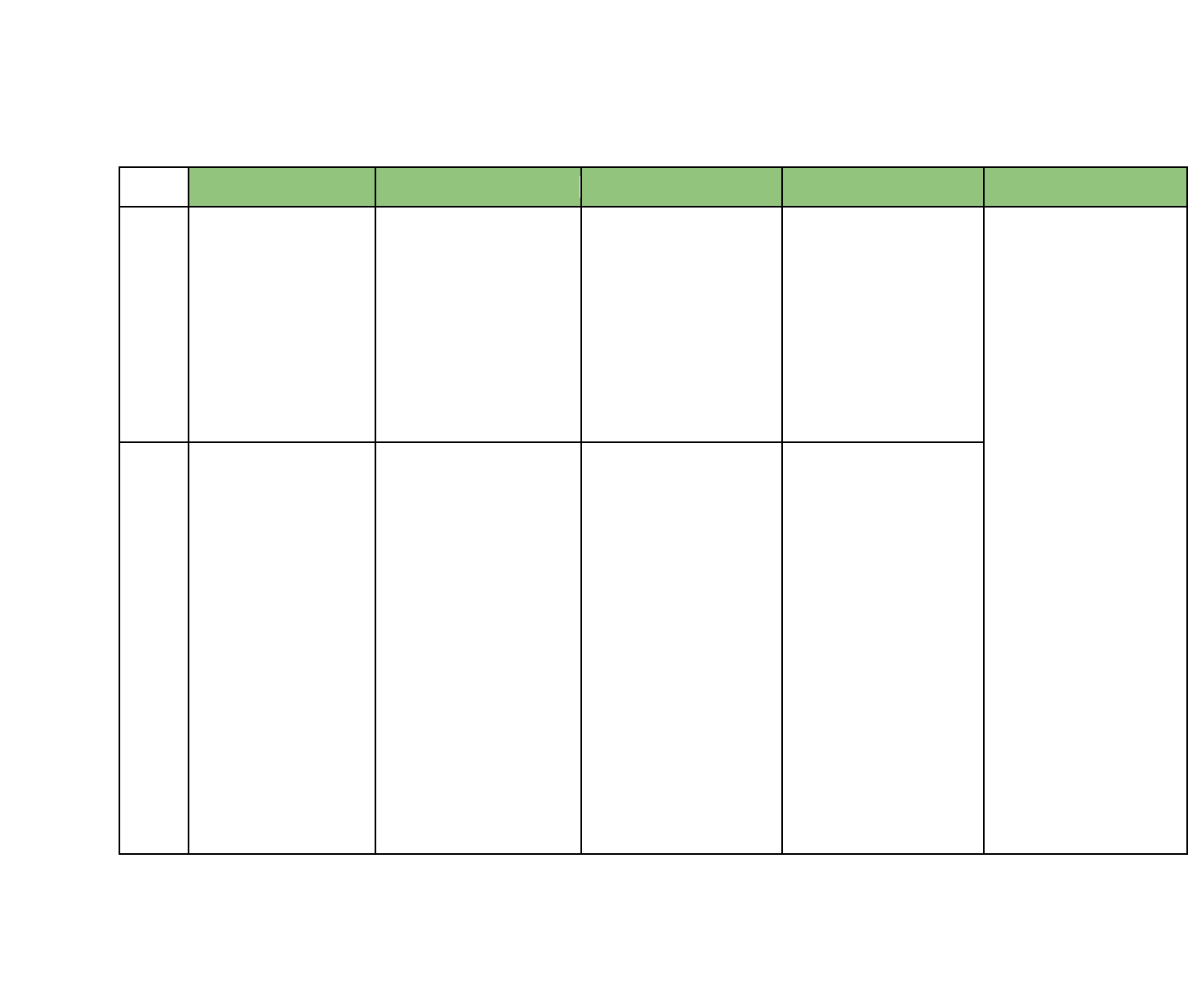
Hawaii Department of Education Standards with Opportunities to Integrate Financial Literacy Concepts
Financial Literacy 1 12/12/16
Grade
ELA
Mathematics
CTE
Social Studies
Science
K
K.RI.10
Actively engage in
group reading activities
with purpose and
understanding.
K.OA.2
Solve addition and
subtraction word
problems, and add and
subtract within 10, e.g.,
by using objects or
drawings to represent the
problem.
CTE.K.2.1
Explain that current
learning relates to life
outside the classroom.
CTE.K.2.2
Identify various workers
and their jobs in the
community.
SS.K.8.1
Explain people's basic
needs and how they fulfill
them.
SS.K.8.2
Differentiate buyers (e.g.,
a parent or caregiver)
and sellers (e.g., a store
owner or other
producer).
K-2-ETS1-1
Ask questions, make
observations, and gather
information about a
situation people want to
change to define a
simple problem that can
be solved through the
development of a new or
improved object or tool.
Science and
Engineering Practices:
Analyzing and
Interpreting Data, Using
Mathematics and
Computational Thinking,
Obtaining, Evaluating,
and Communicating
Information.
1
1.RI.6
Distinguish between
information provided
by pictures or other
illustrations and
information provided
by the words in a text.
1.RI.10
With prompting and
support, read
informational texts
appropriately complex
for grade 1.
1.OA.1
Use addition and
subtraction within 20 to
solve word problems
involving situations of
adding to, taking from,
putting together, taking
apart, and comparing,
with unknowns in all
positions, e.g., by using
objects, drawings, and
equations with a symbol
for the unknown number
to represent the problem.
SS.1.2.1
Use a variety of primary
sources (e.g., artifacts,
letters, photographs) to
gain an understanding of
historical events.
SS.1.3.1
Compare own life with
those of children in
history.
SS.1.8.1
Compare needs and
wants.
SS.1.8.2
Explain how people trade
or use money to obtain
goods and services.
SS.1.8.3 Define various

Hawaii Department of Education Standards with Opportunities to Integrate Financial Literacy Concepts
Financial Literacy 2 12/12/16
Grade
ELA
Mathematics
CTE
Social Studies
Science
1
goods (things that people
need or want) and
services (jobs people
perform that satisfy
people's needs or
wants).
2
2.RI.7
Explain how specific
images (e.g., a
diagram showing how
a machine works)
contribute to and
clarify a text.
2.RI.10
By the end of year,
read and comprehend
informational texts,
including history/social
studies, science, and
technical texts, in the
grades 2/3 text
complexity band
proficiently, with
scaffolding as needed
at the high end of the
range.
2.OA.1
Use addition and
subtraction within 100 to
solve one- and two-step
word problems involving
situations of adding to,
taking from, putting
together, taking apart,
and comparing, with
unknowns in all positions,
e.g., by using drawings
and equations with a
symbol for the unknown
number to represent the
problem.
2.MD.8
Solve word problems
involving dollar bills,
quarters, dimes, nickels,
and pennies, using $
(dollars) and ¢ (cents)
symbols appropriately.
Example: If you have 2
dimes and 3 pennies,
how many cents do you
CTE.2.2.1
Use appropriate
strategies for setting
goals.
SS.2.2.1
Investigate the history of
families using level-
appropriate primary
sources (e.g., artifacts,
photographs, interviews,
documents).
SS.2.8.1
Explain scarcity and its
effects on daily life.
SS.2.8.3
Explain how people
benefit from trade (the
exchange of goods and
services).
SS.2.8.4
Compare the roles of
buyers and sellers and
explain how they depend
upon each other.

Hawaii Department of Education Standards with Opportunities to Integrate Financial Literacy Concepts
Financial Literacy 3 12/12/16
Grade
ELA
Mathematics
CTE
Social Studies
Science
2
have?
3
3.RI.7
Use information gained
from illustrations (e.g.,
maps, photographs)
and the words in a text
to demonstrate
understanding of the
text (e.g., where,
when, why, and how
key events occur).
3.RI.10
By the end of the year,
read and comprehend
informational texts,
including history/social
studies, science, and
technical texts, at the
high end of the grades
2/3 text complexity
band independently
and proficiently.
3.OA.8
Solve two-step word
problems using the four
operations. Represent
these problems using
equations with a letter
standing for the unknown
quantity. Assess the
reasonableness of
answers using mental
computation and
estimation strategies
including rounding. (This
standard is limited to
problems posed with
whole numbers and
having whole-number
answers; students should
know how to perform
operations in the
conventional order when
there are no parentheses
to specify a particular
order.)
3.MD.3
Draw a scaled picture
graph and a scaled bar
graph to represent a data
set with several
SS.3.8.1
Explain that opportunity
cost is the best
alternative given up
when making a choice
SS.3.8.2
Explain that goods and
resources are limited
because there are not
enough natural, human,
and capital resources to
satisfy everyone's wants
SS.3.8.3
Describe how money
makes it easy to trade
goods and services
3-5-ETS1-1
Define a simple design
problem reflecting a need
or a want that includes
specified criteria for
success and constraints
on materials, time, or
cost.
3-5-ETS1-2
Generate and compare
multiple possible
solutions to a problem
based on how well each
is likely to meet the
criteria and constraints of
the problem.
Science and Engineering
Practices: Analyzing and
Interpreting Data, Using
Mathematics and
Computational Thinking,
Obtaining, Evaluating,
and Communicating
Information.

Hawaii Department of Education Standards with Opportunities to Integrate Financial Literacy Concepts
Financial Literacy 4 12/12/16
Grade
ELA
Mathematics
CTE
Social Studies
Science
3
categories. Solve one-
and two-step "how many
more" and "how many
less" problems using
information presented in
scaled bar graphs. For
example, draw a bar
graph in which each
square in the bar graph
might represent 5 pets.
4
4.RI.7
Interpret information
presented visually,
orally, or quantitatively
(e.g., in charts, graphs,
diagrams, time lines,
animations, or
interactive elements on
Web pages) and
explain how the
information contributes
to an understanding of
the text in which it
appears.
4.RI.10
By the end of year,
read and comprehend
informational texts,
including history/social
studies, science, and
technical texts, in the
4.OA.3
Solve multistep word
problems posed with
whole numbers and
having whole-number
answers using the four
operations, including
problems in which
remainders must be
interpreted. Represent
these problems using
equations with a letter
standing for the unknown
quantity. Assess the
reasonableness of
answers using mental
computation and
estimation strategies
including rounding.
4.MD.2
Use the four operations
CTE.4.2.1
Analyze how doing well
in school affects future
career opportunities.
Pre-contact Hawaii
SS.4.3.2
Explain the history of
Hawaii's early economy.

Hawaii Department of Education Standards with Opportunities to Integrate Financial Literacy Concepts
Financial Literacy 5 12/12/16
Grade
ELA
Mathematics
CTE
Social Studies
Science
4
grades 4/5 text
complexity band
proficiently, with
scaffolding as
necessary at the high
end of the range.
to solve word problems
involving distances,
intervals of time, liquid
volumes, masses of
objects, and money,
including problems
involving simple fractions
or decimals, and
problems that require
expressing
measurements given in a
larger unit in terms of a
smaller unit. Represent
measurement quantities
using diagrams such as
number line diagrams
that feature a
measurement scale.
5
5.RI.7
Draw on information
from multiple print or
digital sources,
demonstrating the
ability to locate an
answer to a question
quickly or to solve a
problem efficiently.
5.RI.10
By the end of the year,
read and comprehend
informational texts,
5.NBT.7
Add, subtract, multiply,
and divide decimals to
hundredths, using
concrete models or
drawings and strategies
based on place value,
properties of operations,
and/or the relationship
between addition and
subtraction; relate the
strategy to a written
method and explain the
SS.5.8.1
Explain the opportunity
costs considered by the
settlers before moving to
the colonies.
SS.5.8.2
Recognize that
governments raise
money (i.e., taxes) to pay
for goods and services
and describe why the
American colonists were
dissatisfied with the

Hawaii Department of Education Standards with Opportunities to Integrate Financial Literacy Concepts
Financial Literacy 6 12/12/16
Grade
ELA
Mathematics
CTE
Social Studies
Science
5
including history/social
studies, science, and
technical texts, at the
high end of the grades
4/5 text complexity
band independently
and proficiently.
reasoning used.
colonial system of
taxation.
6
6.RI.7
Integrate information
presented in different
media or formats (e.g.,
visually, quantitatively)
as well as in words to
develop a coherent
understanding of a
topic or issue.
6.RI.10
By the end of the year,
read and comprehend
literary nonfiction in the
grades 6-8 text
complexity band
proficiently, with
scaffolding as needed
at the high end of the
range.
6.NS.5
Understand that positive
and negative numbers
are used together to
describe quantities
having opposite
directions or values (e.g.,
temperature above/below
zero, elevation
above/below sea level,
debits/credits,
positive/negative electric
charge); use positive and
negative numbers to
represent quantities in
real-world contexts,
explaining the meaning of
0 in each situation.
6.EE.6
Use variables to
represent numbers and
write expressions when
solving a real-world or
mathematical problem;
CTE.6.2.1
Establish personal and
learning goals related to
career and life interests.
SS.6.8.2
Describe, in terms of
opportunity cost, why it
was so difficult for
Christopher Columbus to
find financial support for
his voyages.
MS-ETS1-1
Define the criteria and
constraints of a design
problem with sufficient
precision to ensure a
successful solution,
taking into account
relevant scientific
principles and potential
impacts on people and
the natural environment
that may limit possible
solutions.
Science and
Engineering Practices:
Analyzing and
Interpreting Data, Using
Mathematics and
Computational Thinking,
Obtaining, Evaluating,
and Communicating In
formation.
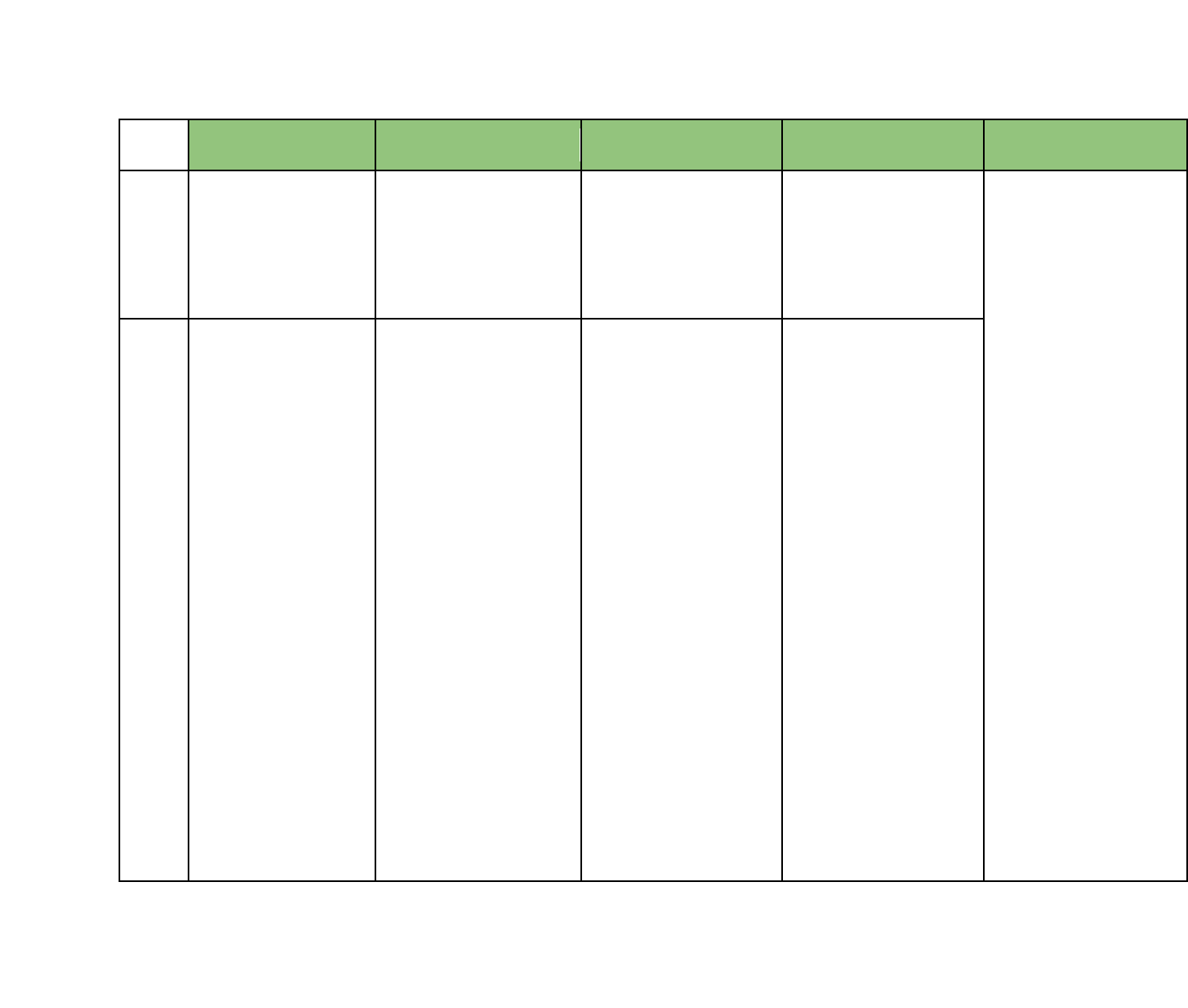
Hawaii Department of Education Standards with Opportunities to Integrate Financial Literacy Concepts
Financial Literacy 7 12/12/16
Grade
ELA
Mathematics
CTE
Social Studies
Science
6
understand that a
variable can represent an
unknown number, or,
depending on the
purpose at hand, any
number in a specified set.
7
7.RI.7
Compare and contrast
a text to an audio,
video, or multimedia
version of the text,
analyzing each
medium’s portrayal of
the subject (e.g., how
the delivery of a
speech affects the
impact of the words).
7.RI.10
By the end of the year,
read and comprehend
literary nonfiction in the
grades 6-8 text
complexity band
proficiently, with
scaffolding as needed
at the high end of the
range.
7.RP.3
Use proportional
relationships to solve
multistep ratio and
percent problems.
Examples: simple
interest, tax, markups
and markdowns,
gratuities and
commissions, fees,
percent increase and
decrease, percent error.
7.EE.3
Solve multi-step real-life
and mathematical
problems posed with
positive and negative
rational numbers in any
form (whole numbers,
fractions, and decimals),
using tools strategically.
Apply properties of
operations as strategies
to calculate with numbers
in any form; convert
CTE.7-8.2.2
Develop a preliminary
individual education and
career plan.
CTE 7-8.2.3
Analyze the relationship
between personal
characteristics, interests,
abilities, and skills and
achieving personal and
career goals.
SS.7HHK7.1
Analyze the relationship
between economic
activities, their location,
and the physical
characteristics of a given
place (including
businesses, plantations,
and trading).
SS.7HHK.8.1
Explain how prices and
products (including
sandalwood, whales, and
sugar) were affected by
the interactions between
producers in Hawaii and
global buyers in this era.
SS.7HHK.8.2
Describe how trade
between Hawaii and
other countries is
affected by regulations.

Hawaii Department of Education Standards with Opportunities to Integrate Financial Literacy Concepts
Financial Literacy 8 12/12/16
Grade
ELA
Mathematics
CTE
Social Studies
Science
7
between forms as
appropriate; and assess
the reasonableness of
answers using mental
computation and
estimation strategies. For
example: If a woman
making $25 an hour gets
a 10% raise, she will
make an additional 1/10
of her salary an hour, or
$2.50, for a new salary of
$27.50. If you want to
place a towel bar 9 3/4
inches long in the center
of a door that is 27 1/2
inches wide, you will
need to place the bar
about 9 inches from each
edge; this estimate can
be used as a check on
the exact computation.
7.EE.4
Use variables to
represent quantities in a
real-world or
mathematical problem,
and construct simple
equations and
inequalities to solve
problems by reasoning
about the quantities.
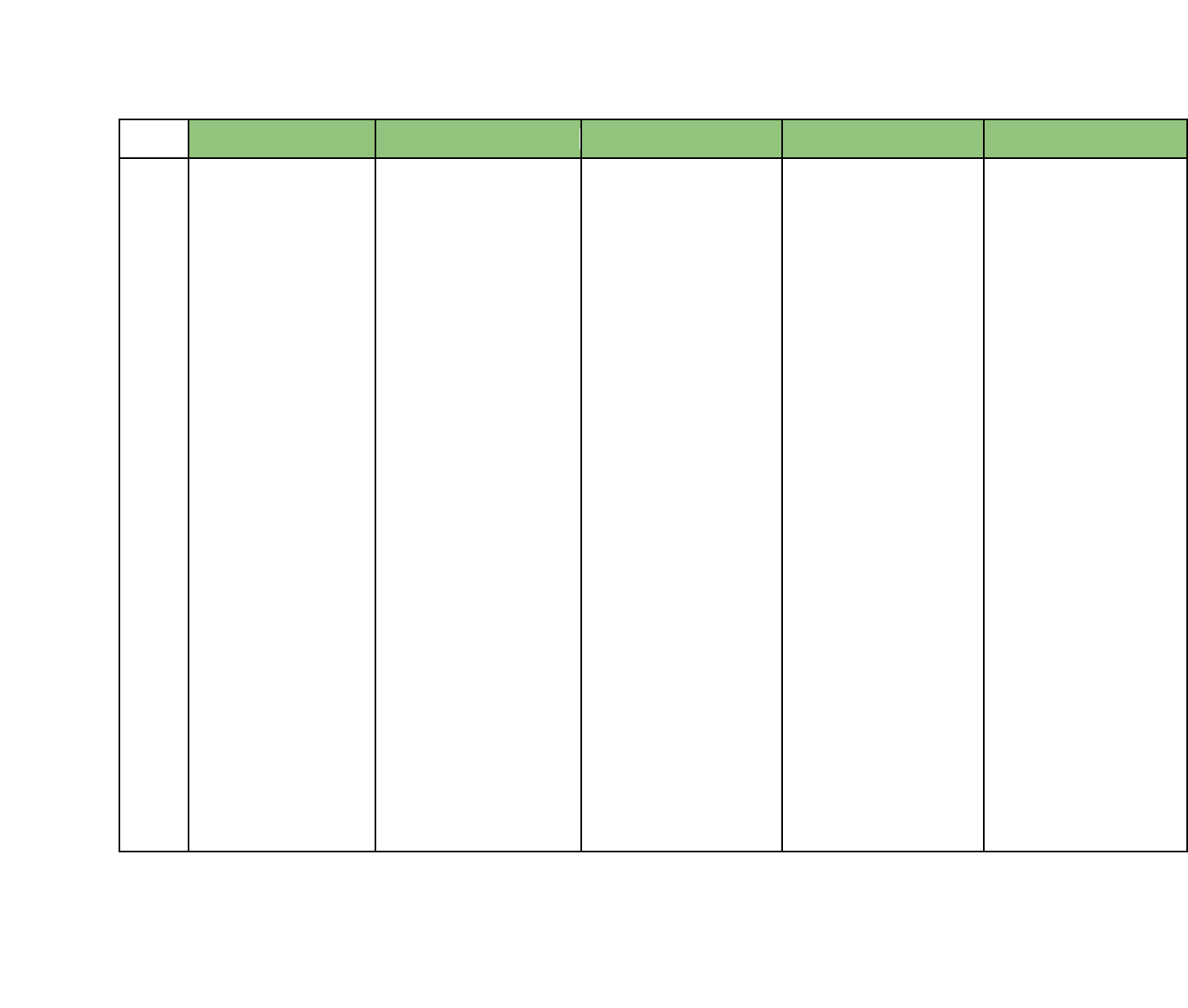
Hawaii Department of Education Standards with Opportunities to Integrate Financial Literacy Concepts
Financial Literacy 9 12/12/16
Grade
ELA
Mathematics
CTE
Social Studies
Science
7
a. Solve word problems
leading to equations of
the form px + q = r and
p(x + q) = r, where p, q,
and r are specific rational
numbers. Solve
equations of these forms
fluently. Compare an
algebraic solution to an
arithmetic solution,
identifying the sequence
of the operations used in
each approach. For
example, the perimeter of
a rectangle is 54 cm. Its
length is 6 cm. What is its
width?
b. Solve word problems
leading to inequalities of
the form px + q > r or px
+ q < r, where p, q, and r
are specific rational
numbers. Graph the
solution set of the
inequality and interpret it
in the context of the
problem. For example: As
a salesperson, you are
paid $50 per week plus
$3 per sale. This week
you want your pay to be

Hawaii Department of Education Standards with Opportunities to Integrate Financial Literacy Concepts
Financial Literacy 10 12/12/16
Grade
ELA
Mathematics
CTE
Social Studies
Science
7
at least $100. Write an
inequality for the number
of sales you need to
make, and describe the
solutions.
8
8.RI.7
Evaluate the
advantages and
disadvantages of using
different mediums
(e.g., print or digital
text, video, multimedia)
to present a particular
topic or idea.
8.RI.10
By the end of the year,
read and comprehend
literary nonfiction at
the high end of the
grades 6-8 text
complexity band
independently and
proficiently.
8.F.4
Construct a function to
model a linear
relationship between two
quantities. Determine the
rate of change and initial
value of the function from
a description of a
relationship or from two
(x, y) values, including
reading these from a
table or from a graph.
Interpret the rate of
change and initial value
of a linear function in
terms of the situation it
models, and in terms of
its graph or a table of
values.
8.F.5
Describe qualitatively the
functional relationship
between two quantities
by analyzing a graph
(e.g., where the function
is increasing or
CTE.7-8.2.2 Develop a
preliminary individual
education and career
plan.
CTE 7-8.2.3 Analyze the
relationship between
personal characteristics,
interests, abilities, and
skills and achieving
personal and career
goals.
SS.8.8.1
Explain productivity in
terms of output per
worker, hour, machine,
or unit of land, and its
effects on standards of
living in 18th and/or 19th
century America.
SS.8.8.2
Describe the factors that
influence production and
consumption decisions in
a market system.
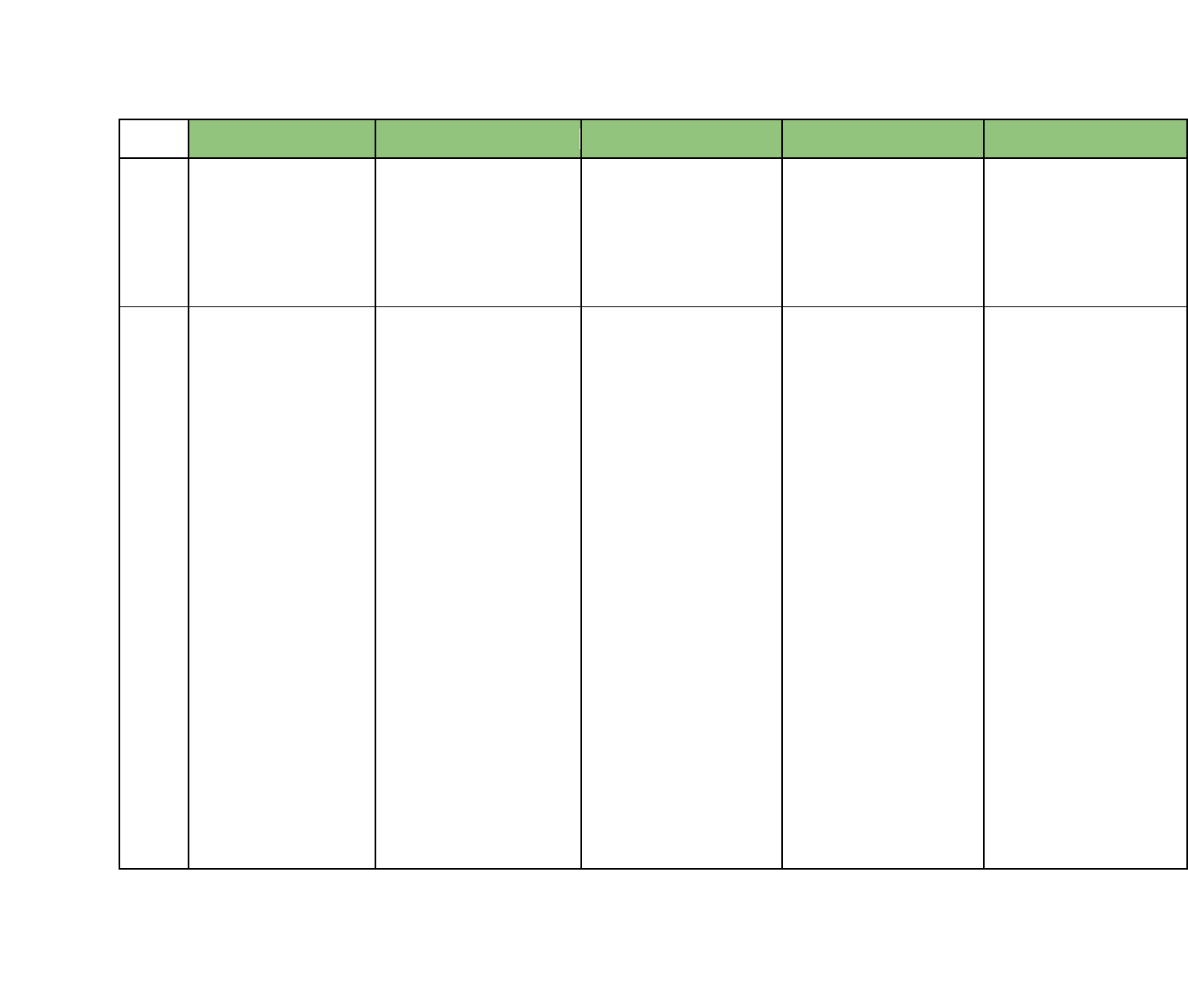
Hawaii Department of Education Standards with Opportunities to Integrate Financial Literacy Concepts
Financial Literacy 11 12/12/16
Grade
ELA
Mathematics
CTE
Social Studies
Science
8
decreasing, linear or
nonlinear). Sketch a
graph that exhibits the
qualitative features of a
function that has been
described verbally.
9
9-10.RI.7
Analyze various
accounts of a subject
told in different
mediums (e.g., a
person’s life story in
both print and
multimedia),
determining which
details are emphasized
in each account.
9-10.RI.10
By the end of grade 9,
read and comprehend
literary nonfiction in the
grades 9-10 text
complexity band
proficiently, with
scaffolding as needed
at the high end of the
range. By the end of
grade 10, read and
comprehend literary
nonfiction at the high
end of the grades 9-10
N.Q.2
Define appropriate
quantities for the purpose
of descriptive modeling.
A.SSE.1
Interpret expressions that
represent a quantity in
terms of its context.*
a. Interpret parts of an
expression, such as
terms, factors, and
coefficients.
b. Interpret complicated
expressions by viewing
one or more of their parts
as a single entity. For
example, interpret
P(1+r)^n as the product
of P and a factor not
depending on P.
A.CED.1
Create equations and
inequalities in one
variable and use them to
solve problems. Include
CTE.9-12.2.8
Assess the
compensation, lifestyle,
and other benefits
associated with careers
of interest.
Modern History of Hawaii
SS.9MHH.1.1
Describe the multiple
social, political, and
economic causes and
effects of change in
modern Hawaii.
SS.9MHH.3.9
Analyze significant
contemporary issues that
influence present day
Hawaii, such as the
Hawaiian Renaissance,
the sovereignty
movement, current land
issues, and the influx of
new immigrant groups.
SS.9PD.8.2
Explain how people,
individually and
collectively, participate in
the U.S. economy.
HS-ETS1-1
Analyze a major global
challenge to specify
qualitative and
quantitative criteria and
constraints for solutions
that account for societal
needs and wants.
HS-ETS1-2
Design a solution to a
complex real-world
problem by breaking it
down into smaller, more
manageable problems
that can be solved
through engineering.
HS-ETS1-3
Evaluate a solution to a
complex real-world
problem based on
prioritized criteria and
trade-offs that account
for a range of constraints,
including cost, safety ,
reliability, and

Hawaii Department of Education Standards with Opportunities to Integrate Financial Literacy Concepts
Financial Literacy 12 12/12/16
Grade
ELA
Mathematics
CTE
Social Studies
Science
9
text complexity band
independently and
proficiently.
equations arising from
linear and quadratic
functions, and simple
rational and exponential
functions.*
A.CED.2
Create equations in two
or more variables to
represent relationships
between quantities; graph
equations on coordinate
axes with labels and
scales.*
aesthetics as well as
possible social, cultural,
and environmental
impacts.
Science and
Engineering Practices:
Analyzing and
Interpreting Data, Using
Mathematics and
Computational Thinking,
Obtaining, Evaluating,
and Communicating
Information.
10
9-10.RI.7
Analyze various
accounts of a subject
told in different
mediums (e.g., a
person’s life story in
both print and
multimedia),
determining which
details are emphasized
in each account.
9-10.RI.10
By the end of grade 9,
read and comprehend
literary nonfiction in the
grades 9-10 text
complexity band
proficiently, with
CTE.9-12.2.8
Assess the
compensation, lifestyle,
and other benefits
associated with careers
of interest.
U.S. History
SS.10.3.32
Explain how the
administrations from
Reagan to the current
president dealt with
major domestic issues.
SS.10.8.1
Explain the
characteristics of the
different market
structures (i.e. monopoly,
oligopoly, monopolistic
competition, and pure
competition) and their
influence on product
differentiation, price,
barriers for entry, and

Hawaii Department of Education Standards with Opportunities to Integrate Financial Literacy Concepts
Financial Literacy 13 12/12/16
Grade
ELA
Mathematics
CTE
Social Studies
Science
10
scaffolding as needed
at the high end of the
range. By the end of
grade 10, read and
comprehend literary
nonfiction at the high
end of the grades 9 10
text complexity band
independently and
proficiently.
market efficiency in a
competitive marketplace.
SS.10.8.2
Describe the function
and responsibilities of
the Federal Reserve
System in setting and
carrying out the nation's
monetary policy.
SS.10.8.3
Explain the purpose
and/or role of
government programs
and policies, including
unemployment, minimum
wage, and Social
Security, and their effect
on the nation's economy.
11
11-12.RI.7
Integrate and evaluate
multiple sources of
information presented
in different media or
formats (e.g., visually,
quantitatively) as well
as in words in order to
address a question or
solve a problem.
11-12.RI.10
By the end of grade
11, read and
A.SSE.3
Choose and produce an
equivalent form of an
expression to reveal and
explain properties of the
quantity represented by
the expression.
a. Factor a quadratic
expression to reveal the
zeros of the function it
defines.
b. Complete the square
in a quadratic expression
CTE.9-12.2.8
Assess the
compensation, lifestyle,
and other benefits
associated with careers
of interest.
World History
SS.11.8.3
Describe how the
determinants of demand
(i.e., income, substitutes,
complements, number of
buyers, tastes,
expectations) affect the
price and availability of
goods and services.
SS.11.8.4
Describe how the
determinants of supply
Hawaii Department of Education Standards with Opportunities to Integrate Financial Literacy Concepts
Financial Literacy 14 12/12/16
Grade
ELA
Mathematics
CTE
Social Studies
Science
11
comprehend literary
nonfiction in the
grades 11 CCR text
complexity band
proficiently, with
scaffolding as needed
at the high end of the
range. By the end of
grade 12, read and
comprehend literary
nonfiction at the high
end of the grades 11
CCR text complexity
band independently
and proficiently.
to reveal the maximum or
minimum value of the
function it defines.
c. Use the properties of
exponents to transform
expressions for
exponential functions. For
example the expression
1.15^t can be rewritten as
[1.15^(1/12)]^(12t) ?
1.012^(12t) to reveal the
approximate equivalent
monthly interest rate if
the annual rate is 15%.
F.IF.4
For a function that
models a relationship
between two quantities,
interpret key features of
graphs and tables in
terms of the quantities,
and sketch graphs
showing key features
given a verbal description
of the relationship. Key
features include:
intercepts; intervals
where the function is
increasing, decreasing,
positive, or negative;
relative maximums and
(i.e., price and availability
of inputs, technology,
government regulation,
number of sellers) affect
the price and availability
of goods and services.

Hawaii Department of Education Standards with Opportunities to Integrate Financial Literacy Concepts
Financial Literacy 15 12/12/16
Grade
ELA
Mathematics
CTE
Social Studies
Science
11
minimums; symmetries;
end behavior; and
periodicity.*
F.LE.5
Interpret the parameters
in a linear, quadratic, or
exponential function in
terms of a context.*
12
11-12.RI.7
Integrate and evaluate
multiple sources of
information presented
in different media or
formats (e.g., visually,
quantitatively) as well
as in words in order to
address a question or
solve a problem.
11-12.RI.10
By the end of grade
11, read and
comprehend literary
nonfiction in the
grades 11 CCR text
complexity band
proficiently, with
scaffolding as needed
at the high end of the
range. By the end of
grade 12, read and
comprehend literary
CTE.9-12.2.8
Assess the
compensation, lifestyle,
and other benefits
associated with careers
of interest.
Economics
SS.12E.4.1
Analyze the types of
personal economic
decisions and choices
that individuals make
(e.g., determining how to
budget money; long-term
financial goals and plans
related to income,
saving, and spending;
utilizing loans and credit
cards; considering
investment options).
SS.12E.4.2
Identify how economic
reasoning is used to
make to make personal
decisions (e.g.,
purchasing a car;
deciding on a college,
career choices).

Hawaii Department of Education Standards with Opportunities to Integrate Financial Literacy Concepts
Financial Literacy 16 12/12/16
Grade
ELA
Mathematics
CTE
Social Studies
Science
12
nonfiction at the high
end of the grades 11
CCR text complexity
band independently
and proficiently.
