
1
Lecture 4-2 (9/14/20)
OUTLINE
Amino Acids
– Definition
• The 4 S’s
• Common Properties
• Five Classes
– Hydrophobic–aliphatic [6]
– Hydrophobic–aromatic [3]
– Special–sulfur [2]
– Hydrophilic–polar [4]
– Hydrophilic–charged [5]
• Other amino acids
• Linking amino acids
• Acid/base properties
– Titrations
– Isoelectric point
• Electrophoresis
Amino&Acids:&
Building&Blocks&of&Protein
Definition
• Proteins are linear heteropolymers of L-
a
-amino
acids.
• These are organic acids with an amino group at the
a
-position, or the 2-position.
• The amino group is basic and the carboxylate group
is acidic (of course). The R-groups are different.
C–C–C–C–C–Functional
e d g b a Group (COO
–
)
6 5 4 3 2 1
1
2
2
Amino&Acids:&
Building&Blocks&of&Protein
Definition
• Proteins are linear heteropolymers of L-
a
-amino
acids.
• These are organic acids with an amino group at the
a
-position, or the 2-position.
• The amino group is basic and the carboxylate group
is acidic (of course). The R-groups are different.
C–C–C–C–C–Functional
e d g b a Group
6 5 4 3 2 1
1
2
Amino&Acids:&
Building&Blocks&of&Protein
The 4 S’s: Size
3 Å diameter
8 Å diameter

3
Amino&Acids:&
Building&Blocks&of&Protein
The “L” configuration means
levorotary, or rotates polarized light
counter-clockwise, or left handed
In R/S, this is what?
The 4 S’s: Shape
Here we have to discuss stereochemistry: particularly
what is meant by the “L” configuration
①
②
③
Clockwise is R
Counterclockwise is S
H
R = D
S = L
Recall:
What is the relationship between
R/S and D/L?
Amino&Acids:&
Building&Blocks&of&Protein
The 4 S’s: Shape
Clockwise is R
Counterclockwise is S
R = D
S = L
Fisher Projection
1. Carbon chain vertical with functional group at top
2. At each carbon the vertical bonds to carbons are
behind, projecting away from the viewer
3. At each carbon the horizontal bonds are projecting
towards the viewer
4. If the functional group (not H) is to the left it’s L
5. If the functional group (not H) is to the right it’s D
(R)
(S)

4
Amino&Acids:&
Building&Blocks&of&Protein
The 4 S’s: Stability
All amino acids are stable to acid, base, and heat
Exceptions are:
1. Trp (oxidation)
2. Cys (oxidation)
3. Asn (deamination)
4. Gln (deamination)
àN-formyl-kynurenine
àDisulfides (R’-S–S-R”)
àHydrolysis of amide: Asp
àHydrolysis of amide: Glu
Amino&Acids:&
Building&Blocks&of&Protein
The 4 S’s: Solubility
• As$zwitterions,$most$amino$acids$are$soluble$to$
some$degree.$$But,$depending$on$the$R$group$they$
are$less$soluble$or$more$soluble
• The$general$grouping$puts$10$as$ less $soluble:
A,$V,$L,$I,$P,$W,$Y,$F,$M,$C
• and$10$as$more$soluble:
G,$S,$T,$N,$Q,$D,$E,$H,$K,$R

5
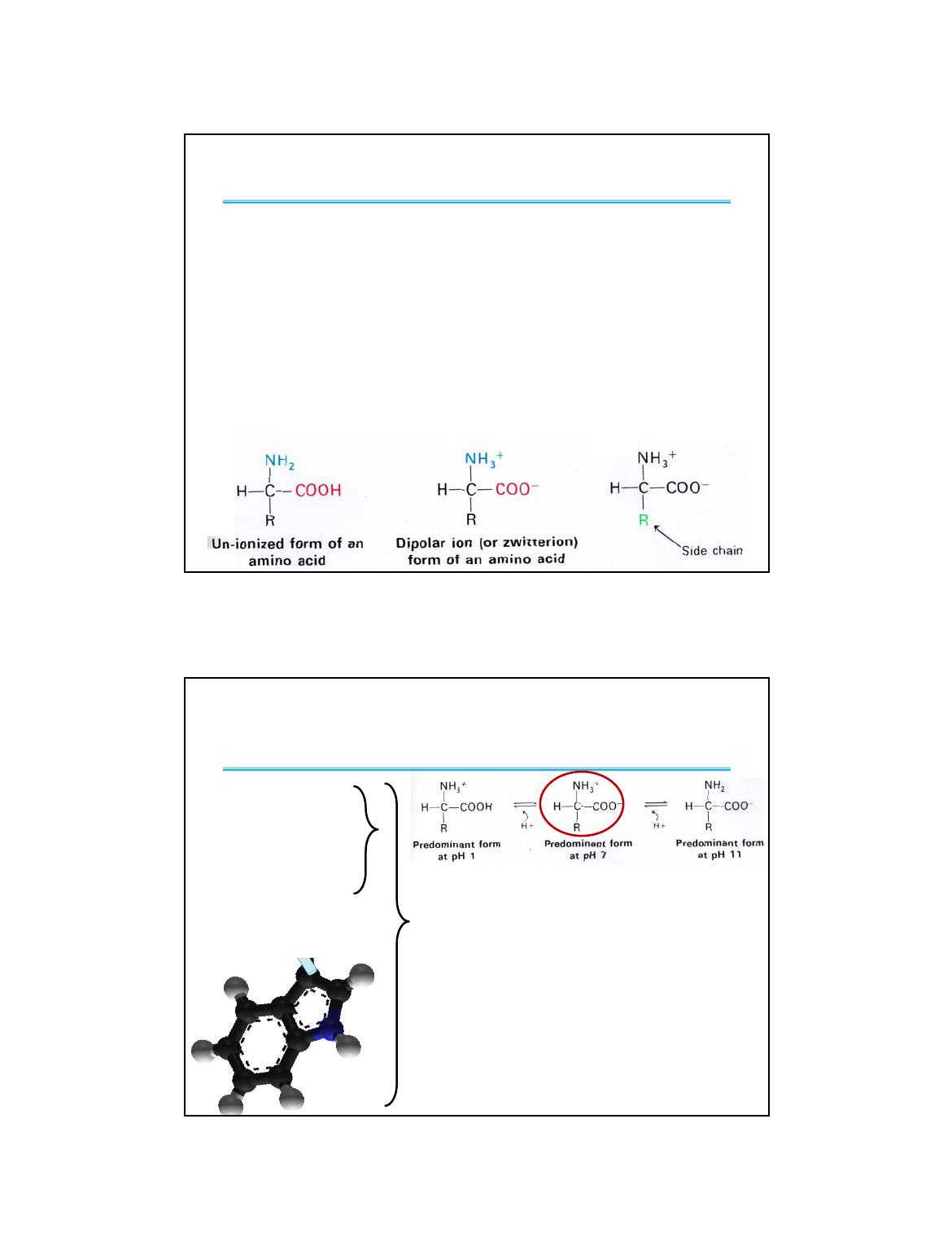
Amino&Acids&Have&Three&Common&Properties
• Groups Attached to the α Carbon. The α carbon
always has four substituents and is tetrahedral.
– an acidic carboxyl group connected to the α carbon
– a basic amino group (1°or 2°) connected to the α carbon
– an α hydrogen connected to the α carbon
– A fourth substituent called an “R group.”
• All Amino Acids are chiral with the L configuration
(except glycine where the R-group is a hydrogen).
• Acid/Base properties:
H
+
H
+
Net Charge = +1
Net Charge = 0
Net Charge = –1
Zwitterion
What is the
predominant form
at physiological
pH (7.4)?
pK
a
= ~2.3 pK
a
= ~9.6
a
Amino&Acids&Have&Three&Common&Properties
• Groups Attached to the α Carbon. The α carbon
always has four substituents and is tetrahedral.
– an acidic carboxyl group connected to the α carbon
– a basic amino group (1°or 2°) connected to the α carbon
– an α hydrogen connected to the α carbon
– A fourth substituent called an “R group.”
• All Amino Acids are chiral with the L configuration
(except glycine where the R-group is a hydrogen).
• Acid/Base properties:
H
+
H
+
Net Charge = +1
Net Charge = 0
Net Charge = –1
Zwitterion
What is the
predominant form
at physiological
pH (7.4)?
pK
a
= ~2.3 pK
a
= ~9.6
a

6
Amino&Acids:&Classification
• The 20 amino acids found in proteins can be
placed in five families based on the physical and
chemical properties of their R groups:
• Hydrophobic, aliphatic (6)
• Hydrophobic, aromatic (3)
• Special (hydrophobic/hydrophilic)(2)
• Hydrophilic, polar (4)
• Hydrophilic, charged (5)
Table:
Name 3-letter
1-letter
%
abundance
in proteins
Year
discovered
NOTES
Structure
mnemonic
device
Essential
✓
Must KNOW
Amino&Acids:&Classification
Hydrophobic, aliphatic
Glycine Gly G 1820 7
Smallest, not chiral H
Alanine Ala A 1888 8
Foundational for ~10 other AA Methyl
Valine Val V 1856 7
isopropyl V-shaped
Leucine Leu L 1819 10
Most abundant, dominant Ala + Val
Isoleucine Ile
I
1904 6
Two chiral centers (L & D) Val + Me
Proline Pro P 1901 5
Only imino acid (2° amine); special
bonds in proteins; is modified by hydroxyl
5-membered ring;
same #C’s as Val
Pro
Name 3-letter
1-letter
%
abundance
in proteins
Year
discovered
NOTES
Structure
mnemonic
device
✓
✓
✓

7
Amino&Acids:&Classification
Hydrophobic, aliphatic
Glycine Gly G 1820 7
Smallest, not chiral H
Alanine Ala A 1888 8
Foundational for ~10 other AA Methyl
Valine Val V 1856 7
isopropyl V-shaped
Leucine Leu L 10
Most hydrophobic Ala + Val
Isoleucine Ile
I
6
Two chiral centers (L & D) Val + Me
Proline Pro P 5
Only imino acid (2° amine); special
bonds in proteins; is modified by hydroxyl
5-membered ring;
same # as Val; 3C
Pro
Name 3-letter
1-letter
%
abundance
in proteins
Year
discovered
NOTES
Structure
mnemonic
device
✓
✓
✓
Gavlip family
1819
1904
1901
Amino&Acids:&Classification
• The 20 amino acids found in proteins can be
placed in five families based on the physical and
chemical properties of their R groups:
• Hydrophobic, aliphatic (6)
• Hydrophobic, aromatic (3)
• Special (hydrophobic/hydrophilic)(2)
• Hydrophilic, polar (4)
• Hydrophilic, charged (5)
Gavlip family

8
Amino&Acids:&Classification
Hydrophobic, aromatic
Phenylalanine Phe F 1879
aromatic
4
Phenyl+Ala
Tyrosine Tyr Y 1846 3
aromatic, can ionize; pK
a
≈10.1
amphipathic
p-phenol+Ala
Tryptophan Trp W 1901 1
aromatic & fluorescent;
least abundant, largest AA
Indole+Ala
Name 3-letter
1-letter
%
abundance
in proteins
Year
discovered
NOTES
Structure
mnemonic
device
✓
✓
Recall:
pK
a
Absorb
UV light
l
max
Extinction
coefficient
(x10
-3
)
259 0.7
278 1.1
279 5.2
Amino&Acids:&Classification
Hydrophobic, aromatic
Phenylalanine Phe F 1879
aromatic
4
Phenyl+Ala
Tyrosine Tyr Y 1846 3
aromatic, can ionize; pK
a
≈10.1
amphipathic
p-phenol+Ala
Tryptophan Trp W 1901 1
aromatic & fluorescent;
least abundant
Indole+Ala
Name 3-letter
1-letter
%
abundance
in proteins
Year
discovered
NOTES
Structure
mnemonic
device
✓
✓
Recall:
pK
a
Absorb
UV light
l
max
Extinction
coefficient
(x10
-3
)
259 0.7
278 1.1
279 5.2
PTT family
(push-to-talk)
360 nm

9
Amino&Acids:&Classification
• The 20 amino acids found in proteins can be
placed in five families based on the physical and
chemical properties of their R groups:
• Hydrophobic, aliphatic (6)
• Hydrophobic, aromatic (3)
• Special (hydrophobic/hydrophilic)(2)
• Hydrophilic, polar (4)
• Hydrophilic, charged (5)
PTT family
Gavlip family
Amino&Acids:&Classification
Special (Sulfur)
Methionine Met M 1922 2
Ala+Me/ether
Cysteine Cys C 1899 2
Most like straight-chain aliphatic
Ala+SH (thiol)
Name 3-letter
1-letter
%
abundance
in proteins
Year
discovered
NOTES
Structure
mnemonic
device
pK
a
can ionize; nucleophile 10.5
AA
Hydropathy
index (
D
G)
Ile 4.5
Val 4.2
Leu 3.8
Phe 2.8
Tyr –1.3
Met 1.9
Cys 2.5
• Cysteine can form disulfide bonds:
R
1
–S–S–R
2
⇌ R
1
–SH + R
2
–SH
Oxidized Reduced
Cystine (1810) Cysteine
• Cysteine can ionize:
Cys–SH ⇌ Cys–S
–
(thiolate anion) + H
+
✓
Hydrophobic
/Hydrophilic (Cys)

10
Amino&Acids:&Classification
Special (Sulfur)
Methionine Met M 1922 2
Ala+Me/ether
Cysteine Cys C 1899 2
Most like straight-chain aliphatic
Ala+SH
Name 3-letter
1-letter
%
abundance
in proteins
Year
discovered
NOTES
Structure
mnemonic
device
pK
a
can ionize; nucleophile 10.5
• Cysteine can form disulfide bonds:
R
1
–S–S–R
2
⇌ R
1
–SH + R
2
–SH
Oxidized Reduced
Cystine (1810) Cysteine
• Cysteine can ionize:
Cys–SH ⇌ Cys–S
–
(thiolate anion) + H
+
✓
MC family
(master of ceremony)
Hydrophobic
/Hydrophilic (Cys)
Amino&Acids:&Classification
• The 20 amino acids found in proteins can be
placed in five families based on the physical and
chemical properties of their R groups:
• Hydrophobic, aliphatic (6)
• Hydrophobic, aromatic (3)
• Special (hydrophobic/hydrophilic)(2)
• Hydrophilic, polar (4)
• Hydrophilic, charged (5)
PTT family
Gavlip family
MC family

11
Amino&Acids:&Classification
Hydrophilic, polar
Glutamine Gln Q 1883
Glx; gets hydrolyzed to Glu
4
Amide of Glu
Asparagine Asn N 1806 4
First isolated from asparagus
Asx; gets hydrolyzed to Asp
Amide of Asp
Serine Ser S 1865 7
Isolated from Sericin, polar
cousin of Ala
hydroxyl+Ala
Name 3-letter
1-letter
%
abundance
in proteins
Year
discovered
NOTES
Structure
mnemonic
device
Threonine Thr T 1935 6
Me+Ser
✓
Gln Asn
Ser Thr
Two chiral centers (L & D)
Amino&Acids:&Classification
Hydrophilic, polar
Qnst family
Glutamine Gln Q 1883 4
Amide of Glu
Asparagine Asn N 1806 4
Amide of Asp
Serine Ser S 1865 7
hydroxyl+Ala
Name 3-letter
1-letter
%
abundance
in proteins
Year
discovered
NOTES
Structure
mnemonic
device
Threonine Thr T 1935 6
Me+Ser
✓
Gln Asn
Ser Thr
These amino acids side chains can form hydrogen
bonds.
Glx; gets hydrolyzed to Glu
First isolated from asparagus
Asx; gets hydrolyzed to Asp
Isolated from Sericin, polar
cousin of Ala
Two chiral centers (L & D)
Amides
Alcohols
