive
Anywhere, OH 43210
614-555-0000
Owner: Keith Young Date: June 8
Animal ID: Goat 101-Saanen Indications: Foot rot
Directions: Give 2 cc per 100 pounds body weight
once daily intramuscularly for 3 days.
Precaution: Avoid muscle of high carcass value.
Warning: Use of this drug must be discontinued for 30
days before slaughter or market for food.
Product/Active Ingredient(s): Hydrocillin
Bottle Label
June
12345
6789101112
13 14 15 16 17 18 19
20 21 22 23 24 25 26
27 28 29 30
July
123
45678910
11 12 13 14 15 16 17
18 19 20 21 22 23 24
25 26 27 28 29 30 31
2–46 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making—Key
• learn about Quality Assurance by
practicing how to record animal
medication information on the
treatment record.
Treatment Record
Treatment Animal ID Condition Estimated Treatment Given Instructed Results Date If this is an extra label or Rx drug,
Date • Name Being Weight (Medication dispensed, Meat/Milk/Egg Withdrawal list the name, address, and phone
• Species Treated amount, and route) Withdrawal Complete number of the licensed
• ID Number veterinarian who prescribed or
• Description directed the treatment.
6-9
6-10
6-11
Goat 101-
Saanen
Goat 101-
Saanen
Goat 101-
Saanen
foot rot
foot rot
foot rot
50 lb
50 lb
50 lb
Hydrocillin 1 cc IM
Hydrocillin 1 cc IM
Hydrocillin 1 cc IM
30 days meat
30 days meat
30 days meat
X
X
X
7/9
7/10
7/11
Susan Q. Veterinarian, DVM
100 Quality Drive
Anywhere, OH 43210
614-555-0000
X = This information was not supplied in the situation,
therefore you do not need to complete this box.
Teaching References: Caring for Animals Discussion Guide and video; the 4-H Goat Handbook; and the Goat Learning Laboratory Kit, which contains a medicine bottle,
syringe, and skeletal poster which are helpful but not necessary for this exercise.
Lesson plan by: Dr. Gary Bowman, OSU Extension Veterinarian
Goat Quality Assurance
Read the situation statement and label of the medication and complete the
treatment record.
Situation Statement
The market goat you have been planning to take to the fair is lame. Today
your veterinarian diagnosed the goat’s problem as foot rot and gave it an
initial treatment at the time of the examination. The veterinarian left addi-
tional medication with you to continue the treatment. The directions on the
medication tell you to give the goat 2 cc’s per 100 pounds body weight once
daily for 3 days, beginning tomorrow, and to give it by intramuscular injection.
Your goat weighs 50 pounds. Remember, your veterinarian treated the goat
today, June 8, and you will treat the goat 3 more days as directed.
Susan Q. Veterinarian, DVM
100 Quality Drive
Anywhere, OH 43210
614-555-0000
Owner: Keith Young Date: June 8
Animal ID: Goat 101-Saanen Indications: Foot rot
Directions: Give 2 cc per 100 pounds body weight
once daily intramuscularly for 3 days.
Precaution: Avoid muscle of high carcass value.
Warning: Use of this drug must be discontinued for 30
days before slaughter or market for food.
Product/Active Ingredient(s): Hydrocillin
Bottle Label
June
12345
6789101112
13 14 15 16 17 18 19
20 21 22 23 24 25 26
27 28 29 30
July
123
45678910
11 12 13 14 15 16 17
18 19 20 21 22 23 24
25 26 27 28 29 30 31

Lift-Off 2–47
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making
• learn about Quality Assurance by
practicing how to record animal
medication information on the
treatment record.
Teaching References: Caring for Animals Discussion Guide and video, the 4-H Market Lamb Resource Handbook #250R, and the 4-H Sheep Breeding Handbook
#194R. The Sheep Learning Laboratory Kit contains a medicine bottle, syringe, and skeletal poster which are helpful but not necessary for this exercise.
Lesson plan by: Dr. Bill Shulaw, OSU Extension Veterinarian
Treatment Record
Treatment Animal ID Condition Estimated Treatment Given Instructed Results Date and Time If this is an extra label or Rx drug,
Date and • Name Being Weight (Medication dispensed, Meat/Milk/Egg Withdrawal list the name, address, and phone
Time • Species Treated amount, and route) Withdrawal Complete number of the licensed
• ID Number veterinarian who prescribed or
• Description directed the treatment.
Sheep Quality Assurance
Read the situation statement and label of the medication and complete the
treatment record.
Situation Statement
Today is May 15. Your name is Lynn Monroe. Your Suffolk market lamb “Elmo”
(ear tag #3159) you are planning to take to the county fair July 2–7 is lame on
the left front leg. When you examine it, you find the foot smells bad and the hoof wall is separating from the sole. These findings
lead you to believe the lamb has foot rot. The veterinarian who regularly cares for your animals is Angela Adams, DVM. She
examined the animal and gave you (prescribed) the bottle of medication listed below and instructed you to give the treatment
today at 3:00 p.m. Your lamb weighs about 100 pounds.
Angela Adams, DVM
100 Quality Avenue
Hometown, OH 43200
614-555-5050
Owner: Lynn Monroe Date: May 15
Animal ID: Lamb #3159 Indications: Foot rot
Directions: Give 5 ml (cc) intramuscularly on May 15,
at 3 p.m.
Precaution: Avoid the muscle tissues of high carcass
value.
Warning: Use of this drug must be discontinued for 10 days
before slaughter or market for food.
Product/Active Ingredient(s): Biomycin
Expiration Date: August 15
Bottle Label
May
1
2345678
9101112131415
16 17 18 19 20 21 22
23 24 25 26 27 28 29
30 31

2–48 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making—Key
• learn about Quality Assurance by
practicing how to record animal
medication information on the
treatment record.
Treatment Record
Treatment Animal ID Condition Estimated Treatment Given Instructed Results Date and Time If this is an extra label or Rx drug,
Date and • Name Being Weight (Medication dispensed, Meat/Milk/Egg Withdrawal list the name, address, and phone
Time • Species Treated amount, and route) Withdrawal Complete number of the licensed
• ID Number veterinarian who prescribed or
• Description directed the treatment.
Sheep Quality Assurance
Read the situation statement and label of the medication and complete the
treatment record.
Situation Statement
Today is May 15. Your name is Lynn Monroe. Your Suffolk market lamb “Elmo”
(ear tag #3159) you are planning to take to the county fair July 2–7 is lame on
the left front leg. When you examine it, you find the foot smells bad and the hoof wall is separating from the sole. These findings
lead you to believe the lamb has foot rot. The veterinarian who regularly cares for your animals is Angela Adams, DVM. She
examined the animal and gave you (prescribed) the bottle of medication listed below and instructed you to give the treatment
today at 3:00 p.m. Your lamb weighs about 100 pounds.
Angela Adams, DVM
100 Quality Avenue
Hometown, OH 43200
614-555-5050
Owner: Lynn Monroe Date: May 15
Animal ID: Lamb #3159 Indications: Foot rot
Directions: Give 5 ml (cc) intramuscularly on May 15,
at 3 p.m.
Precaution: Avoid the muscle tissues of high carcass
value.
Warning: Use of this drug must be discontinued for 10 days
before slaughter or market for food.
Product/Active Ingredient(s): Biomycin
Expiration Date: August 15
Bottle Label
5-15
3:00 p.m.
Elmo Mkt lamb
#3159 Suffolk
Foot rot
100 lb
Biomycin 5 ml IM
10 days Meat X 5-25
3:00 p.m.
Angela Adams, DVM
100 Quality Avenue
Hometown, OH 43200
614-555-5050
X = This information was not supplied in the situation,
therefore you do not need to complete this box.
May
1
2345678
9101112131415
16 17 18 19 20 21 22
23 24 25 26 27 28 29
30 31
Teaching References: Caring for Animals Discussion Guide and video, the 4-H Market Lamb Resource Handbook #250R, and the 4-H Sheep Breeding Handbook
#194R. The Sheep Learning Laboratory Kit contains a medicine bottle, syringe, and skeletal poster which are helpful but not necessary for this exercise.
Lesson plan by: Dr. Bill Shulaw, OSU Extension Veterinarian

Lift-Off 2–49
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
Teaching References: Caring for Animals Discussion Guide and video, and the 4-H Market Hog Handbook #135R. The Swine Learning Laboratory Kit contains a
medicine bottle, syringe, and skeletal poster which are helpful but not necessary for this exercise.
Lesson plan by: Dr. Gary Bowman, OSU Extension Veterinarian
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making
• learn about Quality Assurance by
practicing how to record animal
medication information on the
treatment record.
Bruce E. Losis, DVM
100 Quality Avenue
Hometown, OH 43200
614-555-5050
Owner: Jenny Jones Date: July 11
Animal ID: Hog 36-7 Indications: Pneumonia
Directions: Give 15 ml (cc) subcutaneously on July 12.
Precaution: Use care in injections to avoid infections.
Warning: Use of this drug must be discontinued for 7 days
before slaughter or market for food.
Product/Active Ingredient(s): Biomycin
Expiration Date: August 1
Bottle Label
July
123
45678910
11 12 13 14 15 16 17
18 19 20 21 22 23 24
25 26 27 28 29 30 31
Treatment Record
Treatment Animal ID Condition Estimated Treatment Given Instructed Results Date If this is an extra label or Rx drug,
Date and • Name Being Weight (Medication dispensed, Meat/Milk/Egg Withdrawal list the name, address, and phone
Time • Species Treated amount, and route) Withdrawal Complete number of the licensed
• ID Number veterinarian who prescribed or
• Description directed the treatment.
Swine Quality Assurance
Read the situation statement and label of the medication and complete the
treatment record.
Situation Statement
Today is July 11, and your name is Jenny Jones. The market hog “Spot” (a 200-
pound blue-butt barrow with ear notch 36-7) you have been raising since April
started having difficulty breathing yesterday. This morning the hog failed to eat its feed and was reluctant to move unless forced
to do so. At your request, Dr. Bruce E. Losis, the local veterinarian, examined your hog and diagnosed its problem as pneumonia.
He administered medications at the time of the examination. He has left more medicine for you to give tomorrow, July 12 at
2:00 p.m.

2–50 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making—Key
• learn about Quality Assurance by
practicing how to record animal
medication information on the
treatment record.
Bruce E. Losis, DVM
100 Quality Avenue
Hometown, OH 43200
614-555-5050
Owner: Jenny Jones Date: July 11
Animal ID: Hog 36-7 Indications: Pneumonia
Directions: Give 15 ml (cc) subcutaneously on July 12.
Precaution: Use care in injection to avoid infections.
Warning: Use of this drug must be discontinued for 7 days
before slaughter or market for food.
Product/Active Ingredient(s): Biomycin
Expiration Date: August 1
Bottle Label
Treatment Record
Treatment Animal ID Condition Estimated Treatment Given Instructed Results Date If this is an extra label or Rx drug,
Date and • Name Being Weight (Medication dispensed, Meat/Milk/Egg Withdrawal list the name, address, and phone
Time • Species Treated amount, and route) Withdrawal Complete number of the licensed
• ID Number veterinarian who prescribed or
• Description directed the treatment.
Swine Quality Assurance
Read the situation statement and label of the medication and complete the
treatment record.
Situation Statement
Today is July 11, and your name is Jenny Jones. The market hog “Spot” (a 200-
pound blue-butt barrow with ear notch 36-7) you have been raising since April
started having difficulty breathing yesterday. This morning the hog failed to eat its feed and was reluctant to move unless forced
to do so. At your request, Dr. Bruce E. Losis, the local veterinarian, examined your hog and diagnosed its problem as pneumonia.
He administered medications at the time of the examination. He has left more medicine for you to give tomorrow, July 12.
7-12
2:00 p.m.
“Spot” Market
Hog 36-7 Blue-
Butt barrow
Pneumonia 200 lb Biomycin 15 ml SQ 7 days Meat
X
7-19
2:00 p.m.
Bruce E. Losis, DVM
100 Quality Avenue
Hometown, OH 43200
614-555-5050
X = This information was not supplied in the situation,
therefore you do not need to complete this box.
July
123
45678910
11 12 13 14 15 16 17
18 19 20 21 22 23 24
25 26 27 28 29 30 31
Teaching References: Caring for Animals Discussion Guide and video, and the 4-H Market Hog Handbook #135R. The Swine Learning Laboratory Kit contains a
medicine bottle, syringe, and skeletal poster which are helpful but not necessary for this exercise.
Lesson plan by: Dr. Gary Bowman, OSU Extension Veterinarian

Lift-Off 2–51
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making
• learn about Quality Assurance by
practicing how to record animal
medication information on the
treatment record.
Treatment Record
Treatment Animal ID Condition Estimated Treatment Given Instructed Results Date and Time If this is an extra label or Rx drug,
Date and • Name Being Weight (Medication dispensed, Meat/Milk/Egg Withdrawal list the name, address, and phone
Time • Species Treated amount, and route) Withdrawal Complete number of the licensed
• ID Number veterinarian who prescribed or
• Description directed the treatment.
Superbiotic
(10% Hydrocycline Tartrate)
A broad spectrum antibiotic for oral administration in the
treatment and prevention of respiratory diseases of poultry
caused by susceptible bacteria.
Directions: Mix the contents of this packet in 10 gallons of
drinking water. This medicated drinking water should be the
sole source of drinking water during the period of medication
which must not exceed 14 days.
WARNING: Discontinue use in poultry 5 days before
slaughter.
Store below 77 degrees F. Keep packet dry.
Net Contents: 25 grams
Distributed by USA Animal Health, Inc.
Packet Label
May
1
2345678
9101112131415
16 17 18 19 20 21 22
23 24 25 26 27 28 29
30 31
Poultry Quality Assurance
Read the situation statement and label of the medication and complete the
treatment record.
Situation Statement
Today is May 12. You notice several of the flock of 20 White Leghorn pullets you
purchased 3 weeks ago have a discharge today from their nostrils, watery eyes,
and are coughing. These are the only chickens you have. The flock did not eat nearly as much feed the past day as usual. Because
you could tell your chickens are sick, you take two to the local veterinarian for diagnosis and treatment of the illness. The veteri-
narian diagnoses the condition as a respiratory infection called air sacculitis and tells you that, while he does not carry the needed
medication, Superbiotic™, it is available as an over-the-counter (OTC) drug at the nearby farm supply center. He tells you to
medicate the chickens’ drinking water starting today, continue for a total of 4 days, and replace the medicated water with clear
water on the morning of May 16. Complete the treatment record for May 15.
References: Caring for Animals Discussion Guide and video. The Poultry Learning Laboratory Kit contains items which are helpful but not necessary for this exercise.
Prepared by Drs. Gary Bowman and Teresa Morishita, Ohio State University Extension Veterinarians

2–52 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making—Key
• learn about Quality Assurance by
practicing how to record animal
medication information on the
treatment record.
Treatment Record
Treatment Animal ID Condition Estimated Treatment Given Instructed Results Date and Time If this is an extra label or Rx drug,
Date and • Name Being Weight (Medication dispensed, Meat/Milk/Egg Withdrawal list the name, address, and phone
Time • Species Treated amount, and route) Withdrawal Complete number of the licensed
• ID Number veterinarian who prescribed or
• Description directed the treatment.
Superbiotic
(10% Hydrocycline Tartrate)
A broad spectrum antibiotic for oral administration in the
treatment and prevention of respiratory diseases of poultry
caused by susceptible bacteria.
Directions: Mix the contents of this packet in 10 gallons of
drinking water. This medicated drinking water should be the
sole source of drinking water during the period of medication
which must not exceed 14 days.
WARNING: Discontinue use in poultry 5 days before
slaughter.
Store below 77 degrees F. Keep packet dry.
Net Contents: 25 grams
Distributed by USA Animal Health, Inc.
Packet Label
May
1
2345678
9101112131415
16 17 18 19 20 21 22
23 24 25 26 27 28 29
30 31
Poultry Quality Assurance
Read the situation statement and label of the medication and complete the
treatment record.
Situation Statement
Today is May 12. You notice several of the flock of 20 White Leghorn pullets you
purchased 3 weeks ago have a discharge today from their nostrils, watery eyes,
and are coughing. These are the only chickens you have. The flock did not eat nearly as much feed the past day as usual. Because
you could tell your chickens are sick, you take two to the local veterinarian for diagnosis and treatment of the illness. The veteri-
narian diagnoses the condition as a respiratory infection called air sacculitis and tells you that, while he does not carry the needed
medication, Superbiotic™, it is available as an over-the-counter (OTC) drug at the nearby farm supply center. He tells you to
medicate the chickens’ drinking water starting today, continue for a total of 4 days, and replace the medicated water with clear
water on the morning of May 16. Complete the treatment record for May 15.
X = This information was not supplied in the situation,
therefore you do not need to complete this box.
5-15
20 White
Leghorn
Pullets
Air
Sacculitis
X
Superbiotic
1 packet/10 gallons of
drinking water
5 days X 5-20
No extra label or Rx
drug was given.
References: Caring for Animals Discussion Guide and video. The Poultry Learning Laboratory Kit contains items which are helpful but not necessary for this exercise.
Prepared by Drs. Gary Bowman and Teresa Morishita, Ohio State University Extension Veterinarians

Lift-Off 2–53
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
MGA HEIFER SUPPLEMENT
MEDICATED
SUPPLEMENT FOR GROWING/FINISHING BEEF HEIFERS
FOR INCREASED RATE OF WEIGHT GAIN, IMPROVED FEED EFFICIENCY AND
SUPPRESSION OF ESTRUS (HEAT) IN HEIFERS FED FOR SLAUGHTER.
ACTIVE DRUG INGREDIENT
MELENGESTROL ACETATE ................................................... 0.00022%
(EQUIVALENT TO 1.0 MG/LB.)
GUARANTEED ANALYSIS
CRUDE PROTEIN ............................................................ MIN 10.00%
CRUDE FAT ..................................................................... MIN 2.00%
CRUDE FIBER ................................................................MAX 25.00%
CALCIUM........................................................................ MIN 5.50%
CALCIUM........................................................................ MAX 6.50%
SALT .............................................................................. MIN 4.50%
SALT ..............................................................................MAX 5.50%
POTASSIUM .................................................................... MIN 0.60%
SELENIUM................................................................ MIN 13.00 PPM
VITAMIN A ...................................................... MIN 100,000.0 IU/LB
INGREDIENTS
PROCESSED GRAIN BY-PRODUCTS, ROUGHAGE PRODUCTS, GROUND
LIMESTONE, SLAT, POTASSIUM SULFATE, MAGNESIUM SULFATE, SODIUM
SELENITE, VITAMIN A ACETATE, VITAMIN D-3 SUPPLEMENT, VITAMIN E
SUPPLEMENT, ZINC SULFATE, ZINC OXIDE, COPPER SULFATE, MANGANOUS
OXIDE, CALCIUM IODATE, COBALT CARBONATE FERROUS SULFATE.
FEEDING DIRECTIONS
Each pound of supplement will provide 1.0 mg. of melengestrol acetate.
Thoroughly mix and feed at the rate of 0.5 pound per head per day to
provide 0.5 mg. of melengestrol acetate per head per day. Feed
continuously throughout period heifers are being grown and finished for
slaughter. This supplement should be fed in controlled amounts with
roughage and other feed ingredients.
NOTE
NOT EFFECTIVE FOR SPAYED HEIFERS AND STEERS.
MANUFACTURED BY:
SKILLATHON FEED
NET WEIGHT 50 POUNDS (22.7 KILOGRAMS)
OR AS SHOWN ON SHIPPING DOCUMENT
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making
• learn how to read a feed tag.
Beef: How to Read a Feed Tag
Use the feed tag below to answer the following questions.
1. What is the main ingredient in this feed?
2. What is the active drug ingredient in this ration?
3. For how many days prior to slaughter should this feed be
removed?
4. What is the crude fat level of this diet?
5. What is the crude protein level for this diet?
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences
Adapted from materials created by Dan Frobose, Agr. & Nat. Res. Agent, Wood County

2–54 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
MGA HEIFER SUPPLEMENT
MEDICATED
SUPPLEMENT FOR GROWING/FINISHING BEEF HEIFERS
FOR INCREASED RATE OF WEIGHT GAIN, IMPROVED FEED EFFICIENCY AND
SUPPRESSION OF ESTRUS (HEAT) IN HEIFERS FED FOR SLAUGHTER.
ACTIVE DRUG INGREDIENT
MELENGESTROL ACETATE ................................................... 0.00022%
(EQUIVALENT TO 1.0 MG/LB.)
GUARANTEED ANALYSIS
CRUDE PROTEIN ............................................................ MIN 10.00%
CRUDE FAT ..................................................................... MIN 2.00%
CRUDE FIBER ................................................................MAX 25.00%
CALCIUM........................................................................ MIN 5.50%
CALCIUM........................................................................ MAX 6.50%
SALT .............................................................................. MIN 4.50%
SALT ..............................................................................MAX 5.50%
POTASSIUM .................................................................... MIN 0.60%
SELENIUM................................................................ MIN 13.00 PPM
VITAMIN A ...................................................... MIN 100,000.0 IU/LB
INGREDIENTS
PROCESSED GRAIN BY-PRODUCTS, ROUGHAGE PRODUCTS, GROUND
LIMESTONE, SLAT, POTASSIUM SULFATE, MAGNESIUM SULFATE, SODIUM
SELENITE, VITAMIN A ACETATE, VITAMIN D-3 SUPPLEMENT, VITAMIN E
SUPPLEMENT, ZINC SULFATE, ZINC OXIDE, COPPER SULFATE, MANGANOUS
OXIDE, CALCIUM IODATE, COBALT CARBONATE FERROUS SULFATE.
FEEDING DIRECTIONS
Each pound of supplement will provide 1.0 mg. of melengestrol acetate.
Thoroughly mix and feed at the rate of 0.5 pound per head per day to
provide 0.5 mg. of melengestrol acetate per head per day. Feed
continuously throughout period heifers are being grown and finished for
slaughter. This supplement should be fed in controlled amounts with
roughage and other feed ingredients.
NOTE
NOT EFFECTIVE FOR SPAYED HEIFERS AND STEERS.
MANUFACTURED BY:
SKILLATHON FEED
NET WEIGHT 50 POUNDS (22.7 KILOGRAMS)
OR AS SHOWN ON SHIPPING DOCUMENT
Beef: How to Read a Feed Tag
Use the feed tag below to answer the following questions.
1. What is the main ingredient in this feed?
2. What is the active drug ingredient in this ration?
3. For how many days prior to slaughter should this feed be
removed?
4. What is the crude fat level of this diet?
5. What is the crude protein level for this diet?
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making—Key
• learn how to read a feed tag.
melengestrol acetate
processed grain by-products
None required
2%
10%
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences
Adapted from materials created by Dan Frobose, Agr. & Nat. Res. Agent, Wood County

Lift-Off 2–55
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
DAIRY CONCENTRATE
CONCENTRATE FOR LACTATING DAIRY CATTLE
GUARANTEED ANALYSIS
CRUDE PROTEIN ............................................................... MIN 18.00%
CRUDE FAT ........................................................................ MIN 2.50%
CRUDE FIBER ....................................................................... MAX 7.00
ACID DETERGENT FIBER ...................................................... MAX 9.00%
CALCIUM........................................................................... MIN 0.50%
CALCIUM.......................................................................... MAX 1.00%
PHOSPHORUS ................................................................... MIN 0.60%
SELENIUM.................................................................... MIN 0.70 PPM
VITAMIN A ........................................................... MIN 7,000.00 IU/LB
INGREDIENT USAGE
PROCESSED GRAIN BY-PRODUCTS, GRAIN PRODUCTS, PLANT PROTEIN
PRODUCTS, ROUGHAGE PRODUCTS, GROUND LIMESTONE, SALT, LIGNIN
SULFONATE, SODIUM SELENITE, POTASSIUM SULFATE, MAGNESIUM
SULFATE, CALCIUM PHOSPHATE, MAGNESIUM OXIDE, VITAMIN A ACETATE,
VITAMIN D-3 SUPPLEMENT, VITAMIN E SUPPLEMENT, ZINC SULFATE, ZINC
OXIDE, COPPER SULFATE, MANGANOUS OXIDE, CALCIUM IODATE, COBALT
CARBONATE, FERROUS SULFATE.
FEEDING DIRECTIONS
FEED DAIRY CONCENTRATE AS THE CONCENTRATE PORTION OF THE DAIRY
RATION. THIS CONCENTRATE IS INTENDED FOR USE WHEN THE ROUGHAGE
PORTION OF THE DIET CONSISTS OF 60% OR MORE CORN SILAGE (ON A
DRY MATTER BASIS). THIS FEED CONTAINS IN ADDITION TO OTHER
NUTRIENTS, 0.7 PPM SELENIUM. INTAKE OF SELENIUM SHOULD NOT
EXCEED 0.3 PPM ON A COMPLETE FEED BASIS, THEREFORE, THIS
CONCENTRATE SHOULD NOT EXCEED 42.8% OF THE TOTAL RATION. PROVIDE
CLEAN, FRESH WATER FREE CHOICE AT ALL TIMES. SALT MAY BE FED FOR
FREE CHOICE CONSUMPTION.
DAIRY CONCENTRATE FEEDS ARE FORMULATED TO REGULATE THE AMOUNT
OF BOTH SOLUBLE AND INSOLUBLE PROTEIN AND TO REGULATE THE
AMOUNT OF NON-STRUCTURAL CARBOHYDRATES.
DAIRY CONCENTRATE FEEDS ARE FORMULATED TO REGULATE THE AMOUNT
OF RUMINALLY AVAILABLE PROTEIN.
PATENT NO. X,XXX,XXX
PATENT NOS. X,XXX,XXX & X,XXX,XXX
MANUFACTURED BY:
SKILLATHON FEEDS
NET WEIGHT 50 POUNDS (22.7 KILOGRAMS)
OR AS SHOWN ON SHIPPING DOCUMENT
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making
• learn how to read a feed tag.
Dairy: How to Read a Feed Tag
Use the feed tag below to answer the following questions.
1. What is the main ingredient in this feed?
2. What is the minimum crude protein level?
3. Is this a medicated feed?
4. Is there a withdrawal time for this ration?
5. What is the minimum crude fat level of this diet?
6. Is ground limestone included in the ingredients of this diet?
7. What is the range for calcium content?
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Maurice Eastridge, State Extension Specialist, Animal Sciences
Adapted from materials created by Dan Frobose, Agr. & Nat. Res. Agent, Wood County

2–56 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
1. What is the main ingredient in this feed?
2. What is the minimum crude protein level?
3. Is this a medicated feed?
4. Is there a withdrawal time for this ration?
5. What is the minimum crude fat level of this diet?
6. Is ground limestone included in the ingredients of this diet?
7. What is the range for calcium content?
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making—Key
• learn how to read a feed tag.
DAIRY CONCENTRATE
CONCENTRATE FOR LACTATING DAIRY CATTLE
GUARANTEED ANALYSIS
CRUDE PROTEIN ............................................................... MIN 18.00%
CRUDE FAT ........................................................................ MIN 2.50%
CRUDE FIBER ....................................................................... MAX 7.00
ACID DETERGENT FIBER ...................................................... MAX 9.00%
CALCIUM........................................................................... MIN 0.50%
CALCIUM.......................................................................... MAX 1.00%
PHOSPHORUS ................................................................... MIN 0.60%
SELENIUM.................................................................... MIN 0.70 PPM
VITAMIN A ........................................................... MIN 7,000.00 IU/LB
INGREDIENT USAGE
PROCESSED GRAIN BY-PRODUCTS, GRAIN PRODUCTS, PLANT PROTEIN
PRODUCTS, ROUGHAGE PRODUCTS, GROUND LIMESTONE, SALT, LIGNIN
SULFONATE, SODIUM SELENITE, POTASSIUM SULFATE, MAGNESIUM
SULFATE, CALCIUM PHOSPHATE, MAGNESIUM OXIDE, VITAMIN A ACETATE,
VITAMIN D-3 SUPPLEMENT, VITAMIN E SUPPLEMENT, ZINC SULFATE, ZINC
OXIDE, COPPER SULFATE, MANGANOUS OXIDE, CALCIUM IODATE, COBALT
CARBONATE, FERROUS SULFATE.
FEEDING DIRECTIONS
FEED DAIRY CONCENTRATE AS THE CONCENTRATE PORTION OF THE DAIRY
RATION. THIS CONCENTRATE IS INTENDED FOR USE WHEN THE ROUGHAGE
PORTION OF THE DIET CONSISTS OF 60% OR MORE CORN SILAGE (ON A
DRY MATTER BASIS). THIS FEED CONTAINS IN ADDITION TO OTHER
NUTRIENTS, 0.7 PPM SELENIUM. INTAKE OF SELENIUM SHOULD NOT
EXCEED 0.3 PPM ON A COMPLETE FEED BASIS, THEREFORE, THIS
CONCENTRATE SHOULD NOT EXCEED 42.8% OF THE TOTAL RATION. PROVIDE
CLEAN, FRESH WATER FREE CHOICE AT ALL TIMES. SALT MAY BE FED FOR
FREE CHOICE CONSUMPTION.
DAIRY CONCENTRATE FEEDS ARE FORMULATED TO REGULATE THE AMOUNT
OF BOTH SOLUBLE AND INSOLUBLE PROTEIN AND TO REGULATE THE
AMOUNT OF NON-STRUCTURAL CARBOHYDRATES.
DAIRY CONCENTRATE FEEDS ARE FORMULATED TO REGULATE THE AMOUNT
OF RUMINALLY AVAILABLE PROTEIN.
PATENT NO. X,XXX,XXX
PATENT NOS. X,XXX,XXX & X,XXX,XXX
MANUFACTURED BY:
SKILLATHON FEEDS
NET WEIGHT 50 POUNDS (22.7 KILOGRAMS)
OR AS SHOWN ON SHIPPING DOCUMENT
Dairy: How to Read a Feed Tag
Use the feed tag below to answer the following questions.
processed grain by-products
18%
no
none required or “no”
2.5%
yes
0.5%–1.0%
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Maurice Eastridge, State Extension Specialist, Animal Sciences
Adapted from materials created by Dan Frobose, Agr. & Nat. Res. Agent, Wood County

Lift-Off 2–57
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
NET WEIGHT 50 POUNDS
SKILLATHON
GOAT RATION
Feed for Goats Older Than Four Months of Age
CAUTION: Use Only As Directed
GUARANTEED ANALYSIS
Crude Protein not less than .................................................................................. 17.0000%
Crude Fat not less than ......................................................................................... 2.5000%
Crude Fiber not more than .....................................................................................9.0000%
Calcium (Ca) not less than .................................................................................... 0.8000%
Calcium (Ca) not more than .................................................................................. 1.3000%
Phosphorus (P) not less than ................................................................................. 0.6000%
Salt (NaCl) not less than .......................................................................................0.7500%
Salt (NaCl) not more than .....................................................................................1.2500%
Copper (Cu) not less than............................................................................... 18.0000 PPM
Copper (Cu) not more than............................................................................. 23.0000 PPM
Selenium (Se) not less than ............................................................................. 0.6000 PPM
Vitamin A not less than ............................................................................ 4000.0000 IU/LB
INGREDIENTS
Grain products, processed grain by-products, molasses products, calcium carbonate, salt, dicalcium
phosphate, soybean oil, sodium selenite, propionic acid (a preservative), tetrasodium pyrophos-
phate, vitamin E supplement, vitamin A supplement, vitamin D
3
supplement, ferrous carbonate,
manganous oxide, zinc oxide, cobalt carbonate, calcium idodate, sodium molybdate.
DIRECTIONS
This goat ration can be fed to dry does, growing does, bucks, and as a milking ration. Feed one
pound for every three pounds of milk produced. Use free-choice for young kids. Feed with good
quality roughage to all goats after four months of age.
IMPORTANT
1. When making a ration change, allow 3-5 days for animals to adjust to the new ration.
2. Do not let fine material accumulate in feeders.
3. Provide adequate bunk space for each animal. Bunks should be well protected and well managed
to prevent feed from becoming wet and molding.
4. Provide a source of fresh, clean water at all times.
5. Feed salt free-choice.
6. Consult your veterinarian for a recommended health program for your local area. This includes
internal and external parasite control.
7. This product contains copper and should not be fed to sheep.
CAUTION
Store in a dry area away from insects. Do not feed moldy or insect-infested feed to animals as it
may cause illness, abortion or death.
MANUFACTURED BY:
SKILLATHON FEED
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making
• learn how to read a feed tag.
Goat: How to Read a Feed Tag
Use the feed tag below to answer the following questions.
1. What is the main ingredient in this feed?
2. Is this a medicated feed?
3. What is the minimum crude protein level?
4. What is the minimum crude fat level of this diet?
5. Is calcium carbonate included in the ingredients of
this diet?
6. Can this feed be given to lactating does?
Prepared by Drs. Gary Bowman and Bill Shulaw, Extension Specialists, Veterinary Medicine, and Jodi Black, State 4-H Animal Sciences Extension Associate

2–58 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making—Key
• learn how to read a feed tag.
NET WEIGHT 50 POUNDS
SKILLATHON
GOAT RATION
Feed for Goats Older Than Four Months of Age
CAUTION: Use Only As Directed
GUARANTEED ANALYSIS
Crude Protein not less than .................................................................................. 17.0000%
Crude Fat not less than ......................................................................................... 2.5000%
Crude Fiber not more than .....................................................................................9.0000%
Calcium (Ca) not less than .................................................................................... 0.8000%
Calcium (Ca) not more than .................................................................................. 1.3000%
Phosphorus (P) not less than ................................................................................. 0.6000%
Salt (NaCl) not less than .......................................................................................0.7500%
Salt (NaCl) not more than .....................................................................................1.2500%
Copper (Cu) not less than............................................................................... 18.0000 PPM
Copper (Cu) not more than............................................................................. 23.0000 PPM
Selenium (Se) not less than ............................................................................. 0.6000 PPM
Vitamin A not less than ............................................................................ 4000.0000 IU/LB
INGREDIENTS
Grain products, processed grain by-products, molasses products, calcium carbonate, salt, dicalcium
phosphate, soybean oil, sodium selenite, propionic acid (a preservative), tetrasodium pyrophos-
phate, vitamin E supplement, vitamin A supplement, vitamin D
3
supplement, ferrous carbonate,
manganous oxide, zinc oxide, cobalt carbonate, calcium idodate, sodium molybdate.
DIRECTIONS
This goat ration can be fed to dry does, growing does, bucks, and as a milking ration. Feed one
pound for every three pounds of milk produced. Use free-choice for young kids. Feed with good
quality roughage to all goats after four months of age.
IMPORTANT
1. When making a ration change, allow 3-5 days for animals to adjust to the new ration.
2. Do not let fine material accumulate in feeders.
3. Provide adequate bunk space for each animal. Bunks should be well protected and well managed
to prevent feed from becoming wet and molding.
4. Provide a source of fresh, clean water at all times.
5. Feed salt free-choice.
6. Consult your veterinarian for a recommended health program for your local area. This includes
internal and external parasite control.
7. This product contains copper and should not be fed to sheep.
CAUTION
Store in a dry area away from insects. Do not feed moldy or insect-infested feed to animals as it
may cause illness, abortion or death.
MANUFACTURED BY:
SKILLATHON FEED
Goat: How to Read a Feed Tag
Use the feed tag below to answer the following questions.
1. What is the main ingredient in this feed?
2. Is this a medicated feed?
3. What is the minimum crude protein level?
4. What is the minimum crude fat level of this diet?
5. Is calcium carbonate included in the ingredients of
this diet?
6. Can this feed be given to lactating does?
grain products
no
17%
2.5%
yes
yes
Prepared by Drs. Gary Bowman and Bill Shulaw, Extension Specialists, Veterinary Medicine, and Jodi Black, State 4-H Animal Sciences Extension Associate

Lift-Off 2–59
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
LAMB STARTER
MEDICATED
STARTER FOR GROWING LAMBS
FOR THE PREVENTION OF COCCIDIOSIS CAUSED BY
Eimeria ovina, Eimenria
crandallis, Eimeria ovinoidalis, Eimeria ninakohlyakimovae, Eimeria parva
AND
Eimeria intricata
IN SHEEP MAINTAINED IN CONFINEMENT.
ACTIVE DRUG INGREDIENT
LASALOCID (AS LASALOCID SODIUM) .................................... 90 G/TON
GUARANTEED ANALYSIS
CRUDE PROTEIN .............................................................. MIN 20.00%
CRUDE FAT ....................................................................... MIN 2.50%
CRUDE FIBER ................................................................. MAX 10.00%
CALCIUM.......................................................................... MIN 0.75%
CALCIUM......................................................................... MAX 1.25%
PHOSPHORUS .................................................................. MIN 0.55%
SALT ................................................................................ MIN 0.40%
SALT ............................................................................... MAX 0.90%
SELENIUM................................................................... MIN 0.30 PPM
VITAMIN A .......................................................... MIN 2,000.00 IU/LB
INGREDIENT USAGE
Processed Grain By-Products, Grain Products, Plant Protein Products, Forage
Products, Roughage Products, Molasses Products, Ground Limestone, Salt,
Lignin Sulfonate, Potassium Sulfate, Magnesium Sulfate, Magnesium Oxide,
Sodium Seleniite, Calcium Propionate, Vitamin E Supplement, Vitamin A
Acetate, Vitamin D-3Supplement, Zinc Sulfate, Zinc Oxide, Sodium
Molybdate, Manganous Oxide, Calcium Iodate, Cobalt Carbonate, Ferrous
Sulfate.
FEEDING DIRECTIONS
LAMB STARTER MEDICATED contains 45 mgs. of lasalocid per pound. Feed
continuously as the sole ration to growing lambs from 1 to 6 weeks of age
at the rate of 0.33-1.55 pounds per head per day to provide not less than
15 mgs. and not more than 70 mgs. of lasalocid per head per day. Provide
clean, fresh water at all times.
CAUTION
The safety of lasalocid in unapproved species has not been established; do
not allow horses or other equines access to lasalocid as ingestion may be
fatal; feeding undiluted or mixing errors resulting in excessive concentrations
of lasalocid could be fatal to sheep.
MANUFACTURED BY:
SKILLATHON FEEDS
NET WEIGHT 50 POUNDS (22.7 KILOGRAMS)
OR AS SHOWN ON SHIPPING DOCUMENT
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making
• learn how to read a feed tag.
Lamb: How to Read a Feed Tag
Use the feed tag below to answer the following questions.
1. What is the main ingredient in this feed?
2. What is the active drug ingredient?
3. What is the minimum crude protein level?
4. What is the minimum crude fat level of this diet?
5. Is this a medicated feed?
6. At what growth state of development should this ration to be
fed?
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Roger High, State Sheep Extension Associate
Adapted from materials created by Dan Frobose, Agr. & Nat. Res. Agent, Wood County

2–60 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making—Key
• learn how to read a feed tag.
Lamb: How to Read a Feed Tag
Use the feed tag below to answer the following questions.
1. What is the main ingredient in this feed?
2. What is the active drug ingredient?
3. What is the minimum crude protein level?
4. What is the minimum crude fat level of this diet?
5. Is this a medicated feed?
6. At what growth state of development should this ration to be
fed?
processed grain by-products
lasalocid
20%
2.5%
yes
1-6 weeks of age
LAMB STARTER
MEDICATED
STARTER FOR GROWING LAMBS
FOR THE PREVENTION OF COCCIDIOSIS CAUSED BY
Eimeria ovina, Eimenria
crandallis, Eimeria ovinoidalis, Eimeria ninakohlyakimovae, Eimeria parva
AND
Eimeria intricata
IN SHEEP MAINTAINED IN CONFINEMENT.
ACTIVE DRUG INGREDIENT
LASALOCID (AS LASALOCID SODIUM) .................................... 90 G/TON
GUARANTEED ANALYSIS
CRUDE PROTEIN .............................................................. MIN 20.00%
CRUDE FAT ....................................................................... MIN 2.50%
CRUDE FIBER ................................................................. MAX 10.00%
CALCIUM.......................................................................... MIN 0.75%
CALCIUM......................................................................... MAX 1.25%
PHOSPHORUS .................................................................. MIN 0.55%
SALT ................................................................................ MIN 0.40%
SALT ............................................................................... MAX 0.90%
SELENIUM................................................................... MIN 0.30 PPM
VITAMIN A .......................................................... MIN 2,000.00 IU/LB
INGREDIENT USAGE
Processed Grain By-Products, Grain Products, Plant Protein Products, Forage
Products, Roughage Products, Molasses Products, Ground Limestone, Salt,
Lignin Sulfonate, Potassium Sulfate, Magnesium Sulfate, Magnesium Oxide,
Sodium Seleniite, Calcium Propionate, Vitamin E Supplement, Vitamin A
Acetate, Vitamin D-3Supplement, Zinc Sulfate, Zinc Oxide, Sodium
Molybdate, Manganous Oxide, Calcium Iodate, Cobalt Carbonate, Ferrous
Sulfate.
FEEDING DIRECTIONS
LAMB STARTER MEDICATED contains 45 mgs. of lasalocid per pound. Feed
continuously as the sole ration to growing lambs from 1 to 6 weeks of age
at the rate of 0.33-1.55 pounds per head per day to provide not less than
15 mgs. and not more than 70 mgs. of lasalocid per head per day. Provide
clean, fresh water at all times.
CAUTION
The safety of lasalocid in unapproved species has not been established; do
not allow horses or other equines access to lasalocid as ingestion may be
fatal; feeding undiluted or mixing errors resulting in excessive concentrations
of lasalocid could be fatal to sheep.
MANUFACTURED BY:
SKILLATHON FEEDS
NET WEIGHT 50 POUNDS (22.7 KILOGRAMS)
OR AS SHOWN ON SHIPPING DOCUMENT
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Roger High, State Sheep Extension Associate
Adapted from materials created by Dan Frobose, Agr. & Nat. Res. Agent, Wood County

Lift-Off 2–61
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
PIG GROWER
MEDICATED
FOR PIGS FROM 30 POUNDS TO 75 POUNDS
ADMINISTER TO SWINE IN A COMPLETE FEED FOR REDUCTION OF THE INCIDENCE OF
CERVICAL ABSCESSES; TREATMENT OF BACTERIAL SWINE ENTERITIS (SALMONELLOSIS OR
NECROTIC ENTERITIS CAUSED BY Salmonella choteraesuis AND VIBRIONIC DYSENTERY),
MAINTENANCE OF WEIGHT GAINS IN THE PRESENCE OF ATROPHIC RHINITIS.
ACTIVE DRUG INGREDIENT
CHLORTETRACYCLINE ................................................................................ 100 G/TON
SULFATHIAZOLE......................................................................... 0.011% (100 G/TON)
PENICILLIN ................................................................................................ 50 G/TON
GUARANTEED ANALYSIS
CRUDE PROTEIN ...................................................................................... MIN 18.00%
LYSINE .................................................................................................... MIN 1.10%
CRUDE FAT ............................................................................................... MIN 6.50%
CRUDE FIBER ........................................................................................... MAX 4.00%
CALCIUM.................................................................................................. MIN 0.60%
CALCIUM................................................................................................. MAX 1.10%
PHOSPHORUS .......................................................................................... MIN 0.55%
SALT ........................................................................................................ MIN 0.40%
SALT ....................................................................................................... MAX 0.90%
SELENIUM........................................................................................... MIN 0.30 PPM
ZINC............................................................................................... MIN 140.00 PPM
INGREDIENTS
Grain Products, Plant Protein Products, Processed Grain By-Products, Animal Fat, Animal
Protein Products, Calcium Phosphate, Lignin Sulfonate, Ground Limestone, Salt, L-Lysine
Monohydrochloride, Methionine Supplement, Zinc Oxide, Zinc Sulfate, Ferrous Sulfate,
Manganous Oxide, Copper Sulfate, Calcium Iodate, Sodium Selenite, Vitamin A Acetate,
Vitamin D-3 Supplement, Vitamin E Supplement, Menadione Dimethylpyrimidinol Bisulphite,
Riboflavin Supplement, Niacin, Calcium Pantothenate, Vitamin B-12 Supplement, Thiamine
Monohitrate, Folic Acid, Choline Chloride, Pyridoxine Hydrochloride, Biotin, Ethoxyquin (As A
Preservative)
FEEDING DIRECTIONS
Feed as the only ration to pigs weighing from 30 pounds to 75 pounds bodyweight.
CAUTION: In order to obtain the desired performance results, the animals should be self fed.
WARNING: Withdraw 7 days prior to slaughter; contains high levels of copper; do not feed to
sheep.
MANUFACTURED BY:
SKILLATHON FEED
NET WEIGHT 50 POUNDS (22.7 KILOGRAMS)
OR AS SHOWN ON SHIPPING DOCUMENT
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making
• learn how to read a feed tag.
Pig: How to Read a Feed Tag
Use the feed tag below to answer the following questions.
1. What is the main ingredient in this feed?
2. How many active drug ingredients are in this feed?
3. What is the minimum crude protein level?
4. For how many days prior to slaughter should this feed
be removed?
5. What is the minimum crude fat level of this diet?
6. Is ground limestone included in the ingredients of this
diet?
7. At what weight range should this ration be fed?
8. What is the range for the calcium content of this feed?
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Steven Moeller, State Swine Extension Specialist
Adapted from materials created by Dan Frobose, Agr. & Nat. Res. Agent, Wood County

2–62 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making—Key
• learn how to read a feed tag.
PIG GROWER
MEDICATED
FOR PIGS FROM 30 POUNDS TO 75 POUNDS
ADMINISTER TO SWINE IN A COMPLETE FEED FOR REDUCTION OF THE INCIDENCE OF
CERVICAL ABSCESSES; TREATMENT OF BACTERIAL SWINE ENTERITIS (SALMONELLOSIS OR
NECROTIC ENTERITIS CAUSED BY Salmonella choteraesuis AND VIBRIONIC DYSENTERY),
MAINTENANCE OF WEIGHT GAINS IN THE PRESENCE OF ATROPHIC RHINITIS.
ACTIVE DRUG INGREDIENT
CHLORTETRACYCLINE ................................................................................ 100 G/TON
SULFATHIAZOLE......................................................................... 0.011% (100 G/TON)
PENICILLIN ................................................................................................ 50 G/TON
GUARANTEED ANALYSIS
CRUDE PROTEIN ...................................................................................... MIN 18.00%
LYSINE .................................................................................................... MIN 1.10%
CRUDE FAT ............................................................................................... MIN 6.50%
CRUDE FIBER ........................................................................................... MAX 4.00%
CALCIUM.................................................................................................. MIN 0.60%
CALCIUM................................................................................................. MAX 1.10%
PHOSPHORUS .......................................................................................... MIN 0.55%
SALT ........................................................................................................ MIN 0.40%
SALT ....................................................................................................... MAX 0.90%
SELENIUM........................................................................................... MIN 0.30 PPM
ZINC............................................................................................... MIN 140.00 PPM
INGREDIENTS
Grain Products, Plant Protein Products, Processed Grain By-Products, Animal Fat, Animal
Protein Products, Calcium Phosphate, Lignin Sulfonate, Ground Limestone, Salt, L-Lysine
Monohydrochloride, Methionine Supplement, Zinc Oxide, Zinc Sulfate, Ferrous Sulfate,
Manganous Oxide, Copper Sulfate, Calcium Iodate, Sodium Selenite, Vitamin A Acetate,
Vitamin D-3 Supplement, Vitamin E Supplement, Menadione Dimethylpyrimidinol Bisulphite,
Riboflavin Supplement, Niacin, Calcium Pantothenate, Vitamin B-12 Supplement, Thiamine
Monohitrate, Folic Acid, Choline Chloride, Pyridoxine Hydrochloride, Biotin, Ethoxyquin (As A
Preservative)
FEEDING DIRECTIONS
Feed as the only ration to pigs weighing from 30 pounds to 75 pounds bodyweight.
CAUTION: In order to obtain the desired performance results, the animals should be self fed.
WARNING: Withdraw 7 days prior to slaughter; contains high levels of copper; do not feed to
sheep.
MANUFACTURED BY:
SKILLATHON FEED
NET WEIGHT 50 POUNDS (22.7 KILOGRAMS)
OR AS SHOWN ON SHIPPING DOCUMENT
Pig: How to Read a Feed Tag
Use the feed tag below to answer the following questions.
grain products
3
18%
7
6.5%
yes
pigs weighing between 30 and 75 pounds
1. What is the main ingredient in this feed?
2. How many active drug ingredients are in this feed?
3. What is the minimum crude protein level?
4. For how many days prior to slaughter should this feed
be removed?
5. What is the minimum crude fat level of this diet?
6. Is ground limestone included in the ingredients of this
diet?
7. At what weight range should this ration be fed?
8. What is the range for the calcium content of this feed?
0.60%–1.10%
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Steven Moeller, State Swine Extension Specialist
Adapted from materials created by Dan Frobose, Agr. & Nat. Res. Agent, Wood County

Lift-Off 2–63
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
BROILER
STARTER
MEDICATED
COMPLETE FEED FOR STARTING BROILERS
FOR USE AS AN AID IN THE PREVENTION OF COCCIDIOSIS IN POULTRY FLOCKS; GROWTH PROMOTION AND FEED
EFFICIENCY, AND IMPROVING PIGMENTATION.
ACTIVE DRUG INGREDIENT
NICARBAZIN 0.0125%
BACITRACIN METHYLENE DISALICYLATE 50 G/TON
ROXARSONE 0.005%) 45.4 G/TON
GUARANTEED ANALYSIS
CRUDE PROTEIN MIN 22.00%
LYSINE MIN 1.13%
METHIONINE MIN 0.54%
CRUDE FAT MIN 3.00%
CRUDE FIBER MAX 5.00%
CALCIUM MIN 0.75%
CALCIUM MAX 1.25%
PHOSPHORUS MIN 0.60%
SALT MIN 0.30%
SALT MAX 0.80%
INGREDIENTS
GRAIN PRODUCTS, PLANT PROTEIN PRODUCTS, ANIMAL PROTEIN PRODUCTS, HYDROLYZED ANIMAL AND VEGETABLE FAT,
CALCIUM PHOSPHATE, GROUND LIMESTONE, SALT, METHIONINE SUPPLEMENT, PROPIONIC ACID (ADDED TO RETARD MOLD
GROWTH), VITAMIN A ACETATE, VITAMIN D-3 SUPPLEMENT, VITAMIN E SUPPLEMENT, MENADIONE DIMETHYLPYRIMIDINOL
BISULPHITE, CHOLINE CHLORIDE, RIBOFLAVIN SUPPLEMENT, CALCIUM PANTOTHENATE, NIACIN, VITAMIN B-12
SUPPLEMENT, PYRIDOXINE HYDROCHLORIDE, THIAMINE MONONITRATE, FOLIC ACID, BIOTIN, ZINC OXIDE, MANGANOUS
OXIDE, MANGENESE SULFATE, FERROUS SULFATE, COBALT CARBONATE, CALCIUM IODATE, SODIUM SELENITE.
FEEDING DIRECTIONS
FOR BROILERS AND FRYER CHICKENS ONLY, FEED CONTINUOUSLY AS THE SOLE RATION.
SEE BACK OF TAG FOR WARNING
MANUFACTURED BY:
SKILLATHON FEEDS
NET WEIGHT 50 POUNDS (22.7 KILOGRAMS)
OR AS SHOWN ON SHIPPING DOCUMENT
WARNING
DO NOT FEED TO LAYING HENS. WITHDRAW 5 DAYS BEFORE SLAUGHTER. USE AS THE SOLE SOURCE OF ORGANIC
ARSENIC. FEED CONTINUOUSLY AS THE SOLE RATION FROM TIME CHICKS ARE PLACED ON LITTER UNTIL PAST THE TIME
WHEN COCCIDIOSIS IS ORDINARILY A HAZARD; DO NOT USE AS A TREATMENT FOR COCCIDIOSIS; DO NOT USE IN
FLUSHING MASHES.
DO NOT FEED TO CATTLE OR OTHER RUMINANTS.
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making
• learn how to read a feed tag.
Broiler: How to Read a Feed Tag
Use the feed tag below to answer the following questions.
1. What is the main ingredient in this
broiler ration?
2. What is the minimum crude protein
level of this broiler starter ration?
3. For how many days prior to slaughter
should this feed be removed?
4. How many pounds of ingredients are
included in this bag?
5. Should this diet be fed to laying hens?
6. What is the minimum crude fat level of
this diet?
Prepared by Drs. Gary Bowman and Bill Shulaw, Extension Specialists, Veterinary Medicine

2–64 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making—Key
• learn how to read a feed tag.
BROILER
STARTER
MEDICATED
COMPLETE FEED FOR STARTING BROILERS
FOR USE AS AN AID IN THE PREVENTION OF COCCIDIOSIS IN POULTRY FLOCKS; GROWTH PROMOTION AND FEED
EFFICIENCY, AND IMPROVING PIGMENTATION.
ACTIVE DRUG INGREDIENT
NICARBAZIN 0.0125%
BACITRACIN METHYLENE DISALICYLATE 50 G/TON
ROXARSONE 0.005%) 45.4 G/TON
GUARANTEED ANALYSIS
CRUDE PROTEIN MIN 22.00%
LYSINE MIN 1.13%
METHIONINE MIN 0.54%
CRUDE FAT MIN 3.00%
CRUDE FIBER MAX 5.00%
CALCIUM MIN 0.75%
CALCIUM MAX 1.25%
PHOSPHORUS MIN 0.60%
SALT MIN 0.30%
SALT MAX 0.80%
INGREDIENTS
GRAIN PRODUCTS, PLANT PROTEIN PRODUCTS, ANIMAL PROTEIN PRODUCTS, HYDROLYZED ANIMAL AND VEGETABLE FAT,
CALCIUM PHOSPHATE, GROUND LIMESTONE, SALT, METHIONINE SUPPLEMENT, PROPIONIC ACID (ADDED TO RETARD MOLD
GROWTH), VITAMIN A ACETATE, VITAMIN D-3 SUPPLEMENT, VITAMIN E SUPPLEMENT, MENADIONE DIMETHYLPYRIMIDINOL
BISULPHITE, CHOLINE CHLORIDE, RIBOFLAVIN SUPPLEMENT, CALCIUM PANTOTHENATE, NIACIN, VITAMIN B-12
SUPPLEMENT, PYRIDOXINE HYDROCHLORIDE, THIAMINE MONONITRATE, FOLIC ACID, BIOTIN, ZINC OXIDE, MANGANOUS
OXIDE, MANGENESE SULFATE, FERROUS SULFATE, COBALT CARBONATE, CALCIUM IODATE, SODIUM SELENITE.
FEEDING DIRECTIONS
FOR BROILERS AND FRYER CHICKENS ONLY, FEED CONTINUOUSLY AS THE SOLE RATION.
SEE BACK OF TAG FOR WARNING
MANUFACTURED BY:
SKILLATHON FEEDS
NET WEIGHT 50 POUNDS (22.7 KILOGRAMS)
OR AS SHOWN ON SHIPPING DOCUMENT
WARNING
DO NOT FEED TO LAYING HENS. WITHDRAW 5 DAYS BEFORE SLAUGHTER. USE AS THE SOLE SOURCE OF ORGANIC
ARSENIC. FEED CONTINUOUSLY AS THE SOLE RATION FROM TIME CHICKS ARE PLACED ON LITTER UNTIL PAST THE TIME
WHEN COCCIDIOSIS IS ORDINARILY A HAZARD; DO NOT USE AS A TREATMENT FOR COCCIDIOSIS; DO NOT USE IN
FLUSHING MASHES.
DO NOT FEED TO CATTLE OR OTHER RUMINANTS.
Broiler: How to Read a Feed Tag
Use the feed tag below to answer the following questions.
1. What is the main ingredient in this
broiler ration?
2. What is the minimum crude protein
level of this broiler starter ration?
3. For how many days prior to slaughter
should this feed be removed?
4. How many pounds of ingredients are
included in this bag?
5. Should this diet be fed to laying hens?
6. What is the minimum crude fat level of
this diet?
Prepared by Drs. Gary Bowman and Bill Shulaw, Extension Specialists, Veterinary Medicine
grain products
22%
5
50
no, because the medication
will end up in the eggs
3%

Lift-Off 2–65
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
TURKEY PRESTARTER
MEDICATED
COMPLETE FEED FOR POULTS
For the prevention of coccidiosis in growing turkeys caused by
Eimeria
adenoeides, Eimeria meleagrimitis
and
Eimeria gallapavonis
.
ACTIVE INGREDIENTS
Halofuginone Hydrobromide.................................................... 1.90 g/ton
GUARANTEED ANALYSIS
CRUDE PROTEIN .................................................................. MIN 26.00%
LYSINE ................................................................................ MIN 1.55%
METHIONINE ........................................................................ MIN 0.60%
CRUDE FAT ........................................................................... MIN 2.00%
CRUDE FIBER ........................................................................MAX 5.00%
CALCIUM.............................................................................. MIN 1.15%
CALCIUM..............................................................................MAX 1.65%
PHOSPHORUS ...................................................................... MIN 0.90%
SALT .................................................................................... MIN 0.15%
SALT ....................................................................................MAX 0.65%
INGREDIENTS
GRAIN PRODUCTS, PLANT PROTEIN PRODUCTS, ANIMAL PROTEIN PRODUCTS,
CALCIUM PHOSPHATE, ANIMAL FAT, GROUND LIMESTONE, METHIONINE
SUPPLEMENT, L-LYSINE MONOHYDROCHLORIDE, CALCIUM PROPIONATE, SALT
CHOLINE CHLORIDE, ZINC OXIDE, COPPER SULFATE, MANGANOUS OXIDE,
MANGANESE SULFATE, FERROUS SULFATE, CALCIUM IODATE, SODIUM
SELENITE, VITAMIN A ACETATE, VITAMIN D-3 SUPPLEMENT, VITAMIN E
SUPPLEMENT, MENADIONE DIMETHYLPYRIMIDINOL BISULPHITE, NIACIN,
CALCIUM PANTOTHENATE, RIBOFLAVIN SUPPLEMENT, VITAMIN B-12
SUPPLEMENT, BIOTIN, FOLIC ACID, THIAMINE MONONITRATE, RYRIDOXINE
HYDROCHLORIDE.
FEEDING DIRECTIONS
Feed as the only ration to starting poults from 1 day to 21 days of age. Refer
to current feeding schedules for feeding according to body weight or
consumption.
WARNING
Feed continuously as sole ration. Withdraw 7 days before slaughter.
MANUFACTURED BY:
SKILLATHON FEEDS
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making
• learn how to read a feed tag.
Turkey: How to Read a Feed Tag
Use the feed tag below to answer the following questions.
1. What is the main ingredient in this feed?
2. What is the active drug ingredient?
3. What is the minimum crude protein level?
4. For how many days prior to slaughter should this feed be
removed?
5. What is the minimum crude fat level of this diet?
6. Is ground limestone included in the ingredients of this diet?
7. This ration should be fed to turkey poults of what age?
Prepared by Drs. Gary Bowman and Bill Shulaw, Extension Specialists, Veterinary Medicine

2–66 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making—Key
• learn how to read a feed tag.
TURKEY PRESTARTER
MEDICATED
COMPLETE FEED FOR POULTS
For the prevention of coccidiosis in growing turkeys caused by
Eimeria
adenoeides, Eimeria meleagrimitis
and
Eimeria gallapavonis
.
ACTIVE INGREDIENTS
Halofuginone Hydrobromide.................................................... 1.90 g/ton
GUARANTEED ANALYSIS
CRUDE PROTEIN .................................................................. MIN 26.00%
LYSINE ................................................................................ MIN 1.55%
METHIONINE ........................................................................ MIN 0.60%
CRUDE FAT ........................................................................... MIN 2.00%
CRUDE FIBER ........................................................................MAX 5.00%
CALCIUM.............................................................................. MIN 1.15%
CALCIUM..............................................................................MAX 1.65%
PHOSPHORUS ...................................................................... MIN 0.90%
SALT .................................................................................... MIN 0.15%
SALT ....................................................................................MAX 0.65%
INGREDIENTS
GRAIN PRODUCTS, PLANT PROTEIN PRODUCTS, ANIMAL PROTEIN PRODUCTS,
CALCIUM PHOSPHATE, ANIMAL FAT, GROUND LIMESTONE, METHIONINE
SUPPLEMENT, L-LYSINE MONOHYDROCHLORIDE, CALCIUM PROPIONATE, SALT
CHOLINE CHLORIDE, ZINC OXIDE, COPPER SULFATE, MANGANOUS OXIDE,
MANGANESE SULFATE, FERROUS SULFATE, CALCIUM IODATE, SODIUM
SELENITE, VITAMIN A ACETATE, VITAMIN D-3 SUPPLEMENT, VITAMIN E
SUPPLEMENT, MENADIONE DIMETHYLPYRIMIDINOL BISULPHITE, NIACIN,
CALCIUM PANTOTHENATE, RIBOFLAVIN SUPPLEMENT, VITAMIN B-12
SUPPLEMENT, BIOTIN, FOLIC ACID, THIAMINE MONONITRATE, RYRIDOXINE
HYDROCHLORIDE.
FEEDING DIRECTIONS
Feed as the only ration to starting poults from 1 day to 21 days of age. Refer
to current feeding schedules for feeding according to body weight or
consumption.
WARNING
Feed continuously as sole ration. Withdraw 7 days before slaughter.
MANUFACTURED BY:
SKILLATHON FEEDS
Turkey: How to Read a Feed Tag
Use the feed tag below to answer the following questions.
1. What is the main ingredient in this feed?
2. What is the active drug ingredient?
3. What is the minimum crude protein level?
4. For how many days prior to slaughter should this feed be
removed?
5. What is the minimum crude fat level of this diet?
6. Is ground limestone included in the ingredients of this diet?
7. This ration should be fed to turkey poults of what age?
Prepared by Drs. Gary Bowman and Bill Shulaw, Extension Specialists, Veterinary Medicine
halofuginone hydrobromide
grain products
26%
7
2%
yes
from 1 day to 21 days

Lift-Off 2–67
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
RABBIT PELLETS
MEDICATED
For the prevention of coccidiosis caused by
Eimeria stiedae
.
ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Lasalocid (as lasalocid sodium) ............................................. 113 g/ton
GUARANTEED ANALYSIS
CRUDE PROTEIN ............................................................... MIN 16.00%
CRUDE FAT ........................................................................ MIN 3.00%
CRUDE FIBER ..................................................................... MIN 13.0%
CRUDE FIBER .................................................................. MAX 18.00%
CALCIUM............................................................................. MIN .75%
CALCIUM.......................................................................... MAX 1.25%
PHOSPHORUS ..................................................................... MIN 0.5%
SALT ................................................................................... MIN .30%
SALT .................................................................................. MAX .80%
VITAMIN A ....................................................................4,000.0 IU/LB
INGREDIENTS
DEHYDRATED ALFALFA MEAL, WHEAT MIDDLINGS, DRIED DISTILLERS GRAINS
WITH SOLUBLES, CANE MOLASSES, ANIMAL FAT (PRESERVED WITH
BHAANDBHT), DICALCIUM PHOSPHATE, CALCIUM CARBONATE, SOYBEAN
MEAL, SALT, VITAMIN A ACETATE IN GELATIN, VITAMIN D3 SUPPLEMENT,
VITAMIN E SUPPLEMENT, RIBOFLAVIN SUPPLEMENT, D-CALCIUM
PANTOTHENATE, NIACIN SUPPLEMENT, VITAMIN B12 SUPPLEMENT,
MENADIONE DIMETHYLPYRIMIDINOL BISULFITE(SOURCE OF VITAMIN K
ACTIVITY), CHOLINE CHLORIDE, FOLIC ACID, B-BIOTIN, ZINC OXIDE, FERROUS
SULFATE, MANGOUS OXIDE, COPPER OXIDE, ETHYLENE DIAMINE
DIHYDRIDIDE, COBALT CARBONATE, AND SODIUM SELENITE.
USE DIRECTIONS
Feed continuously to young rabbits as sole ration up to 6 1/2 weeks of age.
CAUTION
The safety of lasalocid in unapproved species has not been established.
MANUFACTURED BY:
SKILLATHON FEED
NEW WEIGHT 50 POUNDS (22.7 KILOGRAMS)
OR AS SHOWN ON SHIPPING DOCUMENT
Net Weight 20 lbs. (9.7 Kg.)
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making
• learn how to read a feed tag.
Rabbit: How to Read a Feed Tag
Use the feed tag below to answer the following questions.
1. What is the main ingredient in this feed?
2. What is the active drug ingredient?
3. What is the minimum crude protein level?
4. Does this feed require withholding before slaughter?
5. What is the minimum crude fat level of this diet?
6. Is calcium carbonate included in the ingredients of this diet?
7. To what age should this ration be fed?
Prepared by Drs. Gary Bowman and Bill Shulaw, Extension Specialists, Veterinary Medicine, and Jodi Black, State 4-H Animal Sciences Extension Associate

2–68 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Decision-Making—Key
• learn how to read a feed tag.
RABBIT PELLETS
MEDICATED
For the prevention of coccidiosis caused by
Eimeria stiedae
.
ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Lasalocid (as lasalocid sodium) ............................................. 113 g/ton
GUARANTEED ANALYSIS
CRUDE PROTEIN ............................................................... MIN 16.00%
CRUDE FAT ........................................................................ MIN 3.00%
CRUDE FIBER ..................................................................... MIN 13.0%
CRUDE FIBER .................................................................. MAX 18.00%
CALCIUM............................................................................. MIN .75%
CALCIUM.......................................................................... MAX 1.25%
PHOSPHORUS ..................................................................... MIN 0.5%
SALT ................................................................................... MIN .30%
SALT .................................................................................. MAX .80%
VITAMIN A ....................................................................4,000.0 IU/LB
INGREDIENTS
DEHYDRATED ALFALFA MEAL, WHEAT MIDDLINGS, DRIED DISTILLERS GRAINS
WITH SOLUBLES, CANE MOLASSES, ANIMAL FAT (PRESERVED WITH
BHAANDBHT), DICALCIUM PHOSPHATE, CALCIUM CARBONATE, SOYBEAN
MEAL, SALT, VITAMIN A ACETATE IN GELATIN, VITAMIN D3 SUPPLEMENT,
VITAMIN E SUPPLEMENT, RIBOFLAVIN SUPPLEMENT, D-CALCIUM
PANTOTHENATE, NIACIN SUPPLEMENT, VITAMIN B12 SUPPLEMENT,
MENADIONE DIMETHYLPYRIMIDINOL BISULFITE(SOURCE OF VITAMIN K
ACTIVITY), CHOLINE CHLORIDE, FOLIC ACID, B-BIOTIN, ZINC OXIDE, FERROUS
SULFATE, MANGOUS OXIDE, COPPER OXIDE, ETHYLENE DIAMINE
DIHYDRIDIDE, COBALT CARBONATE, AND SODIUM SELENITE.
USE DIRECTIONS
Feed continuously to young rabbits as sole ration up to 6 1/2 weeks of age.
CAUTION
The safety of lasalocid in unapproved species has not been established.
MANUFACTURED BY:
SKILLATHON FEED
NEW WEIGHT 50 POUNDS (22.7 KILOGRAMS)
OR AS SHOWN ON SHIPPING DOCUMENT
Net Weight 20 lbs. (9.7 Kg.)
Rabbit: How to Read a Feed Tag
Use the feed tag below to answer the following questions.
1. What is the main ingredient in this feed?
2. What is the active drug ingredient?
3. What is the minimum crude protein level?
4. Does this feed require withholding before slaughter?
5. What is the minimum crude fat level of this diet?
6. Is calcium carbonate included in the ingredients of this diet?
7. To what age should this ration be fed?
up to 6 1/2 weeks of age
dehydrated alfalfa meal
lasalocid
16%
no
3%
yes
Prepared by Drs. Gary Bowman and Bill Shulaw, Extension Specialists, Veterinary Medicine, and Jodi Black, State 4-H Animal Sciences Extension Associate
Lift-Off 2–69
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Word Search
• learn words and associate them with
particular groups.
Beef Word Search
Circle the beef words listed in the puzzle below.
Beef Types
steer
heifer
cow
calf
Grading
prime
choice
select
standard
commercial
utility
cutter
canner
Color
black
white
gray
red
cream
roan
Wholesale Cuts
round
loin
flank
rib
plate
chuck
shank
brisket
Reference: Beef Learning Laboratory Kit and the Beef, Sheep and Swine Evaluation and Selection Book
COMMERCIALXBK
AHSDTSUTI L I TY
NAORVSTEERLMA
NETIHWTAHJANR
EIDZCCEHNEREG
REOJEERGRDQMP
RCYLCHUCKEAIM
EWEBR I SKETGRC
FSKLOFHFLACPD
IQSAUTARPLMOD
EZJCNYNVWPXFW
HCDKDXKNALFHL

2–70 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Word Search—Key
• learn words and associate them with
particular groups.
Beef Word Search
Circle the beef words listed in the puzzle below.
Beef Types
steer
heifer
cow
calf
Grading
prime
choice
select
standard
commercial
utility
cutter
canner
Color
black
white
gray
red
cream
roan
Wholesale Cuts
round
loin
flank
rib
plate
chuck
shank
brisket
Reference: Beef Learning Laboratory Kit and the Beef, Sheep and Swine Evaluation and Selection Book
COMMERCIALXBK
AHSDTSUTI L ITY
NAORVSTEERLMA
NETIHWTAHJANR
EIDZCCEHNEREG
REOJEERGRDQMP
RCYLCHUCKEAIM
EWEBR I SKETGRC
FSKLOFHFLACPD
IQSAUTARPLMOD
EZJCNYNVWPXFW
HCDKDXKNALFHL

Lift-Off 2–71
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Word Search
• learn words and associate them with
particular groups.
Goat Word Search
Circle the goat words listed in the puzzle below.
Color
black
gray
cream
white
tan
Goat Types
doe
buck
kids
dairy
meat
harness
Wholesale Cuts
shoulder
rack
loin
leg
fore shank
breast
References: Goat Learning Laboratory Kit and the 4-H Goat Manual
REDDISHBROWNC
MTBJOHJQGCDWX
WAFR L ERYARGOK
PLAVENDEREHRR
TOWKDAFKCALBT
ZCNNPSSLGMJFX
COVQZNETIHWSH
SHOULDERAGMJL
YCAYDVDFMNPVQ
WFORESHANKKBY
CLOINMCKIDSUN
TRESDEHWZRACK
FSGGRASTNKYKX
LVCHGTFSDPQMJ
brown
reddish brown
fawn
chocolate
lavender

2–72 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Word Search—Key
• learn words and associate them with
particular groups.
Goat Word Search
Circle the goat words listed in the puzzle below.
Color
black
gray
cream
white
tan
Goat Types
doe
buck
kids
dairy
meat
harness
Wholesale Cuts
shoulder
rack
loin
leg
fore shank
breast
References: Goat Learning Laboratory Kit and the 4-H Goat Manual
REDDISHBROWNC
MTBJOHJQGCDWX
WAFR L ERYARGOK
PLAVENDEREHRR
TOWKDAFKCALBT
ZCNNPSSLGMJFX
COVQZNETIHWSH
SHOULDERAGMJL
YCAYDVDFMNPVQ
WFORESHANKKBY
CLOINMCKIDSUN
TRESDEHWZRACK
FSGGRASTNKYKX
LVCHGTFSDPQMJ
brown
reddish brown
fawn
chocolate
lavender

Lift-Off 2–73
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Word Search
• learn words and associate them with
particular groups.
Sheep Word Search
Circle the sheep words listed in the puzzle below.
Sheep Types
breeding
market
ewe
ram
lamb
Mouth Structure
parrot
monkey
Wholesale Cuts
leg
loin
rack
shoulder
breast
foreshank
References: Sheep Learning Laboratory Kit; 4-H Beef, Sheep and Swine Evaluation and Selection Book; 4-H Sheep Resource Handbook
DPMBZCSMQPQF
RFORESHANKSC
LNYEJKORHNYJ
KLTEWWUKDDTS
RXODVELEOGIC
MYR I YFDTOHLH
LERNNXETGZIM
DKAGFBREASTP
YNPWCULLMGUJ
COVZXNLAVTQG
TMFKCAREMI RP
HGCHOICEWBSK
Grading
prime
choice
good
utility
cull

2–74 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Word Search—Key
• learn words and associate them with
particular groups.
Sheep Word Search
Circle the sheep words listed in the puzzle below.
Sheep Types
breeding
market
ewe
ram
lamb
Mouth Structure
parrot
monkey
Wholesale Cuts
leg
loin
rack
shoulder
breast
foreshank
DPMBZCSMQPQF
RFORESHANKSC
LNYEJKORHNYJ
KLTEWWUKDDTS
RXODVELEOGIC
MYR I YFDTOHLH
LERNNXETGZIM
DKAGFBREASTP
YNPWCULLMGUJ
COVZXNLAVTQG
TMFKCAREMI RP
HGCHOICEWBSK
Grading
prime
choice
good
utility
cull
References: Sheep Learning Laboratory Kit; 4-H Beef, Sheep and Swine Evaluation and Selection Book; 4-H Sheep Resource Handbook

Lift-Off 2–75
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Word Search
• learn words and associate them with
particular groups.
Swine Word Search
Circle the swine words listed in the puzzle below.
Meat Cuts
bacon
chops
ribs
Swine Types
breeding
market
gilt
boar
barrow
sow
Wholesale Cuts
Boston butt
picnic
loin
side
ham
References: 4-H Beef, Sheep and Swine Evaluation and Selection Book; 4-H Swine Resource Handbook
Grading
acceptable
unacceptable
Colors
white
black
red
UCPLHDKRFB
NMI T C J Z I T R
ACCEPTABLE
CHNKBXMSIK
COIRWAYDGC
EPCAHPRGGA
PSNMMBHRWL
TTUBNOTSOB
APQLVAJFSW
BACONRQKVS
LETIHWESIN
ERTNTWYDCL
SBGNIDEERB

2–76 Lift-Off
Prepared By: Jodi Black, State Extension Associate, 4-H/Animal Sciences; Andrea Auker, Animal Sciences Student
Livestock
In this activity you will:
Word Search—Key
• learn words and associate them with
particular groups.
Swine Word Search
Circle the swine words listed in the puzzle below.
Meat Cuts
bacon
chops
ribs
Swine Types
breeding
market
gilt
boar
barrow
sow
Wholesale Cuts
Boston butt
picnic
loin
side
ham
Grading
acceptable
unacceptable
Colors
white
black
red
UCPLHDKRFB
NMI T C J Z I TR
ACCEPTABLE
CHNKBXMS I K
COIRWAYDGC
EPCAHPRGGA
PSNMMBHRWL
TTUBNOTSOB
APQLVAJFSW
BACONRQKVS
LETIHWESIN
ERTNTWYDCL
SBGNIDEERB
References: 4-H Beef, Sheep and Swine Evaluation and Selection Book; 4-H Swine Resource Handbook
